By Witness Radio team.
For decades, development projects have been funded to address some of the World’s most pressing problems, including poverty, wildlife conservation, and climate change. However, what unfolds on the ground is sometimes the opposite of development. Instead of benefits, these projects have often harmed the very people they are supposed to support.
The effort to address such harm has led to the establishment of Independent Accountability Mechanisms (IAMs) by various development banks. Yet, communities affected by these projects often face betrayal by national court systems, leaving them feeling overlooked and vulnerable, emotions that underscore the urgent need for effective justice.
According to experts in development financing, since the early 1990s, development banks have sought to address and mitigate harm through IAMs—non-judicial grievance mechanisms that provide a direct avenue for impacted communities to raise concerns, engage with project implementers, and obtain remedies for the harm they have experienced.
The study, conducted by Accountability Counsel and titled Accountability in Action or Inaction? An Empirical Study of Remedy Delivery in Independent Accountability Mechanisms shows that while IAMs exist, their relevance has fallen short, underscoring the urgent need for reform to restore community trust and hope.
In compiling the report, researchers reviewed 2,270 complaints across 16 IAMs and conducted 45 interviews covering 25 cases globally.
The report reveals a persistent gap between the promise of remedies and their realization, highlighting that only 15% of closed complaints led to commitments, and just 10% achieved full completion, underscoring the urgent need for effective remedies for communities.
The findings highlight ongoing challenges, including inadequate implementation, limited monitoring, and persistent power imbalances, which continue to block communities from accessing meaningful remedies and demand immediate reform.
“The consequences of these institutional gaps are severe. As these cases show, institutional silence can exacerbate risk, while meaningful intervention can help de-escalate it.” The Report adds.
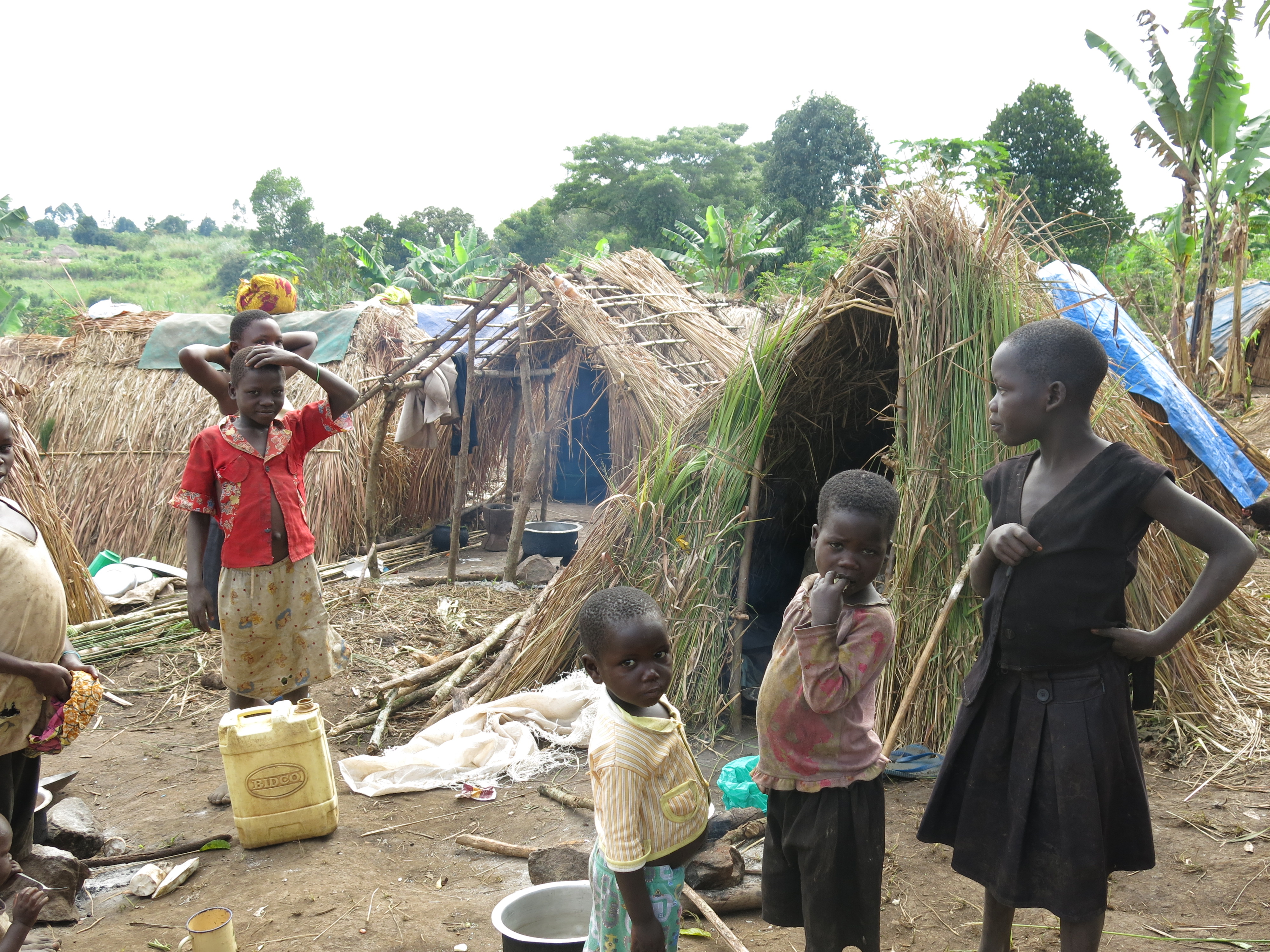
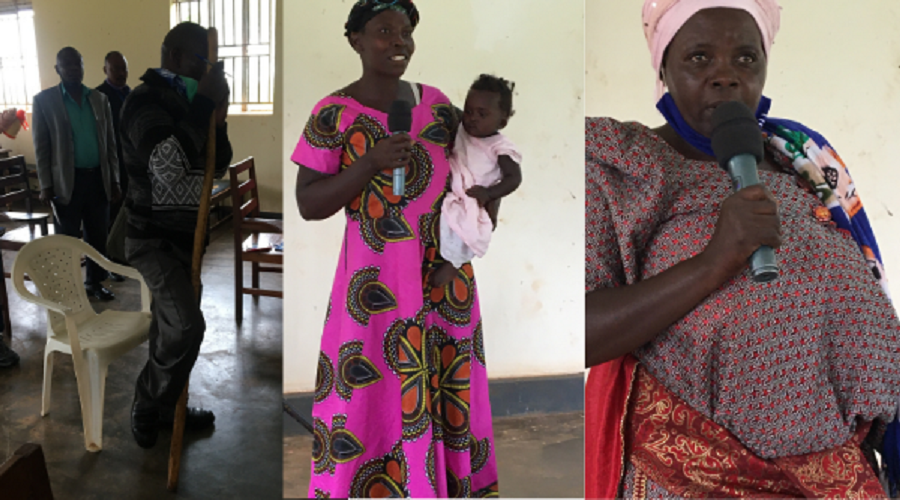
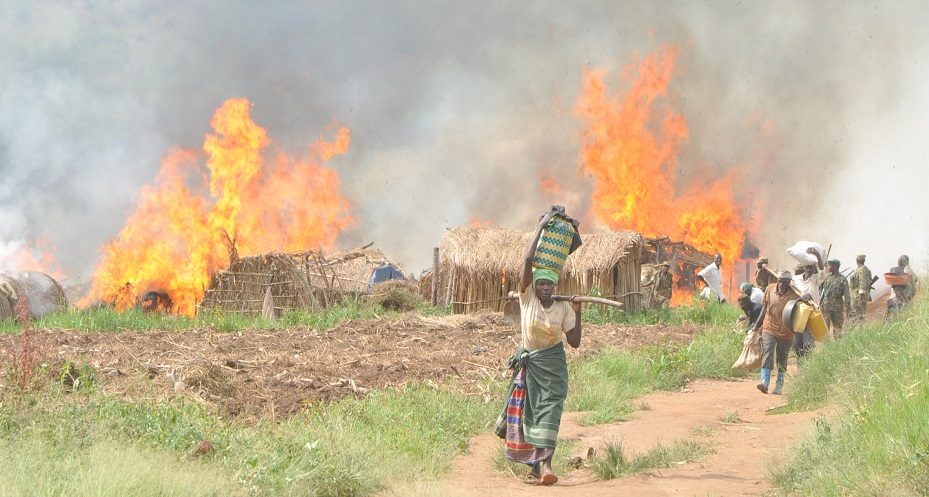
Uganda is among the countries where communities have sought justice using these accountability mechanisms. Between 2006 and 2010, communities in one of the districts of Uganda were brutally evicted by the UK-based Company, which was growing trees in the area.
