MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
The African Development Bank and the Tree Plantations Industry
Published
5 years agoon
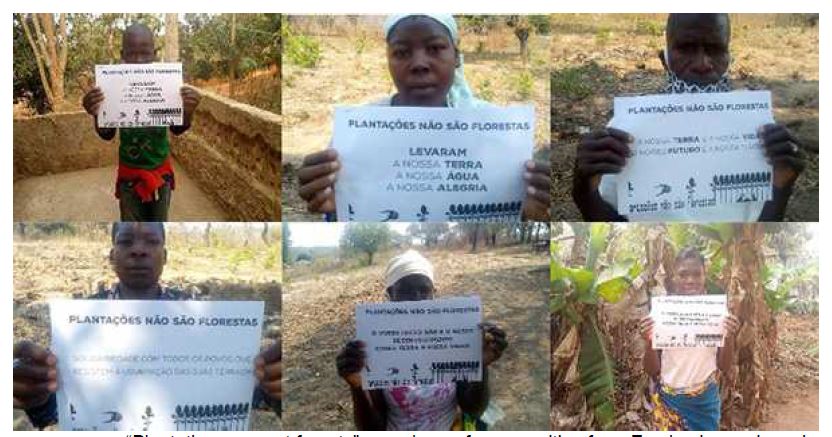

“Plantations are not forests”, members of communities from Zambezia province, in Mozambique.
In June 2019, the report “Towards Large-Scale Commercial Investment in African Forestry,”
(1) made a call to development-funding agencies, mainly from Europe, and the World Bank,
to provide aid money to a new Fund for financing 100,000 hectares of (new) industrial tree
plantations, to support the potential development of 500,000 hectares, in Eastern and
Southern Africa. This money, according to the report, would be crucial for private investors to
generate profits from the plantations. The new Fund would be headquartered in the tax
haven of Mauritius.
The African Development Bank (AfDB) and WWF Kenya produced this report with funding
from the World Bank’s Climate Investment Funds. The purpose of the report is to assist the
AfDB “in evaluating and designing alternative private funding models for commercial forestry
in Africa with a view to ultimately establishing, or aiding the establishment of, a specialized
investment vehicle for commercial forestry plantations.” The report declares that the
development agencies from Finland, Sweden, Norway, Denmark, Iceland, the United
Kingdom and The Netherlands are interested.
Essentially, the report is a praise to industrial monoculture plantations. It repeats, without
providing any evidence, most of the deceiving arguments that plantations companies use in
their propagandas to cover up the impacts of this devastating industry. The report’s focus is
on outlining the possible financial instruments that would attract companies to this region and
make their investments most profitable.
The report identifies “readily available projects with the potential to establish almost 500,000
ha of new forest (sic) on about 1 million ha of landscape, not including areas that existing
companies and developers are already planning to use for own expansion. It also excludes
early stage or speculative projects.” (italics added) In particular, the report identifies “viable
plantation land” in ten countries: Angola, Republic of Congo, Ghana, Mozambique, Malawi,
South Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia and Zimbabwe.
The report further affirms that “Africa may be positioned to have the most profitable
afforestation potential worldwide.” And, then, it goes into explaining the possible investment
schemes that can make profit-oriented business and afforestation objectives (from climate or
voluntary targets) to be aligned and, thus, generate more profits for shareholders.
None of the pages in the report mention, however, not even indirectly, the overwhelming
amount of information that evidences the many negative impacts that industrial plantations
cause to communities and their environments. The report’s authors chose to ignore
plantations companies’ destruction of forests and savannahs; erosion of soils; contamination
and dry-up of water sources; overall violence inflicted on communities which include
restriction of movement, criminalization when resistance emerges, abuse, harassment and
sexual violence in particular to women and girls; destruction of livelihoods and food
sovereignty; destruction of cultural, spiritual and social fabrics within and among
neighbouring communities; few precarious and hazardous jobs; unfulfilled “social” projects or
promises made to communities; destruction of ways of living; rise in HIV/AIDS; and the list
goes on.
In front of this, on September 21, 2020, the International Day of Struggle against
Monoculture Plantations, 121 organisations from 47 countries and 730 members from
different rural communities in Mozambique that are facing industrial tree plantations,
disseminated an open letter to demand the immediate abandonment of any and every
afforestation programme based on large-scale monoculture plantations. (2)
The report, nonetheless, brags about having used a “sector-wide consultation exercise.”
For the authors, the sector includes “industry participants ranging from investors, industrial
players, and Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) through to forestry fund managers
(…) To further enrich and triangulate inputs to the study, the team also participated in three
forestry industry events and consulted with a broad range of personal contacts in the sector.”
