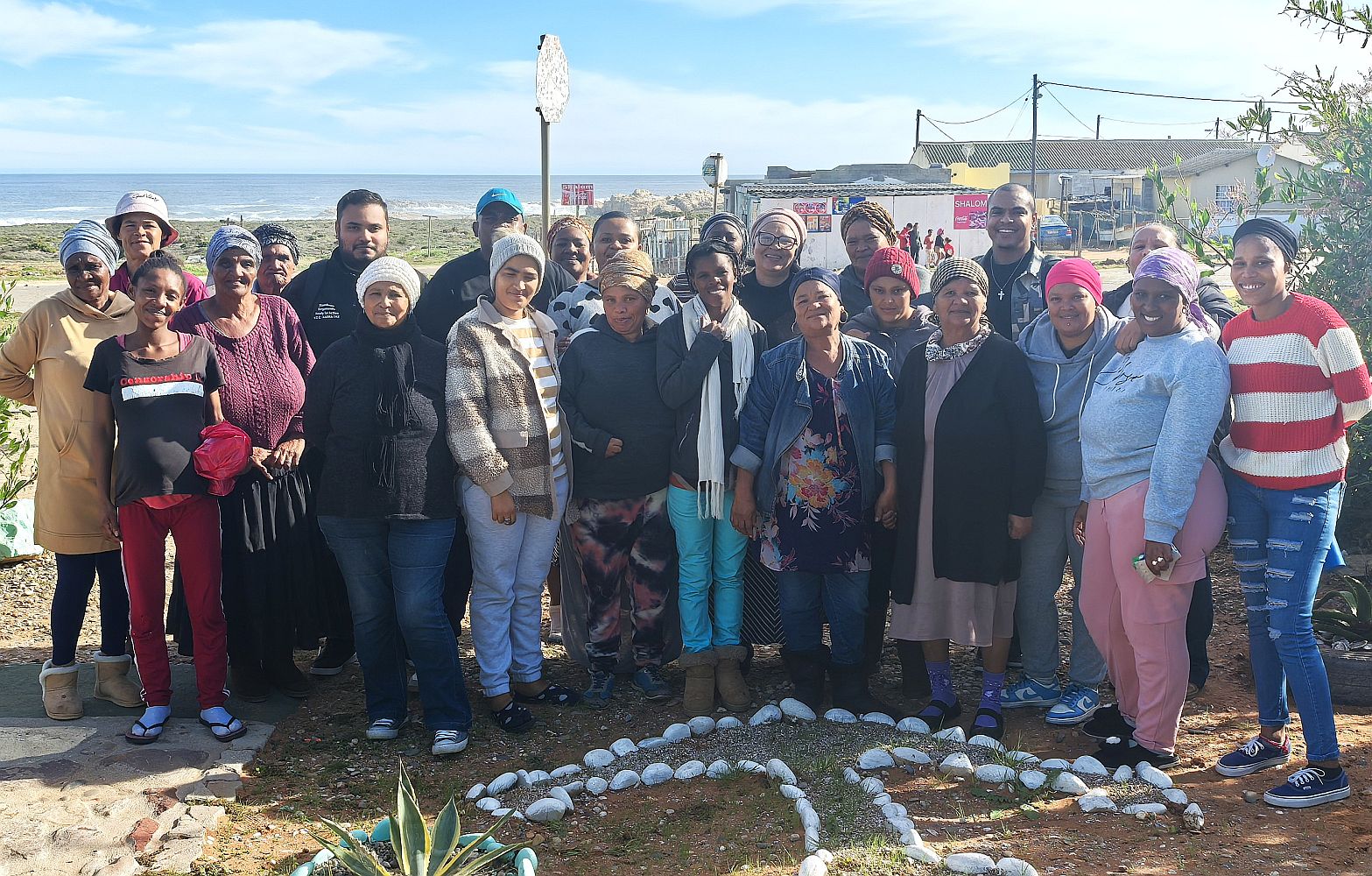
Fisher women play a vital role in sustaining household food security, yet remain under‑recognised, excluded from permits, and denied equal income opportunities in the fishing sector.Photo Credit: The Green Connection.
By Witness Radio team.
South Africa produces enough food to feed its population, yet millions go to bed hungry every night.
According to Statistics South Africa’s General Household Survey 2024, released in 2025, about 14 million people experienced hunger, representing 22.2% of households reporting inadequate or severely inadequate access to food. The Northern Cape (34.3%), Eastern Cape (31.3%), and Mpumalanga (30.4%) recorded the highest levels of food insecurity.
