By Witness Radio team.
In 2014, the NFA used force to evict thousands from what it claimed was a forest reserve, and 11 years later, the land is now privately used for cattle and crops, highlighting ongoing land injustice.
The land-grab victims were residents of Buwaya and Nairambi sub-counties, and of Buvuma Town Council in Buvuma District. Buvuma is an island district in Uganda’s Central Region, comprising 52 islands on Lake Victoria.
The NFA claimed that the land was part of Kakonwa Central Forest Reserve.
Victims revealed that between 15th and 18th July 2014, security agencies’ personnel and NFA workers stormed their homes, fired tear gas, burned houses, looted valuable properties, and destroyed crops and other property, claiming they had unlawfully occupied forest reserve land.
Testimonies reveal families were displaced without consultation or compensation, leaving them devastated and struggling to rebuild their lives, urging urgent attention.
Many residents confirm that as soon as their land was grabbed, UPDF soldiers established a detachment to guard it and turned it into private property for some individuals.
“They said we were illegally occupying a forest reserve. Why is it that today the same land is used for grazing and by private farmers? We don’t know who benefits from this, but there is an Army detachment on the land guarding it, and we also see some rich farmers and cattle keepers using the same land. Why should other people benefit while we, the former owners, continue suffering?” Said Bwire Martin.
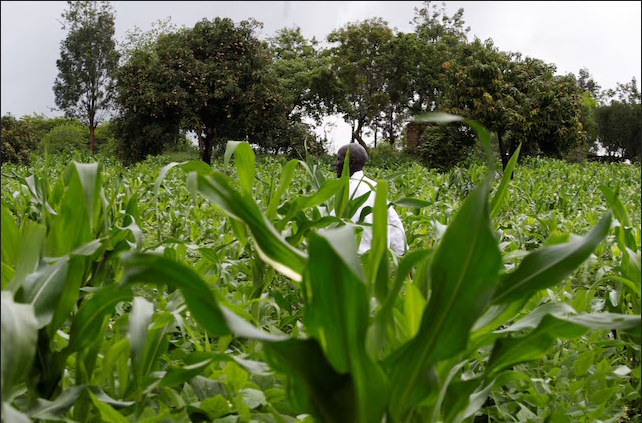
Bwire 42, one of the victims formerly of Mpolwe village, says he had lived and cultivated his land for many years before his home was demolished. “We were reduced to laborers from landlords, with the majority of my fellow victims now working on other people’s plantations, especially oil palm growers, just to survive.
The affected families say they have made numerous attempts to seek redress from various government offices, including the Ministry of Lands, but without success.
“We have tried all offices to get justice, but nothing is possible,” Wandera added. “People are suffering. Many are now staying in informal settlements, living as refugees because they were robbed of their livelihood.”
Residents insist that they will continue to demand what they believe is rightfully theirs. When contacted, NFA spokesperson Mr. Aldon Walukamba dismissed the renewed demands, describing the former residents as “illegal encroachers” allegedly being influenced by politicians and “self-seekers.”
He insisted that the contested area is part of the Kakwona Central Forest Reserve and denied the evictees’ claims of legitimate ownership of the land. Asked about residents’ claims of having land ownership documents, Walukamba responded, “If people can own land titles in wetlands or lakes, why can’t these also get such documents?”
Mr. Walukamba, however, requested Witness Radio to speak to the Permanent secretary, Ministry of Water and Environment, Mr. Alfred Okot Okidi for more information about the case. However, despite multiple attempts to speak to Mr. Okidi, his known contacts remained un answered by the time of publication of the article.
Mr. Wandera Alphonse, now living in Kiteredde village, is one of the thousands who lost their livelihoods during the evictions. He says he and his family had settled on the land in 2008 and were living on six acres when the eviction occurred.
“Police and soldiers destroyed my permanent house, and all my crops. I now rent in Kiteredde, so my family of eight can have somewhere to live. We were never consulted, compensated, or resettled. They call us illegal settlers, but this has been our home for years.” Wandera said in an interview with the Witness Radio team
Before the eviction, Wandera and his family were thriving well in Bukinarwa parish, using the land for agricultural purposes. “I was a farmer who depended a lot on seasonal harvests to support my family’s livelihood. I used to cultivate beans, rice, and bananas, and I earned more than a million (1,000,000/= Uganda Shillings), which was enough to take care of everything. But now, the NFA has rendered me hopeless,” he said.
Similarly, Nakagoro Hajira, who settled on the land with her husband in 2000, says her family was left devastated.
“This has been our home for years. We never settled in a forest reserve,” she said. “After the eviction, our ten children stopped going to school because we lost our only source of income. We now rent and survive by laboring on other people’s plantations.”
Victims have renewed their call for the return of their land, insisting they were unjustly displaced and need support to rebuild their lives.


 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 days ago
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK18 hours ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK18 hours ago
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 days ago
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK20 hours ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK20 hours ago
 STATEMENTS3 days ago
STATEMENTS3 days ago