The report also mentions consultations made to Development Finance Institutions and
agencies as well as oil and other industrial companies. It is clear however how communities
living in or around the almost 500,000 hectares of land identified to be transformed into
industrial monocultures, are not considered part of the sector. Nor were considered the many
communities and groups that have been resisting for decades the plantations in the countries
the report use as examples: Tanzania, Mozambique, Ghana and Brazil. (3)
The report further sustains that the NGO Conservation International confirmed “that it sees
potential in associating large global businesses with the forestry sector.” It further mentions
WWF and The Nature Conservancy – namely, the same category of NGOs mainly concerned
on promoting programs and policies that are aligned with corporate interests as an easy way
to keep their funding, projects and investments.
The purely financial focus of this report, with an eye on how to make most profits, should not
come as a surprise though. It was prepared by a company called Acacia Sustainable
Business Advisors (4), which was set up by Martin Poulsen, a development banker active in
rising private Equity Funds particularly in Africa. Equity Funds try to offer big returns by
spreading investments across companies from different sectors. (5) One co-author of the
report was Mads Asprem, the ex-director of Green Resources, a Norwegian industrial tree
plantation and carbon offsets company. Green Resources’ tree plantations in Mozambique,
Tanzania, and Uganda have resulted in land grabs, evictions, loss of livelihoods and
increased hunger for local communities. (6)
The report also shows the possible responses that investors could have to potential
“barriers”. One “structural barrier” identified is called “stakeholder relations,” a very vague
concept that seems to be related to possible conflicts with communities living in or around
the plantation projects. The term “conflicts” however is not mentioned once in the whole
report. The recommended response to this “barrier” is to “Use AfDB or other MDB
[Multilateral Development Bank] “honest broker” profile to convene stakeholders.” So it
seems that the strategy is to use development banks to make communities believe that the
project has the intention of improving (developing) people’s lives. Another “structural barrier”
identified in the report is “land tenure challenges,” to which the recommended response is to
“Follow FSC and other best practices.” This, of course, is recommended despite the vast
amount of information that shows how, in practice, FSC certifies as “sustainable” industrial
tree plantations that destroy peoples’ livelihoods.
When the climate and development agendas blend for profit
It is relevant to underline how the report makes use of the Sustainable Development Goals
(SDG) and the need for climate change mitigation and adaptation in the African region to
promote the further expansion of industrial plantations. It goes as far as to conclude that
“Channelling financial resources to such efforts [afforestation in the framework of the SDGs]
is within the mandate of international development organizations and special climate funds.”
The report also states that “preliminary interviews yielded information that some oil
companies are already forming alliances with sustainable forestry investment companies.”
This despite the fact that oil and gas companies are a fundamental driver of climate change,
which would undermine any possible positive outcome for the climate. Besides, these
‘alliances’ also give these companies an easy way out of any responsibility for their business
operations. This is clearly exemplified with the announcement of oil giant companies, such as
Italian ENI and Anglo-Dutch Shell, to invest in mega tree plantation projects to supposedly
“compensate” their mega levels of pollution they provoke. These two companies are
responsible for environmental disasters and crimes as a result of their fossil fuel activities in
many places across the globe. (7)
The African Development Bank is complicit in this strategy. While the Bank finances this
report encouraging the expansion of industrial plantations in Africa as a climate solution, it
finances in Mozambique a new gas extraction mega-project in the Cabo Delgado province,
undertaken by a consortium of companies including ENI.
This report is one more proof of how investments from profit-seeking corporations are put in
front of the social well being of people in the name of development and now also of
addressing climate change. There is no “unused” or “degraded” land available at the scale
proposed, which means countless people in Africa will be directly and indirectly affected if
this expansion plan materialise.
Another relevant omission of the report is how it bluntly assumes that the current scarcity of
investment in large-scale tree plantations in this African region is due to the few investment
opportunities available. However, the communities and groups on the ground organizing
almost on a daily basis to oppose the seizing of their lands and lives by these plantations
companies, have clear that their resistance has been successful to halt the expansion of
these plantations in many places. And as the open letter launched on September 21st said,
communities around the world “will certainly resist this new and insane expansion plan
proposed in the AfDB and WWF-Kenya.”
