WITNESS RADIO MILESTONES
Africa’s green revolution stumbles at Congo project to solve food shortages
Published
7 years agoon
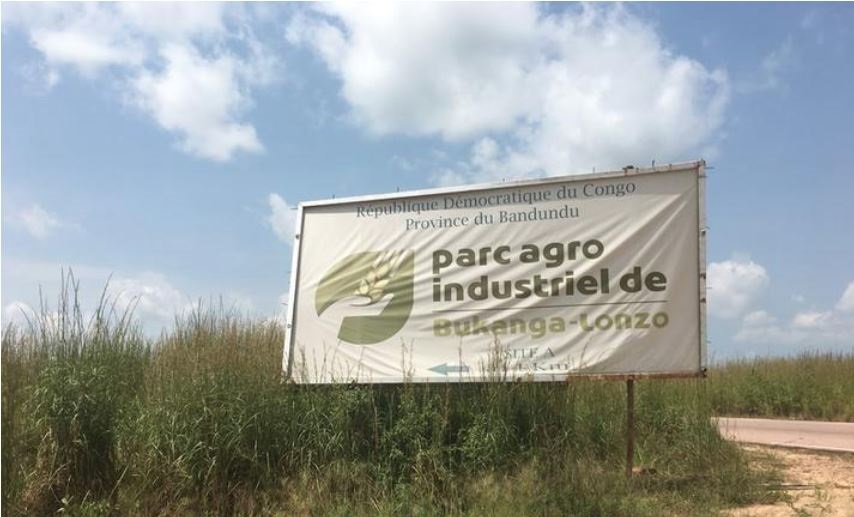