One in four children in South Africa is stunted due to chronic malnutrition. In the Eastern Cape alone, 70 children under the age of five reportedly died from malnutrition-related complications between January and July 2025.
In response to the growing problem, the South African Human Rights Commission, a national institution established to support constitutional democracy, declared last year that it would hold a National Public Inquiry into the Constitutional Right to Food. This inquiry will examine how communities, corporations, laws, and policies shape food systems and seek to address the structural causes of hunger.
As a result, the investigation will try to describe a future in which food is once again understood as sustenance, dignity, and justice.
Thousands of small-scale fishers along South Africa’s 3,000 km coastline depend on marine resources for their livelihoods, highlighting their vital role in the nation’s food security and cultural fabric.
Many fishing families struggle to make ends meet, even though they harvest food from the ocean. The livelihoods and food security of about 28,000 small-scale fishermen are directly reliant on marine resources. Yet, existing policies-such as restrictive permits and limited market access-exclude them from full participation, perpetuating food insecurity.
For these communities, food systems are not abstract policy concepts. They shape daily survival, dignity, livelihoods, and cultural identity.
“As part of our submission, we emphasize that concrete policy changes-such as recognizing customary fishing rights and improving market access-will directly enhance the livelihoods and food security of small-scale fishers and coastal communities, making the case for urgent reform.” Says Buthelezi
The Green Connection, a registered non-profit organisation, works with coastal communities to promote environmental justice, human rights, and accountable governance.
In the submission, the Green Connection states that the inquiry is timely as it will examine the structural and economic dynamics that perpetuate hunger. “It will assess the concentration of power in the food value chain, affordability and access, land and tenure security, policy coordination, and the realization of the constitutional right to food. This includes its links to dignity, health, water, culture, and a healthy environment.” The submission reads.
The Green Connection further argues that the Commission’s examination of governance, participation, and accountability must include scrutiny of marine and ocean policy.
“Poor implementation of the Small-Scale Fisheries Policy, limited market access, inadequate infrastructure, and weak consultation processes continue to undermine the sector. Women – who make up less than 30% of participants – remain under-recognised. At the same time, young people leave coastal communities due to declining economic prospects,” says Khetha Buthelezi, Economics Officer at The Green Connection, adding that, “Food and the systems we put in place to produce it cannot be separated from human dignity, livelihoods, and cultural rights. These issues are not abstract policy debates. For small-scale fishing communities, food from the ocean is not merely a commodity – it is a foundation of identity, survival, and social cohesion.”
The organisation also raises concerns about the potential impacts of offshore oil and gas expansion under Operation Phakisa. It further adds that Seismic surveys, drilling, and increased shipping activity can threaten fish stocks and restrict access to traditional fishing grounds, thereby directly affecting food security and livelihoods.
“For small-scale fishers, these are not abstract environmental issues. It is about income stability, cultural survival, and the constitutional rights to food, livelihoods, and participation in decision-making, and protecting these rights and resources for future generations,” says Buthelezi
Several fishing communities consulted shared testimonies describing worsening conditions.
“While small‑scale fishers support around 28000 people in South Africa, many of us can no longer catch or sell enough fish to feed our own families. Walter Steenkamp says on behalf of Aukotowa Small‑Scale Fishers Co‑operative in Port Nolloth, Northern Cape.
Steenkamp adds that Decisions are often made without consulting them, which reflects an intended exclusion from decision-making. “We hope this inquiry will result in the recognition of our customary rights, the return of our fishing grounds, and for the government to listen to those of us who live from the sea, so that we can feed our families with dignity.”
According to Kristie Links from the Sal-Diaz Small-Scale Fisher Co-operative in Saldanha Bay, Western Cape, farmers are forced to use larger boats that they cannot afford. “We have no money for the bigger boats they want us to use, and the areas we are given have little or no fish.
Industrial boats continue to overfish, especially at night, while our communities struggle to put food on the table. This situation is destroying our livelihoods, our food security, and our right to be recognised as small-scale fishers,” Kristie adds.
The organisation argues that poor implementation of the Small-Scale Fisheries Policy, weak consultation processes, and inadequate infrastructure continue to undermine the sector.
“Our message to the SAHRC is clear. If South Africa is serious about tackling hunger and inequality, it must ensure food systems governance is transparent, inclusive, and accountable. Coastal communities are not asking for charity – they are demanding justice.” Buthelezi concludes
The deadline for written submissions has been extended to 27 February 2026, with public hearings scheduled for March during Human Rights Month.


 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK13 hours ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK13 hours ago