(1) AfDB, CIF, WWF, Acacia Sustainable, Towards large-scale investment in African forestry, 2019,
http://redd-monitor.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/towards_largescale_
commercial_investment_in_african_forestry.pdf
(2) Open Letter about investments in monoculture tree plantations in the Global South, especially in
Africa, and in solidarity with communities resisting the occupation of their territories, 2020,
https://wrm.org.uy/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/carta-con-firmas-en-inglés_upd201008.pdf
(3) See more information on resistance struggles against plantations here: https://wrm.org.uy/browseby-
subject/international-movement-building/local-struggles-against-plantations/
(4) Acacia Sustainable Business Advisors, https://www.acaciasba.com/about
(5) Groww, Equity Mutual Funds, https://groww.in/p/equity-funds/
(6) REDD-Monitor, How WWF and the African Development Bank are promoting lang grabs in Africa,
2020, https://redd-monitor.org/2020/09/22/international-day-of-struggle-against-monoculture-treeplantations-
how-wwf-and-the-african-development-bank-are-promoting-land-grabs-in-africa/ ; The
Expansion of Tree Plantations on Peasant Territories in the Nacala Territories: Green Resources in
Mozambique, 2018, https://wrm.org.uy/articles-from-the-wrm-bulletin/recommended/the-expansion-oftree-
plantations-on-peasant-territories-in-the-nacala-corridor-green-resources-in-mozambique/ ; WRM
bulletin, Green Resources Mozambique: More False Promises! 2018, https://wrm.org.uy/articles-fromthe-
wrm-bulletin/section1/green-resources-mozambique-more-false-promises/ ; WRM bulletin, Carbon
Colonialism: Failure of Green Resources’ Carbon Offset Project in Uganda, 2018,
https://wrm.org.uy/articles-from-the-wrm-bulletin/section1/carbon-colonialism-failure-of-greenresources-
carbon-offset-project-in-uganda/ ; WRM bulletin, Tanzania: Community resistance against
monoculture tree plantations, 2018,
https://wrm.org.uy/articles-from-the-wrm-bulletin/section1/tanzania-community-resistance-againstmonoculture-
tree-plantations/ ; and WRM bulletin, The farce of “Smart forestry”: The cases of Green
Resources in Mozambique and Suzano in Brazil, 2015, https://wrm.org.uy/articles-from-the-wrmbulletin/
section1/the-farce-of-smart-forestry-the-cases-of-green-resources-in-mozambique-andsuzano-
in-brazil/
(7) REDD-Monitor, NGOs oppose the oil industry’s Natural Climate Solutions and demand that ENI
and Shell keep fossil fuels in the ground, 2019, https://wrm.org.uy/other-relevant-information/ngosoppose-
the-oil-industrys-natural-climate-solutions-and-demand-that-eni-and-shell-keep-fossil-fuels-in the-
ground /
WRM Bulletin
Related posts:

 The enduring legacy of a little-known World Bank project to secure African plantations for European billionaires
The enduring legacy of a little-known World Bank project to secure African plantations for European billionaires
 Witness Radio – Uganda, Community members from Mozambique and other organizations around the world say NO to more industrial tree plantations
Witness Radio – Uganda, Community members from Mozambique and other organizations around the world say NO to more industrial tree plantations
 CSOs to African Development Bank: Don’t fund EACOP
CSOs to African Development Bank: Don’t fund EACOP
 Open letter to African Development Bank and Nordic Development Fund: Address reprisals against Paten Clan
Open letter to African Development Bank and Nordic Development Fund: Address reprisals against Paten Clan
You may like
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
Decades of land loss and chronic poverty: Salala Rubber Plantation prioritizes profit over the well-being of local Liberian communities.
Published
2 hours agoon
February 6, 2026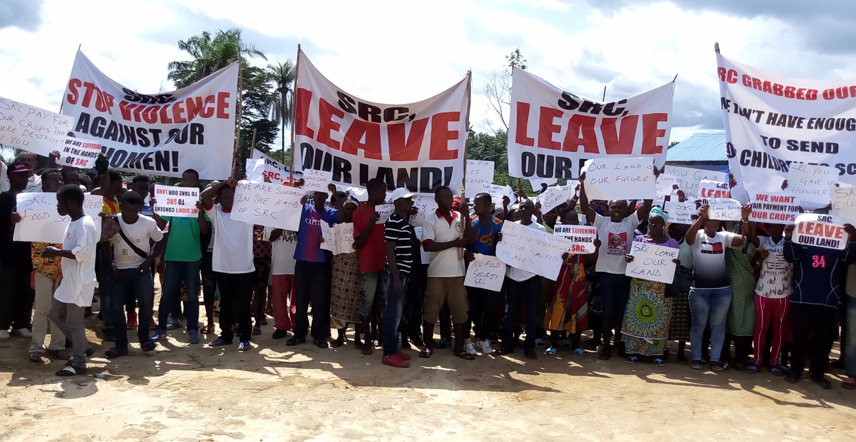
By Witness Radio team.
What began in 1959 as a promise of jobs and development has, according to affected communities and civil society advocates supporting these communities, evolved into a prolonged struggle marked by land loss, environmental destruction, and unfulfilled commitments.
In 1959, the Liberian government granted the Salala Rubber Plantation (SRC) a 70-year lease on a 40,500-hectare land concession in District 5, Margibi County, and in District 6, Bong County, respectively, and developed a rubber plantation on 8,500 hectares.
According to the company’s objectives, it aimed to develop the community by creating job opportunities and providing fair compensation to landowners.
“When the company came to Liberia, it presented itself as supporting the government by creating jobs for Liberians. That message appealed both to the government and to the local communities.” John Brownell revealed in an interview with Witness Radio.
But the expected joy never materialized. The arrival of the rubber company brought consequences whose effects are still inherited to this day. For more than six decades, communities in central Liberia have endured hardship, misery, and persistent poverty passed from one generation to the next.