DAKAR (Reuters) – In 2014, Democratic Republic of Congo officials trumpeted the launch of a sweeping initiative they said would solve food shortages in one of the world’s poorest countries.
The plan: to transform land covering more than 17,900 square kilometres of the central African nation – more than half the landmass of former colonial master Belgium – into use for industrial-scale agriculture to boost food production.
That summer, President Joseph Kabila inaugurated an 800-square-kilometre plot in western Congo called Bukanga Lonzo, the first of 22 planned projects across the country to produce everything from maize to sunflowers to poultry.
Three years later, the pilot had collapsed. Activity on site ground to a halt after the South African company brought in as a co-investor and to manage the park left, saying it hadn’t been paid by the Congolese government in nearly a year.
With more than 60 percent of the world’s unexploited arable land but struggling to feed its surging population, Africa has become the latest laboratory for governments, development agencies and researchers trying to lead a new green revolution.
But experiments like Bukanga Lonzo serve as cautionary tales for those in search of quick fixes, showing how weak investor interest, poor infrastructure and byzantine land regulations can stymie Africa’s agricultural potential.
These days, police guard the park entrance, where a billboard partially obscured by overgrown grass still displays the insignia of a hand cupping a stalk of wheat.
Congolese officials acknowledge the project’s collapse but express hope the pilot, and the broader initiative, can be revived.
In an interview, Congo’s economy minister Joseph Kapika said that Bukanga Lonzo “completely failed.” The minister blamed the South African company that had managed the park and said it had left “in bad faith.” He added that the government plans to re-launch the park with a focus on livestock.
The company, Africom Commodities Pty Ltd, disputes Kapika’s claims about what went wrong. Africom’s chief executive, Christo Grobler, said the problem was high costs and an unreliable government partner that would change its mind from day to day about the project’s direction. He said the company had incurred more than $50 million in losses at Bukanga Lonzo.
The company said it and the government spent more than $250 million combined on the project plus a related market and fertilizer factory but the park had produced at most 15,000 tonnes of maize in total – a fraction of the 350,000 tonnes annually forecasted by next year in marketing material.
The economy minister, in the interview, declined to comment on the cost of the project. Congo’s agriculture ministry declined to comment. The portfolio minister, who oversees state contracts, did not respond to multiple requests for comment.
Park officials declined to be interviewed or grant Reuters access to the site. Kabila’s deputy chief of staff did not respond to a request for comment. LIMITED SUCCESS
With a food-import deficit running into the tens of billions of dollars and a spiraling numbers of undernourished inhabitants, Africa is casting about for ways to boost agricultural productivity.
Some countries, including Nigeria and Tanzania, have turned to agro-industrial parks — concentrations of large farms, processing factories and related infrastructure – modeled after similar sites in India, Brazil and Vietnam.
But efforts in Africa so far have met limited success, according to a 2017 report by the United Nations.
Some specialists in agricultural innovation say industrial-scale farming can work but the approach in Africa is often flawed. “No one’s figured out the model that can make this work at sufficient scale,” said Patrick Guyver, who has consulted on agriculture projects across Africa.
The African Development Bank is nevertheless accelerating a push for projects such as Bukanga Lonzo, for which it provided about $1 million to finance a feasibility study.
The bank said it committed last year to 101 million euros for an Ivory Coast project and that it is due this year to consider funding for three others. It held a conference in Tunis in February to discuss new projects in Ethiopia, Togo, Mozambique, and elsewhere.
African Development Bank spokesman Chawki Chahed, in emailed responses to questions, said Bukanga Lonzo had not failed and could still be resurrected. He added that in general such projects “are complex and so their development and design are gradual.” He said the Bank plans to spend $2.2 million on feasibility studies for three more agro-industrial parks planned in central and southeastern Congo, without specifying when the studies would begin.
“PEOPLE ARE STARVING”
A key proponent of Congo’s plan was John Ulimwengu, an advocate of industrial-scale agriculture in Africa and a fellow at the International Food Policy Research Institute in Washington D.C.
In 2013, Ulimwengu was advising Congo’s then-Prime Minister Augustin Matata Ponyo and pushed for a pilot project to produce food for export and domestic consumption, according to Ulimwengu and other officials involved in the project. Some people urged the government to do further research before embarking on the Bukango Lonzo initiative. That included Calestous Juma, a professor of farming innovation at Harvard University in Cambridge, Mass., whom Ulimwengu briefed on the project in a January 2014 meeting, both men told Reuters. Juma has since passed away.
The prime minister insisted on moving more quickly, according to Ulimwengu. “I remember the prime minister telling us, ‘I am a politician. I made some promises to the population. While we are doing this, people are dying, people are starving,’” Ulimwengu said.
Gloria Mangoni, who worked in the prime minister’s office at the time, also said they were under pressure to produce results quickly and that political considerations sometimes prevailed over economic ones. Matata, who was replaced as prime minister in late 2016, did not respond to a request for comment. In a recent speech, he blamed Bukanga Lonzo’s problems on the site’s poor soil quality.
Ulimwengu said he continues to support the agro-industrial approach and lays most of the blame for Bukanga Lonzo’s difficulties on political instability in Congo that has scared off investors. RED FLAGS In early 2014, the Congolese government signed a five-year contract with Africom, whose subsidiary was partnering with the government on a fertilizer factory in southwestern Congo. The government invested a total of $161.2 million in Bukanga Lonzo as well as a market in Kinshasa intended to sell the produce and the fertilizer factor, according to Africom. Africom said it invested $91.3 million in those projects.
The following year, in 2015, audit firm Ernst & Young raised red flags in a report commissioned by the finance ministry. Ernst & Young said prices the park paid for equipment from Africom’s sister companies were “excessively higher” than those offered by competitors and that promised infrastructure had not materialised, according to the report. In a response to Ernst & Young reviewed by Reuters, Africom said the audit firm failed to account for the high costs of providing warrantees and spare parts in Congo and also misunderstood the nature of some of the promised work. Ernst & Young declined to comment.
In early 2016, the government fell behind on its monthly $4.8 million payments to Africom to manage the park as low prices for Congo’s main exports copper and cobalt ate into public finances, said Grobler, Africom’s CEO.
After September of that year, the government stopped paying Africom altogether, he added.
Additional reporting by Patient Ligodi; Editing by Cassell Bryan-Low
Source: Reuters
Related posts:

 CSOs urge banks and other IFIs not to finance E.Africa oil pipeline project…
CSOs urge banks and other IFIs not to finance E.Africa oil pipeline project…
 About 41 million people food insecure in E. Africa amid COVID-19 pandemic: UN
About 41 million people food insecure in E. Africa amid COVID-19 pandemic: UN
 Green Resources’ forestry projects are negatively impacting on local communities – donor
Green Resources’ forestry projects are negatively impacting on local communities – donor
 World Bank branch indirectly backs coal megaproject despite green pledge
World Bank branch indirectly backs coal megaproject despite green pledge
WITNESS RADIO MILESTONES
Top 10 agribusiness giants: corporate concentration in food & farming in 2025
Published
3 weeks agoon
June 19, 2025
Today a handful of agribusiness corporations have consolidated unprecedented control over the world’s food supply, with devastating consequences for farmers, consumers and the planet. A new report by ETC Group and GRAIN examines the state of corporate concentration in six sectors critical to agriculture: commercial seeds, pesticides, synthetic fertilisers, farm machinery, animal pharmaceuticals and livestock genetics.
Corporate consolidation is increasing in most of these sectors and four of them– seeds, pesticides, agricultural machinery and animal pharmaceuticals– now meet the definition of an oligopoly, in which four companies control more than 40% of a market. Concentration can be even higher at the national level, as is the case with synthetic fertilisers.
Top findings from the report include:
- Oligopolies dominate key sectors: Bayer, Corteva, Syngenta, and BASF control 56% of the global commercial seeds market, and 61% of the pesticides market.
- Profiteering amid global crises: Agribusiness giants have exploited crises like the Ukraine war and the COVID-19 pandemic to inflate prices. Fertiliser companies, for instance, saw revenues soar by 57% from 2020 to 2023, with some accused of price gouging.
- Digital and biotech expansion: Corporations are rapidly integrating AI, gene editing, and digital platforms into agriculture through partnerships with Big Tech companies. These technologies enable data extraction from farmers, facilitate carbon credit schemes, and tighter control over food systems—while raising concerns about biosafety, privacy, and corporate monopolies.
Source: grassrootsonline
Related posts:

 A corporate cartel fertilises food inflation
A corporate cartel fertilises food inflation
 Food inflation: The math doesn’t add up without factoring in corporate power
Food inflation: The math doesn’t add up without factoring in corporate power
 African governments are giving in to corporate pressure and undermining local seed systems – report
African governments are giving in to corporate pressure and undermining local seed systems – report
 The United Nations Food Systems Summit is a corporate food summit —not a “people’s” food summit
The United Nations Food Systems Summit is a corporate food summit —not a “people’s” food summit
WITNESS RADIO MILESTONES
Land grabbers evict 360,000 Ugandans in 2024
Published
8 months agoon
November 20, 2024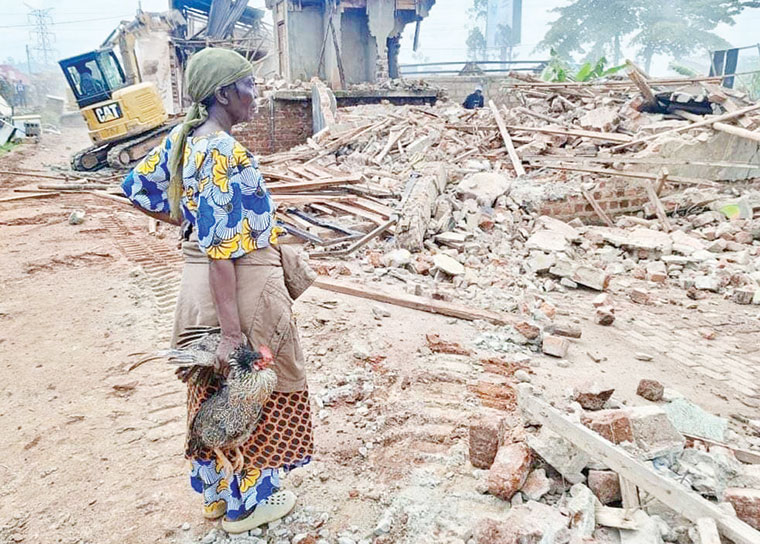
A staggering 363,021 Ugandans were displaced due to forced land evictions between January and June 2024, according to a new report by Witness Radio Uganda.
The report documented 90 cases of land evictions during this period, with nearly four incidents occurring weekly, affecting over 15,126 people and threatening 5,060 hectares of land nationwide.
The Central region was the epicenter, recording 52 eviction cases, followed by 24 in the Western region, eight in the Northern region, and six in the Eastern region. Alarmingly, the report estimated that 2,160 Ugandans face eviction daily, with 723 hectares of land at risk of being grabbed every day.
VIOLENCE AND HUMAN RIGHTS VIOLATIONS
Despite government promises and directives from President Museveni to halt evictions, land grabbers have routinely ignored these orders, often resorting to violence. Armed security forces, private militias, and police were reported to have carried out the majority of the evictions.
Of the reported cases, 37 were enforced by armed gangs on behalf of evictors, 25 involved Uganda Police, five were carried out with the participation of UPDF soldiers, and four were linked to private security companies.
“The egregious levels of impunity exhibited by land grabbers have left communities defenseless, creating an environment where their human rights are trampled without consequence,” said Jeff Wokulira Ssebaggala, country director of Witness Radio Uganda.
He called for accountability and justice, warning that the unchecked power of influential individuals and entities leaves marginalized communities vulnerable and without recourse.
DRIVERS OF EVICTIONS: INDUSTRIALIZATION AND LAND-BASED INVESTMENTS
The report identified the government’s push for industrialization and land-based investments as the primary drivers of forced evictions. Land is increasingly targeted for oil and gas extraction, mining, agribusiness and tree plantations for carbon offsets. While some of this land is already under development, other parcels remain vacant but are guarded by military personnel and private security firms.
Ssebaggala emphasized that industrialization must balance economic development with the protection of smallholder farmers’ rights to land and food security.

