WITNESS RADIO MILESTONES
Food Sovereignty: A Manifesto for the Future of Our Planet
Published
4 years agoon

“It is for the future of humanity that we defend our food sovereignty,” says La Via Campesina.
An official statement marking 25 years of collective struggles for food sovereignty.
Food Sovereignty is a philosophy of life.
It offers a vision for our collective future, and defines the principles around which we organize our daily living and co-exist with Mother Earth. It is a celebration of life and all the diversity around us. It embraces every element of our cosmos; the sky above our heads, the land beneath our feet, the air we breathe, the forests, the mountains, valleys, farms, oceans, rivers and ponds. It recognizes and protects the inter-dependency between eight million species that share this home with us.
We inherited this collective wisdom from our ancestors, who ploughed the land and waded the waters for 10,000 years, a period in which we evolved into an agrarian society. Food Sovereignty promotes justice, equality, dignity, fraternity and solidarity. Food Sovereignty is also the science of life – built through lived realities spread across countless generations, each teaching their progeny something new, inventing new methods and techniques which sat harmoniously with nature.
As holders of this rich heritage, it is our collective responsibility to defend it and preserve it.
Food Sovereignty promotes justice, equality, dignity, fraternity and solidarity. Food Sovereignty is also the science of life.
Recognizing this as our duty – especially in the late ’90s when conflicts, acute hunger, global warming and extreme poverty were too visible to ignore – La Via Campesina(LVC) brought the paradigm of Food Sovereignty into international policy-making spaces. LVC reminded the world that this philosophy of life must guide the principles of our shared living.
The ’80s and the ’90s were an era of unbridled capitalist expansion – at a pace never seen before in human history. Cities were expanding, growing on the backs of cheap, unpaid and underpaid labour. The countryside was being pushed into oblivion. Rural communities and rural ways of living were swept under the carpet by a new ideology that wanted to turn everybody into a mere consumer of things and an object of exploitation for profit. Popular culture and consciousness were under the spell of glittery advertisements goading people to “buy more”. In all this, though, the ones who produced – the working class in the rural areas, coasts and cities, which included the peasants and other small-scale food producers – remained invisible, while the ones who could afford to consume with wander took centre stage. Pushed to the edges, peasant1 workers and indigenous communities worldwide recognized the urgent necessity for an organized and internationalist response to this globalizing, free-market ideology propagated by the defenders of the capitalist world order. Food Sovereignty became one of the expressions of this collective response.

At the 1996 World Food Summit, in a debate about how we organize our global food systems, La Via Campesina coined the term food sovereignty; to insist upon the centrality of the small-scale food producers, the accumulated wisdom of generations, the autonomy and diversity of rural and urban communities and solidarity between peoples, as essential components for crafting policies around food and agriculture.
In the ensuing decade, social movements and civil society actors worked together to define it further “as the right of peoples to healthy and culturally appropriate food produced through ecologically sound and sustainable methods, and their right to define their own food and agriculture systems. It puts the aspirations and needs of those who produce, distribute and consume food at the heart of food systems and policies rather than the demands of markets and corporations.”
The introduction of Food Sovereignty as a collective right changed how the world understood poverty and hunger.
Until then, especially in the early years of the 21st century, a narrow idea of “Food Security” dominated governance and policy-making circles. Noble in its intent, food security treated those affected by hunger as objects of compassion, risked reducing them to passive consumers of food produced elsewhere. While it recognized food as a fundamental human right, it did not defend the objective conditions for producing food. Who produces? For Whom? How? Where? And Why? All these questions were absent, and the focus was decidedly on merely “feeding the people”. An overt emphasis on people’s food security ignored the hazardous consequences of industrial food production and factory farming, built on the sweat and labour of migrant workers.
Food Sovereignty, on the other hand, presents a radical overhaul. It recognizes people and local communities as the principal actors in the fight against poverty and hunger. It calls for strong local communities and defends their right to produce and consume before trading the surplus. It demands autonomy and objective conditions to use local resources, calls for agrarian reform and collective ownership of territories. It defends the rights of peasant communities to use, save, exchange seeds. It stands for the rights of people to eat healthy, nutritious food. It encourages agroecological production cycles, respecting climatic and cultural diversities in every community. Social peace, social justice, gender justice and solidarity economies are essential pre-conditions for realizing food sovereignty. It calls for an international trade order based on cooperation and compassion as against competition and coercion. It calls for a society that rejects discrimination in all forms – caste, class, racial and gender – and urges people to fight patriarchy and parochialism. A tree is only strong as its roots. Food Sovereignty, defined by social movements in the ‘90s and subsequently at the Nyeleni Forum in Mali in 2007, intends to do precisely that.
This year we celebrate 25 years of this collective construction.
The world is nowhere near perfect. Capitalism and free-market ideology continue to dominate policy circles even in the face of unprecedented inequality, rising hunger and extreme poverty. Worse, new attempts are also being made to envision a digital future – of farming without farmers, fishing without fishers- all under the garb of digitalisation of agriculture and to create new markets for synthetic food.
All these challenges notwithstanding, the Food Sovereignty Movement, which is now much more extensive than La Via Campesina and comprises several actors, has made significant advances.