Some people, especially in Lango, Tartee Towns & Deedeta 1 & 2 areas, were evicted from their land to make way for a large-scale Rubber plantation. In contrast, others who have endured violence are still placed in the middle of the company plantations. According to reports, many others whose homesteads border the company plantations are still facing land grabbing as the company extends its expansions.
Salala Rubber Plantation was established in 1959, during a period when Liberia’s land governance system recognized only public land and private land tenures, excluding customary land tenure. Although the land was officially classified as public, community members in the area, including indigenous groups, had already been cultivating it for farming, burial grounds, water sources, and cultural practices.
“Whereas the land was given to the Company for a Rubber project, it was never an abandoned land. Liberians already occupied it from the Kpelle and Bassa, and other ethnic groups. The company didn’t honor their existence; instead, it forced them off their land,” John added.
At least 22 affected communities across Bong and Margibi Counties continue to demand justice, accountability for the damages caused, and redress, highlighting the need to advocate for change.
Although the SRC concession required that land be selected exclusively from unencumbered public lands and prohibited the evacuation of villages within the concession or development area, the land ultimately selected was heavily encumbered, resulting in the eviction of several villages.
According to the concession agreement, the Concessionaire had to pay rental for public lands to be used for the project, “If the Concessionaire cannot reach a satisfactory agreement with any private owner for any land which may be mentioned as aforementioned, the Concessionaire may bring the matter to the attention of the government which agrees to use its for good offices in obtaining for the Concessionaire the use of the land in a manner equitable to the Concessionaire and the respective private owner for just and reasonable compensation.” Part of the agreement, Witness Radio obtained a copy of it, mentioned.
This meant that the company had to compensate the communities whose land was to be used for the project; instead, the company forcefully took over the community lands.
Following Liberia’s civil war, which disrupted and damaged the plantations’ investments, the Socfin Group acquired the Salala Rubber Corporation (SRC) and invested to optimize the plantation and improve social infrastructure. SRC applied for a US$10 million loan from the International Finance Corporation (IFC), an arm of the World Bank, in 2007 to rehabilitate and expand project operations. According to the documents seen by Witness Radio, the 12-year loan investment from IFC was approved in 2008.
Community representatives say that despite the earlier injustices brought to the communities after the government allocated land that was occupied by people to the company, shortly after receiving the IFC loan, the company expanded beyond its concession boundaries, encroaching on the community’s land and deliberately causing other human rights violations.
“During the operations and expansions between 2007 and 2012, they destroyed community sacred sites, polluted water sources, and destroyed their crops without adequate compensation,” Paul added.
Some villages were forced to relocate again. Between 2012 and 2013, affected communities filed complaints with civil society organizations, triggering investigations that found the company liable for multiple allegations.
“And so, by 2012 and 2013, the community then decided to file a complaint with our office. Our office had to work with them to get the government and the company to restore the economic, cultural, and social benefits that the company had destroyed for them. An investigation was conducted and found the company liable for the allegations,” Paul added.
Despite supporting the communities, advocates found engaging with the company challenging. “The communities fought for dialogue with the company, but it failed. We tried to write several letters, but the company refused to honor the dialogue with the community,” he adds.
According to the Alliance for Rural Democracy, when their engagements with the company failed, they filed a complaint with the IFC against the company’s operation.
“When dialogue attempts failed, communities escalated the matter internationally. In May 2019, Green Advocates International, Natural Resource Women Platform, and the Alliance for Rural Democracy supported them in filing a formal complaint with the IFC’s Compliance Advisor Ombudsman (CAO). The complaint involved allegations of: Physical Displacement, Economic Displacement, and Loss of Livelihood; Historical Land Claims by extension, Land Grab; Grievance Handling; and Threats and Reprisals against Complainants—gender-based violence and Harassment, among others —violations that the communities believed infringed on their human rights.
In September 2020, following a compliance appraisal, CAO initiated an investigation into IFC’s environmental and social (E&S) performance concerning the issues raised in the complaint. However, the investigation stalled until June 2023, when the communities staged a peaceful mass action at the World Bank office in Monrovia, demanding redress to their complaint.
Under pressure from communities, CAO finalized its Investigation Report in December 2023 and submitted it to the World Bank’s Board. The CAO report found harm and indications of damage to the affected communities in relation to compensation, consultation, gender-based violence and harassment (GBVH), security threats, land acquisition, Indigenous Peoples, cultural heritage, water quality, and labor practices.
In addition, Socfinaf S.A, owner of SRC, commissioned its own independent investigation led by Earthworm Foundation. The final Earthworm report corroborated the communities’ allegations against the Salala Rubber Corporation.
In response to CAO’s investigations, on March 13, 2025, the World Bank Board approved and issued the Management Action Plan (MAP). The MAP commits IFC to implement a Community Development Program to support livelihood restoration, GBVH prevention, and support to survivors. IFC management was supposed to supervise SRC’s implementation of the MAP actions.
While grievances remain unresolved, Socfinaf S.A. put the plantation up for sale and, in 2024, officially announced the sale of its subsidiary, Salala Rubber Corporation (SRC), to Jetty Rubber LLC. And community advocates also report that IFC’s Management Action Plan (MAP) has never been implemented.