TRAGIC STORIES
The report highlighted harrowing cases that underscore the human toll of forced evictions. In Nakasongola, smallholder farmer Dan Ssebyala was ambushed and killed by armed men following a confrontation over disputed land. The district has become a hotspot for violent evictions involving absentee landlords and powerful investors.
Ismael Bwowe, a disabled father of 20, recounted how his land was confiscated after he demanded fair compensation. He faced intimidation, arrests and false charges from state authorities, including being accused of robbing an influential individual. Bwowe claimed that Total Energies offered legal support and representation on the condition that he accept their compensation terms.
“I refused,” he said, adding that the pressure to relinquish his land remains intense. The report underscores the urgent need for reforms to address forced evictions, ensure accountability, and protect the rights of vulnerable communities. Without meaningful intervention, Uganda risks deepening inequality and undermining the livelihoods of smallholder farmers who are essential to the country’s food security.
FAMILY JAILED AMID LAND DISPUTE
The plight of Richard Ssebagala, his wife Prossy Namande, and their relative Anania Ngabirano, residents of Kabubu-Kabongo village in Nansana Municipality, Wakiso district, highlights the human toll of Uganda’s ongoing land disputes. The family spent nine months in prison following their arrest on January 10, 2024, under controversial circumstances.
ARREST AND ALLEGATIONS
The arrests occurred at 1am, during a raid by officers from Luweero police station. Police reportedly banged on the doors and forcefully detained the family, accusing them of aggravated robbery. However, the family believes the arrest was a tactic linked to a land dispute with Benon Ntambi, a man who allegedly grabbed their land.
Before the arrests, Ntambi had reportedly destroyed crops, including tomatoes, potatoes, and bananas, on the contested land. While the family was incarcerated, a new building was constructed on their land, which is now occupied, raising further questions about the motivations behind their detention.
CALLS FOR JUSTICE
The case has drawn attention from Witness Radio Uganda, which has urged the government to take immediate action to address land grabbing and illegal evictions. The organization emphasized the need to strengthen land laws and protect vulnerable communities from abuses.
It also called for greater accountability in institutions such as the Uganda Police Force, the army and land registries, which are often accused of corruption and favoritism toward the wealthy.
“The government must prioritize justice for victims of illegal evictions and address systemic corruption that leaves the poor defenseless against land grabbers,” Witness Radio Uganda stated.
BROADER CONTEXT
This case underscores the broader issue of land conflicts in Uganda, where vulnerable families are often caught in disputes with powerful individuals or entities. Advocacy groups warn that the failure to address these issues not only erodes public trust but also perpetuates inequality and injustice.
As the government faces mounting pressure to act, the story of Ssebagala and his family serves as a stark reminder of the urgent need for reforms to protect land rights and ensure justice for those impacted by land disputes.
Source: The Observer
Related posts:

 Local land grabbers evict villagers at night; foreign investors cultivate the same lands the next day
Local land grabbers evict villagers at night; foreign investors cultivate the same lands the next day
 Uganda: Land-grab victim communities will join counterparts in commemorating the 2024 International Day of Struggle Against Industrial Plantations.
Uganda: Land-grab victim communities will join counterparts in commemorating the 2024 International Day of Struggle Against Industrial Plantations.
 Mubende Land Grab: Witnessradio.org presents another petition to Land Inquiry Commission, Wants All Titles being used to evict Natives to be Investigated
Mubende Land Grab: Witnessradio.org presents another petition to Land Inquiry Commission, Wants All Titles being used to evict Natives to be Investigated
 A Nullity? Ugandans Query Constitutional Land Amendment Bill
A Nullity? Ugandans Query Constitutional Land Amendment Bill
WITNESS RADIO MILESTONES
Uganda: Community members violently evicted by security forces, allegedly related to EACOP; incl. co. responses
Published
8 months agoon
November 18, 2024
On 10 February 2023, more than 2,500 community members were forcibly evicted from their land in Kapapi village in Hoima district in Western Uganda by security forces, receiving no compensation or resettlement.
Witness Radio, an Ugandan non-profit organisation comprised of human rights investigative journalists, lawyers, and social workers, said that many people were wounded during the eviction, women were raped, and houses were destroyed.
Witness Radio said its investigations found that this eviction occurred to clear the path for the Tilenga feeder pipeline, part of the East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP). According to Witness Radio, in 2022 Kapapi community members’ land was surveyed for the Tilenga pipeline and people were informed they would be compensated for the land. Instead, they were forcibly evicted, which Witness Radio allege was backed and financed by Swacoff Intertrade Company Limited, known to TotalEnergies. They also allege that guards from private security company Magnum Security were involved. Witness Radio has also found that dozens of local farmers who were evicted have been arbitrarily arrested and face criminal charges.
The Business & Human Rights Resource Centre invited TotalEnergies, Swacoff Intertrade Company Limited, and Magnum Security to respond to the allegations. TotalEnergies responded and stated that no land eviction activities had been carried out by or on behalf of TotalEnergies EP Uganda (TEPU) and EACOP Ltd and that none of the affected people are Tilenga or EACOP Project Affected Persons. Swacoff responded and said that the company has never engaged in forceful eviction of any sort and asserts that these allegations are completely false. Their full responses and rejoinders from Witness Radio are available below. Magnum Security did not respond.
Related posts:

 Uganda: NGO claims Agilis Partners & Great Seasons violently evicted locals to pave the way for agribusiness; Agilis Partners responds
Uganda: NGO claims Agilis Partners & Great Seasons violently evicted locals to pave the way for agribusiness; Agilis Partners responds
 A son of the community defender is shot dead, another critically injured in a retaliatory attack by security guards evicting locals off their land to give way to large-scale sugarcane growing.
A son of the community defender is shot dead, another critically injured in a retaliatory attack by security guards evicting locals off their land to give way to large-scale sugarcane growing.
 Breaking: Criminal trial for seven community defenders opposed to EACOP/Tilenga project forced land eviction has been fixed.
Breaking: Criminal trial for seven community defenders opposed to EACOP/Tilenga project forced land eviction has been fixed.
 Uganda: CSOs claim Agilis Partners forcibly evicting local communities to pave way for agribusiness; company did not respond
Uganda: CSOs claim Agilis Partners forcibly evicting local communities to pave way for agribusiness; company did not respond

Activism on Trial: Despite the increasing repressive measures, Uganda’s EACOP protesters are achieving unexpected victories in the country’s justice systems.

Communities Under Siege: New Report Reveals World Bank Failures in Safeguard Compliance and Human Rights Oversight in Tanzania

A decade of displacement: How Uganda’s Oil refinery victims are dying before realizing justice as EACOP secures financial backing to further significant environmental harm.

Carbon Markets Are Not the Solution: The Failed Relaunch of Emission Trading and the Clean Development Mechanism

A decade of displacement: How Uganda’s Oil refinery victims are dying before realizing justice as EACOP secures financial backing to further significant environmental harm.

Govt launches Central Account for Busuulu to protect tenants from evictions

Activism on Trial: Despite the increasing repressive measures, Uganda’s EACOP protesters are achieving unexpected victories in the country’s justice systems.

Top 10 agribusiness giants: corporate concentration in food & farming in 2025

Innovative Finance from Canada projects positive impact on local communities.
Over 5000 Indigenous Communities evicted in Kiryandongo District
Petition To Land Inquiry Commission Over Human Rights In Kiryandongo District
Invisible victims of Uganda Land Grabs
Resource Center
- LAND GRABS AT GUNPOINT REPORT IN KIRYANDONGO DISTRICT
- RESEARCH BRIEF -TOURISM POTENTIAL OF GREATER MASAKA -MARCH 2025
- The Mouila Declaration of the Informal Alliance against the Expansion of Industrial Monocultures
- FORCED LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA TRENDS RIGHTS OF DEFENDERS IMPACT AND CALL FOR ACTION
- 12 KEY DEMANDS FROM CSOS TO WORLD LEADERS AT THE OPENING OF COP16 IN SAUDI ARABIA
- PRESENDIANTIAL DIRECTIVE BANNING ALL LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA
- FROM LAND GRABBERS TO CARBON COWBOYS A NEW SCRAMBLE FOR COMMUNITY LANDS TAKES OFF
- African Faith Leaders Demand Reparations From The Gates Foundation.
Legal Framework
READ BY CATEGORY
Newsletter
Trending
-

 SPECIAL REPORTS AND PROJECTS4 days ago
SPECIAL REPORTS AND PROJECTS4 days agoActivism on Trial: Despite the increasing repressive measures, Uganda’s EACOP protesters are achieving unexpected victories in the country’s justice systems.
-

 NGO WORK1 week ago
NGO WORK1 week agoCommunities Under Siege: New Report Reveals World Bank Failures in Safeguard Compliance and Human Rights Oversight in Tanzania