Thanks to our joint struggles, global governance institutions such as the FAO 2 have come to recognize the centrality of peoples’ food sovereignty in international policy-making. The UN Declaration on Rights Peasants and Other People Working in Rural Areas further re-emphasizes this in Article 15.4, when it states, “ Peasants and other people working in rural areas have the right to determine their own food and agriculture systems, recognized by many States and regions as the right to food sovereignty. This includes the right to participate in decision-making processes on food and agriculture policy and the right to healthy and adequate food produced through ecologically sound and sustainable methods that respect their cultures.”
Some nations have also given constitutional recognition to Food Sovereignty. The disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic in the industrial food chains have further reminded national governments of the importance of creating robust local economies.
Peasant Agroecology, which is fundamental to ensuring food sovereignty in our territories, is now recognized at the FAO as central to our fight against global warming. Current and previous Special Rapporteurs of the United Nations have endorsed food sovereignty as a simple but powerful idea that can transform the global food system favouring small-scale food producers. Sustained campaign by social movements have also resulted in several legal victories against corporations producing agro-toxins, other chemical inputs and transgenic seeds.
Yet, what lies ahead of us is a road ridden with many barriers.
The promoters of the capitalist world order realize that food sovereignty is an idea that impinges on their financial interests. They prefer a world of monoculture and homogenous tastes, where food can be mass-produced using cheap labour in faraway factories, disregarding its ecological, human and social impacts. They prefer economies of scale to robust local economies. They choose a global-free market (based on speculation and cut-throat competition) over solidarity economies that require more robust territorial markets (local peasant markets) and active participation of local food producers. They prefer to have land banks where industrial-scale contract farming would replace small-holder producers. They inject our soil with agro-toxics for better short-term yields, ignoring the irreversible damage to soil health. Their trawlers will again crawl the oceans and rivers, netting fishes for a global market while the coastal communities starve. They will continue to try to hijack indigenous peasant seeds through patents and seed treaties. The trade agreements they craft will again aim to bring down tariffs that protect our local economies.
Food sovereignty… is an idea that unites humanity and puts us at the service of Mother Earth that feeds and nourishes us.
An exodus of unemployed youth, deserting village farms and choosing wage work in cities, sits perfectly with their urge to find a regular supply of cheap labour. Their unrelenting focus on “margins” would mean that they will find all means to depress farm-gate prices while trading it at higher prices at retail supermarkets. In the end, the ones who lose are the people – both the producers and consumers. Those who resist will be criminalized. A happy co-existence of the global financial elite with authoritarian governments would mean that even the highest institutions – nationally and globally – meant to oversee and arrest human rights violations will look away. Billionaires would use their philanthropic foundations to fund agencies that churn out “research reports” and “scientific journals” to justify this corporate vision of our food systems. Every global governance space, where the social movements and civil society members campaigned hard to gain a seat at the table, will make way for Corporate Conglomerates who will enter the scene as “stakeholders”. Every attempt will be made to deride those of us who defend Food Sovereignty as unscientific, primitive, impractical and idealistic. All this will happen, as it did over the last two decades.
None of this is new to us. Those condemned to the peripheries of our societies by a cruel and all-devouring capitalist system have no choice but to fight back. We must resist and show that we exist. It is not just about our survival, but also about future generations and a way of life handed down through generations. It is for the future of humanity that we defend our food sovereignty.
This is only possible if we insist that any local, national or global policy proposal on food and agriculture must build from the principles of food sovereignty. The young peasants and workers of our worldwide movement must lead this fight. We must remind ourselves that the only way to make our voice heard is by uniting and building new alliances within and across every border. Rural and Urban Social Movements, Trade Unions and civil society actors, progressive governments, academics, scientists and technology enthusiasts must come together to defend this vision for our future. Peasant women and other oppressed gender minorities must find equal space in the leadership of our movement at all levels. We must sow the seeds of solidarity in our communities and address all forms of discrimination that keep rural societies divided.
Food Sovereignty offers a manifesto for the future, a feminist vision that embraces diversity. It is an idea that unites humanity and puts us at the service of Mother Earth that feeds and nourishes us.
In its defence, we stand united.
Globalize the Struggle, Globalize Hope.
#NoFutureWithoutFoodSovereignty
La Via Campesina
Original Source: commondreams.org
Related posts:

 UN Food Systems Summit: The Battle Over Global Food and Agriculture Governance
UN Food Systems Summit: The Battle Over Global Food and Agriculture Governance
 Food Sovereignty is the only solution and way forward.
Food Sovereignty is the only solution and way forward.
 Food sovereignty is Africa’s only solution to climate chaos
Food sovereignty is Africa’s only solution to climate chaos
 La Via Campesina calls on States to exit the WTO and to create a new framework based on food sovereignty
La Via Campesina calls on States to exit the WTO and to create a new framework based on food sovereignty
You may like
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
Young activists fight to be heard as officials push forward on devastating project: ‘It is corporate greed’
Published
3 months agoon
August 27, 2025
“We refuse to inherit a damaged planet and devastated communities.”