“Before the sale of SRC, the affected communities and supporting Civil Society and Human Rights organizations wrote an open letter to Socfin Management, the Government of Liberia, and Jetty Rubber regarding the liabilities and the active IFC complaint. However, these institutions ignored the content of the letter, thereby allowing Socfin to divest, and Jetty took over the plantation.” Said Windor B.K. Smith of the Alliance for Rural Democracy.
The new owner, Jetty Rubber LLC, has not committed to implementing the IFC’s Management Action Plan. The 22 affected communities are in limbo because they do not know where to turn for justice and redress to their plight.
Related posts:

 We are unwaveringly committing ourselves to fight land grabs for tree plantation projects in Africa – leaders of victim communities.
We are unwaveringly committing ourselves to fight land grabs for tree plantation projects in Africa – leaders of victim communities.
 Details Revealed: Who’s a Taiwanese Investor linked to forcefully taking over 2500 hectares of land that belonged to local farmers in the Mubende district for a tree plantation project?
Details Revealed: Who’s a Taiwanese Investor linked to forcefully taking over 2500 hectares of land that belonged to local farmers in the Mubende district for a tree plantation project?
 Profiting from misery: A case of a multimillion-dollar tree project sold off before resolving land grab and human rights violation claims with local communities.
Profiting from misery: A case of a multimillion-dollar tree project sold off before resolving land grab and human rights violation claims with local communities.
 Happy 2025 to you all! Please join Witness Radio again this year to protect thousands of local farmers who are losing their land to a tree plantation owned by a Taiwan investor.
Happy 2025 to you all! Please join Witness Radio again this year to protect thousands of local farmers who are losing their land to a tree plantation owned by a Taiwan investor.
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
Indigenous communities’ complaint against World Bank-linked Nepal Cable Car Project declared eligible for investigation.
Published
1 day agoon
February 5, 2026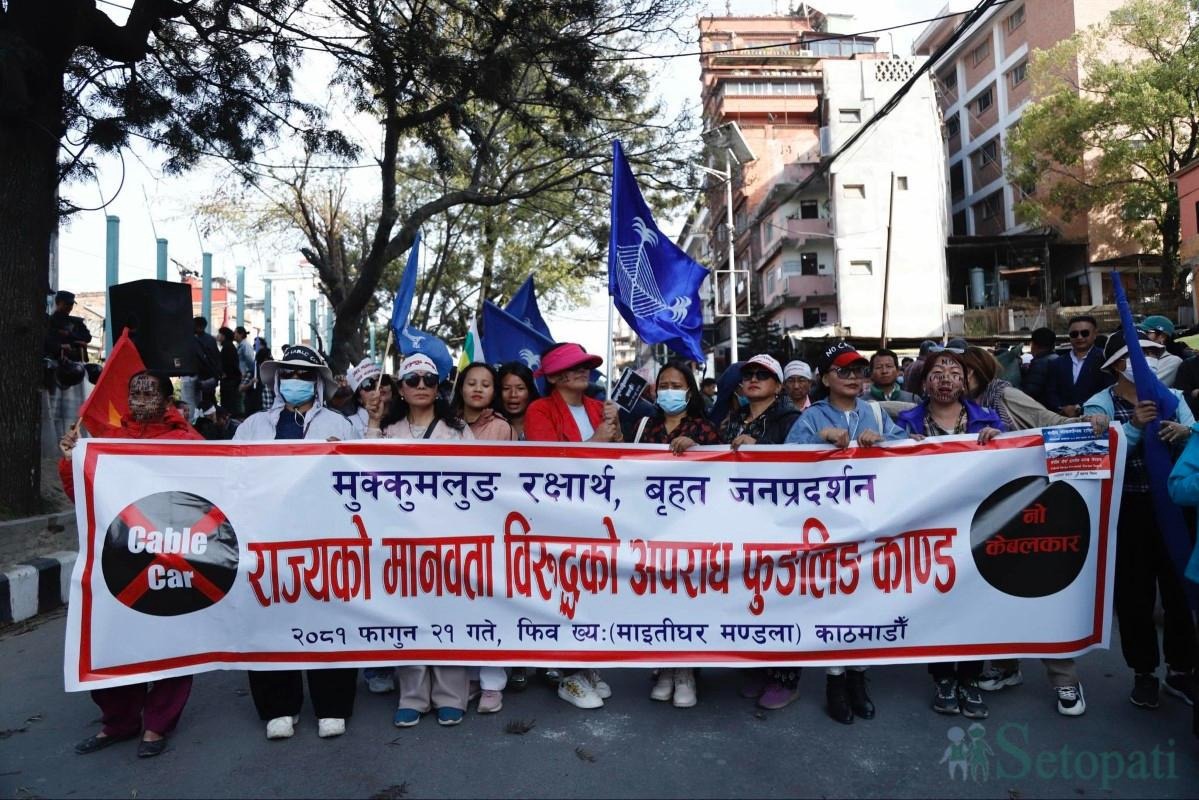
By Witness Radio team
Indigenous Yakthung (Limbu) communities in eastern Nepal have fought hard for recognition after the World Bank Group’s accountability mechanism acknowledged a complaint about rights violations, underscoring their ongoing struggle to protect their land and culture.