The company was formerly an investee of the Agri-Vie Agribusiness Fund, a private equity fund supported by the International Finance Corporation (IFC), the private sector arm of the World Bank Group. The community filed a Complaint with the IFC’s accountability mechanism, the Compliance Advisor Ombudsman (CAO).
“We complained to this body in 2011, hoping for justice, but over 15 years later our people are still struggling, living miserably, some without homes,” a community land and environmental defender told the Witness Radio team.
According to the affected residents, the CAO process did not lead to success or meaningful compensation, as they had hoped.
Between 2013 and 2014, the communities, with support from the CAO, signed a final agreement with the Company to address the harm. Among other commitments, this included resettlement of the affected communities.
In its 28-page report published in 2015 titled: A Story of Community-Company Dispute Resolution in Uganda, the CAO wrote,” With the agreements concluded, implementation is gathering pace. As agreed, the company has begun extending development assistance to both cooperatives, and the process of restoring and enhancing livelihoods has commenced.
The first step taken by both cooperatives was to acquire land. In late 2013, the Mubende Cooperative bought 500 acres of ‘fertile agricultural land’ in the Mubende district. Their vision was to allocate a certain percentage of the land for resettlement, with the remainder utilized for farming projects.
Reports from the ground indicate that communities remain dissatisfied with the process, claiming it failed to address their concerns fully and highlighting the urgent need for more effective remedy systems.
“When you say that people are well, it is really a total lie. Many people were never compensated or resettled. Even those who got a portion of land say they have never seen a fertile land—I have never seen it, because people are living or cultivating on rocky, infertile lands,” the defender further revealed.
The struggle faced by the Ugandan community is not unique. Their experience mirrors what the Accountability Counsel report identifies worldwide. Despite registering more than 2000 complaints by communities harmed by bank-financed projects globally, there has been no comprehensive system-wide analysis of whether and how often these mechanisms deliver meaningful remedies, defined as tangible, material outcomes that repair harm and improve lives.
In addition to the slow success of such IAMs, the report notes that, across interviews covering 25 complaints, 84% referenced retaliation, violence, or threats of violence-an alarming indicator of the risks faced by communities seeking justice, demanding immediate attention and action.
“Government officials and company representatives were frequently implicated in efforts to suppress dissent. This not only reduces the likelihood of achieving a substantial remedy, but also suppresses the willingness of community members to speak honestly and openly about Complaint outcomes.” The report further adds,
Further, it reveals that communities described a range of retaliatory tactics, including physical clashes, arrests, detentions, fatalities, intimidation and harassment, death threats, and anonymous warning letters, among others.
“Remedy must be reimagined not as a peripheral concern but as a core responsibility of development institutions. It must be adequately resourced, independently monitored, and centered around the needs and voices of affected people,” the report adds.
The report recommends that development banks and IAMs establish a Remedy Framework with clear standards to ensure remedies are timely, adequate, and community-centered, and to encourage stakeholders to prioritize systemic reform for better justice outcomes.
The report also urges development banks and their accountability mechanisms to make remedies a foundational element of responsible finance. Adopting institutional frameworks that prioritize redress, empowering IAMs to oversee and enforce commitments, and incorporating the outcomes of IAM processes into project evaluations and institutional learning.


 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
 FARM NEWS2 weeks ago
FARM NEWS2 weeks ago
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK4 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK4 days ago
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK6 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK6 days ago
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK3 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK3 days ago
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 days ago