The Compliance Advisor Ombudsman (CAO), the independent watchdog of the World Bank Group, accepted the complaint for further assessment and formally registered the case in December 2025. The decision clears the way for a potential mediation process or a full compliance investigation into whether the project breached the IFC’s environmental and social safeguard standards.
In August 2025, Indigenous Yakthung leaders, supported by lawyers and civil society organizations, filed a complaint against the IFC’s advisory support to IME Group for the $22 million Pathivara (Mukkumlung) cable car project in Taplejung District. This filing marks a critical step in holding the project accountable for alleged rights violations and environmental harm.
The cable car is being constructed on Mukkumlung Mountain, a sacred ancestral landscape central to the Yakthung people’s spirituality and Identity, risking irreversible damage to their cultural heritage and Identity.
According to the complainants, construction has already resulted in the felling of more than 10,000 trees in and around the Kanchenjunga Conservation Area, threatening habitats of endangered species such as red pandas, snow leopards, and Himalayan musk deer, underscoring the project’s severe environmental consequences.
“The reason the Complainants and their advisors seek to engage with the CAO is because of the social and environmental harms caused by one of the cable car projects in particular, the Pathivara project. This cable car project has severe impacts on one of the most sacred sites of the Limbu (Yakthung) Indigenous Peoples, including their forests, flora, fauna, heritage (tangible and intangible), and Mukkumlung mountain. The Pathivara project has been imposed on the local Indigenous communities without their Free, Prior, and Informed Consent (FPIC), and has proceeded to destroy their lands, forests, sacred sites, and livelihoods. When the people protest, they have been met with extreme violence and repression by security forces.” The community complaint submitted to the Ombudsman in August 2025 read.
Between August 2022 and July 2024, the IFC provided advisory services to IME Group related to four cable car projects in Nepal, including the Pathivara project. The complainants allege that the IFC failed to ensure that its Environmental and Social Performance Standards, particularly those protecting Indigenous Peoples, were applied.
“The cable car project is tantamount to cultural genocide of the Limbu nation in violation of our rights guaranteed in Nepal’s constitution, the Treaty of 1774 with the Gorkha kingdom, and the UN Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples,” said Advocate Shankar Limbu, Vice-Chair of LAHURNIP.
Community members say they were unaware of IFC’s involvement until July 2024, nearly two years after construction began, due to the delayed public disclosure of the advisory support.
Accordingly, the complaints stated that the project did not meet the IFC Performance Standards, including failures to assess and manage project impacts, conduct land acquisition, and address involuntary resettlement, among others.
“The IFC’s inability to ensure its client integrated the Performance Standards into the implementation of its plan for delivering cable car projects around Nepal has led to severe breaches of the protections that were supposed to safeguard vulnerable and marginalized communities. Today, Indigenous Limbu communities are being beaten, shot at, arrested, and terrorized for trying to defend their land and way of life,” the community complaints read.
Although the IFC exited the advisory role in 2024, it continues to invest in Global IME Bank, Nepal’s largest commercial bank and a core company within the IME Group. Over the past decade, the IFC has provided more than $50 million in financing to the conglomerate, along with a $500 million trade finance guarantee, which critics say gives the institution ongoing leverage and responsibility.
In its eligibility determination, the CAO found that the complaint met the required criteria, including a plausible link between IFC-supported activities and the alleged environmental and human rights harms. The case has now entered a 90-day assessment phase, during which the CAO will consult with the affected communities, the IFC, and the company involved.
At the end of the assessment, the parties may choose to engage in dispute resolution through mediation or proceed to a full compliance investigation examining whether the IFC failed to follow its own safeguard policies.
The advocates representing the communities welcomed the CAO’s decision.
“We welcome the fact that the CAO has found this complaint eligible, and look forward to working with investigators to uncover how things went so badly wrong. The IFC is currently reviewing its Performance Standards and must learn lessons on consultation, safeguarding cultural heritage and biodiversity, respecting Indigenous Peoples’ rights, and protecting them against retaliation,” Kate Geary, Programme Director at Recourse, one of the organizations that supported the communities in the complaint, reveals.
Further, their appeal is for the CAO to handle the case with utmost urgency. “The CAO investigation into the complaint against the cable car project should move swiftly to remedy ongoing impacts of the project, including retaliations against the local communities,” added Advocate Shankar Limbu.
Indigenous leaders are demanding an immediate halt to construction, the withdrawal of security forces from the area, the release of all IFC-related project documents, and an independent investigation into alleged human rights abuses, urging urgent action to protect their rights and environment.
Related posts:

 CSOs call for meaningful changes in the World Bank’s Dispute Resolution Service to foster access to justice for project-affected communities.
CSOs call for meaningful changes in the World Bank’s Dispute Resolution Service to foster access to justice for project-affected communities.
 The World Bank Must Be Held Accountable for Harm Inflicted on Tanzanian Communities by Tourism Project
The World Bank Must Be Held Accountable for Harm Inflicted on Tanzanian Communities by Tourism Project
 Witness Radio – Uganda and partners welcome a public acknowledgment of the complaint lodged before the World Bank’s Inspection Panel.
Witness Radio – Uganda and partners welcome a public acknowledgment of the complaint lodged before the World Bank’s Inspection Panel.
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
The Witness Radio and Seed Savers Network Joint Radio program boosts Farmers’ knowledge of seed and food sovereignty.
Published
2 days agoon
February 4, 2026
By Witness Radio team
Across Africa, seed laws are increasingly structured to favor commercial seed systems, leaving smallholder farmers with limited control over the seeds they rely on for food production. While governments often justify these laws as necessary for quality control and increased productivity, farmers and civil society organizations argue that they deepen dependency, erode Indigenous knowledge, and undermine food sovereignty.
Smallholder farmers produce the majority of the world’s food. Recognizing practices such as saving, exchanging, and replanting seeds can empower farmers and reinforce their vital role in food security.
In response to this challenge, Witness Radio, in partnership with the Seed Savers Network (SSN) in Kenya, is joining hands to save African indigenous seeds by using media to build power and share knowledge and skills with smallholder farmers across Africa and beyond on seed sovereignty and farmer-led food systems.
Last Thursday, Witness Radio and the Seed Savers Network aired the first episode of the program live, featuring representatives of smallholder farmers and civil society organizations from across the African continent. The discussion, which was live on Witness Radio, focused on sharing Indigenous knowledge and practical approaches to saving and conserving African Indigenous seeds.
“It is a crucial time to speak about food sovereignty because, as Indigenous People, talking about food sovereignty is not just an agricultural issue, according to us. It’s a vital act of decolonization and a sign of cultural survival to us and also self-determination.” Said June Bartuin, the Executive Director for Indigenous Peoples’ for peace and climate justice, Kenya, during the first episode of the program.
Across Africa, several policies and laws restrict farmers’ rights to save, exchange, and sell their own seeds. In East Africa, the recently introduced EAC Seed and Plant Varieties Draft Bill 2025 has sparked protests from smallholder farmers and activists, who argue that some of its provisions threaten farmer-led seed systems and favor multinational seed companies.
In Ghana, the Plant Variety Protection Act of 2020 restricts farmers’ seed management practices, underscoring the urgent need for policy reforms that support farmer-led seed systems.
“We have this Plant Variety Protection Act of 2020, which has made it easier for seed companies and the commercial sector to control the seed system,” said Atim Robert Anaab, who works with Trax Ghana and the Beela Project in Northern Ghana, adding that, “The law requires seeds to be certified according to standards that most small-scale farmers simply cannot meet.”
Such laws have reshaped Africa’s food systems by pushing farmers toward commercial seeds that must be purchased every planting season. These seeds are often sold alongside chemical fertilizers and pesticides, significantly increasing production costs for smallholder farmers.
Priscilla Nakato, Chairperson of the Informal Alliance of Communities Affected by Irresponsible Land-Based Investments in Uganda, noted that these policies have also displaced traditional storage and seed preservation practices.
“In the past, every household had a granary, used not only to store food but also to preserve seeds for the next planting season. Many communities still hold this resilience, and reviving these practices can inspire hope for food sovereignty.”
Beyond economics, restrictive seed laws are accelerating the erosion of Indigenous knowledge and cultural practices. June Bartuin explained that women were traditionally the custodians of seeds, preserving them using low-cost methods such as smoke storage in traditional houses.
“This maize could be stored for two, three, even five years, and when planted, it germinated very well,” she added.
The collaboration between Witness Radio and the Seed Savers Network brings together grassroots organizing and community media to amplify farmers’ voices. The Seed Savers Network, a grassroots organization based in Kenya, works with more than 500,000 farmers and supports 121 community seed banks across the country.
According to Mercy Ambani, Resource Mobilization Officer at Seed Savers Network, the organization focuses on rebuilding farmers’ confidence, knowledge, and rights, making platforms such as Witness Radio ideal for reaching farmers directly.
“Our vision is to protect seed sovereignty, conserve biodiversity, and strengthen farmers’ rights through policy advocacy and practical action,” she said.
Through initiatives such as the Seed School, farmers, researchers, and activists are trained in seed selection, storage, preservation, and community seed bank management.
“In December 2024, Kenyan farmers achieved a landmark court ruling that struck down parts of the Seed and Plant Varieties Act, showing the power of collective action and legal advocacy to protect farmers’ rights.”
“This ruling showed that there is power in numbers,” said Ambani. “When farmers raise their voices together, change is possible.”
Regional knowledge exchange is also growing. Farmers from Uganda and Ghana who attended the Seed Savers Boot Camp have returned to their communities to establish household seed banks, kitchen gardens, and farmer field schools.
“My home has become a farmer’s field school. People are hungry for this knowledge,” said Nakato.
Without reforms that recognize and protect farmer-managed seed systems, farmers risk losing control over their seeds — and with them, control over food, culture, and livelihoods.
“If we lose our seeds, we lose our culture, our food, and our future,” Bartuin emphasized.
Wokulira Geoffrey Ssebaggala, Team Leader at Witness Radio, highlighted the importance of creating space for farmers to share knowledge and experiences.
“We are providing a platform where farmers and experts can exchange knowledge on sustainable farming practices. We believe this radio content will have a real impact on food and seed sovereignty across Africa.” Mr. Ssebaggala added.
The radio series will continue to provide practical knowledge, farmer voices, and policy analysis to support sustainable agriculture across Africa.
Related posts:

 Happening shortly! Kenya’s upcoming court ruling on the Seed Law could have a significant impact on farmers’ rights, food sovereignty, and the country’s food system.
Happening shortly! Kenya’s upcoming court ruling on the Seed Law could have a significant impact on farmers’ rights, food sovereignty, and the country’s food system.
 Seed Sovereignty: Most existing and emerging laws and policies on seeds are endangering seed saving and conservation on the African continent.
Seed Sovereignty: Most existing and emerging laws and policies on seeds are endangering seed saving and conservation on the African continent.
 The EAC Seed & Plant Varieties Bill, 2025, is a potential threat to smallholder farmers, as it aims to disengage them from the agriculture business, according to experts.
The EAC Seed & Plant Varieties Bill, 2025, is a potential threat to smallholder farmers, as it aims to disengage them from the agriculture business, according to experts.
 Seed Boot Camp: A struggle to conserve local and indigenous seeds from extinction.
Seed Boot Camp: A struggle to conserve local and indigenous seeds from extinction.

Decades of land loss and chronic poverty: Salala Rubber Plantation prioritizes profit over the well-being of local Liberian communities.

US-DRC Strategic Partnership Agreement Faces Constitutional Challenge in Court

Indigenous communities’ complaint against World Bank-linked Nepal Cable Car Project declared eligible for investigation.

The Witness Radio and Seed Savers Network Joint Radio program boosts Farmers’ knowledge of seed and food sovereignty.

Will Uganda’s next government break the land-grabbing cycle?

Women environmental rights defenders in Africa are at the most significant risk of threats and attacks – ALLIED New report

Swedish pension fund drops TotalEnergies amid rising EACOP risks

Uganda moves toward a Bamboo Policy to boost environmental conservation and green growth.

Innovative Finance from Canada projects positive impact on local communities.
Over 5000 Indigenous Communities evicted in Kiryandongo District
Petition To Land Inquiry Commission Over Human Rights In Kiryandongo District
Invisible victims of Uganda Land Grabs
Resource Center
- Land And Environment Rights In Uganda Experiences From Karamoja And Mid Western Sub Regions
- REPARATORY AND CLIMATE JUSTICE MUST BE AT THE CORE OF COP30, SAY GLOBAL LEADERS AND MOVEMENTS
- LAND GRABS AT GUNPOINT REPORT IN KIRYANDONGO DISTRICT
- THOSE OIL LIARS! THEY DESTROYED MY BUSINESS!
- RESEARCH BRIEF -TOURISM POTENTIAL OF GREATER MASAKA -MARCH 2025
- The Mouila Declaration of the Informal Alliance against the Expansion of Industrial Monocultures
- FORCED LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA TRENDS RIGHTS OF DEFENDERS IMPACT AND CALL FOR ACTION
- 12 KEY DEMANDS FROM CSOS TO WORLD LEADERS AT THE OPENING OF COP16 IN SAUDI ARABIA
Legal Framework
READ BY CATEGORY
Newsletter
Trending
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks agoWomen environmental rights defenders in Africa are at the most significant risk of threats and attacks – ALLIED New report
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week agoEvicted from their land to host Refugees: A case of Uganda’s Kyangwali refugee settlement expansion, which left host communities landless.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week agoWitness Radio and Seed Savers Network are partnering to produce radio content to save indigenous seeds in Africa.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK4 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK4 days agoIndigenous communities in Eastern Nepal accuse the World Bank’s Linked Cable Car Project of rights violations.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK6 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK6 days agoWhy govt is launching a comprehensive digital land registry
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK3 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK3 days agoClose to six years on, Pangero Chiefdom subjects still linger in pain after the government army’s forceful takeover of their ancestral land.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 days agoThe Witness Radio and Seed Savers Network Joint Radio program boosts Farmers’ knowledge of seed and food sovereignty.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 day ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 day agoIndigenous communities’ complaint against World Bank-linked Nepal Cable Car Project declared eligible for investigation.