Youth climate activists in Uganda protesting the East African Crude Oil Pipeline, or EACOP, are frustrated with the government’s response to their demonstration as the years-long project moves forward.
According to the country’s Daily Monitor, youth activists organized with End Fossil Occupy Uganda took to the streets of Kampala in early August to protest EACOP. The pipeline, under construction since about 2017 and now 62 percent complete, is set to transport crude oil from Uganda’s Tilenga and Kingfisher fields through Tanzania to the Indian Ocean port of Tanga by 2026.
Activists noted the devastating toll, with group spokesperson Felix Musinguzi saying that already around 13,000 people “have lost their land with unfair compensation” and estimating that around 90,000 more in Uganda and Tanzania could be affected. End Fossil Occupy Uganda has also warned of risks to vital water sources, including Lake Victoria, which it says 40 million people rely on.
The group has been calling on financial institutions to withdraw funding for the project. Following a demonstration at Stanbic Bank earlier in the month, 12 activists were arrested, according to the Daily Monitor.
Some protesters were seen holding signs reading “Every loan to big oil is a debt to our children” and “It’s not economic development; it is corporate greed.”
Meanwhile, the regional newspaper says the government has described the activist efforts as driven by foreign actors who mean to subvert economic progress.
EACOP’s site notes that its shareholders include French multinational TotalEnergies — owning 62 percent of the company’s shares — Uganda National Oil Company, Tanzania Petroleum Development Corporation, and China National Offshore Oil Corporation.
The wave of young people taking action against EACOP could be seen as a sign of growing public frustration over infrastructural projects that promise economic gain while bringing harm to local communities and ecosystems. Activists say residents face costly threats from pipeline development, such as forced displacement and the loss of livelihoods.
Environmental hazards to Lake Victoria could also disrupt water supplies and food systems, bringing the potential for both financial and health impacts. Just 10 years ago, an oil spill in Kenya caused a humanitarian crisis. The Kenya Pipeline Company reportedly attributed the spill to pipeline corrosion, which led to contamination of the Thange River and severe illness.
The EACOP project has already locked the region into close to a decade of development, and concerns about the pipeline and continued investments in carbon-intensive systems go back just as long. Youth activists, as well as concerned citizens of all ages, say efforts to move toward climate resilience can’t wait. “As young people, we refuse to inherit a damaged planet and devastated communities,” Musinguzi said, per the Monitor.
Source: The Cool Down
Related posts:

 Put people above profits – Climate Activists urge Total to defund EACOP
Put people above profits – Climate Activists urge Total to defund EACOP
 EACOP: The number of activists arrested for opposing the project is already soaring in just a few months of 2025
EACOP: The number of activists arrested for opposing the project is already soaring in just a few months of 2025
 EACOP activism under Siege: Activists are reportedly criminalized for opposing oil pipeline project in Uganda.
EACOP activism under Siege: Activists are reportedly criminalized for opposing oil pipeline project in Uganda.
 The East African Court of Justice fixes the ruling date for a petition challenging the EACOP project.
The East African Court of Justice fixes the ruling date for a petition challenging the EACOP project.
WITNESS RADIO MILESTONES
Why matooke farming is losing ground in Bukedi
Published
3 months agoon
August 27, 2025
On a humid morning in Namusango Village, Kamonkoli South Ward, Kamonkoli Town Council in Budaka District, 58-year-old farmer James Kainja walks at the edge of what used to be his flourishing matooke garden. For generations, the green banana plant—matooke—stood tall in Uganda’s farmlands, its broad leaves swaying in the wind and its heavy bunches promising a warm, hearty meal. But in Bukedi Sub-region today, that story is fading. Between the tired banana stools, spear grass has taken over. A few bunches hang small and low quality. “We used to harvest every week,” Mr Kainja says, dusting his palms.
“Now, it is once in a while and the money is not worth the struggle,” he adds. Across Bukedi, particularly in Pallisa, Budaka, Butebo, and Kibuku, the banana plants are shrinking back, replaced by maize, cassava, rice, and other faster-growing crops. The sub-region that once sent truckloads of matooke to nearby districts now measures its banana harvest in small piles under tarpaulin. Where the green canopy of banana leaves once dominated, the landscape has changed. For many farmers, the decision is not about abandoning tradition but about survival.
Matooke as culture
In many Bukedi households, matooke still holds cultural value, especially during weddings, funerals, and community gatherings. But with fewer plantations, sourcing enough bunches has become harder and more expensive. Matooke is now imported into Bukedi from Mbale and Mbarara. Mr Abubakar Nanghejje, an elder in Kibuku, warns: “If this trend continues, our children may only know matooke from stories. We are losing more than a crop—we are losing a piece of who we are.”
He adds that matooke, once abundant, is now a luxury: “People only access matooke during ceremonies because the cost of a bunch has turned expensive,” he explains. Within Kibuku Town Council, women sell matooke in pieces: three or four fingers for Shs1,000, while a complete bunch costs between Shs30,000 and Shs35,000. This contrasts sharply with central and western Uganda, where matooke is more than a crop—it is an identity, a culture, and a livelihood. Yet across the country, banana plantations are thinning out, replaced by maize, beans, or simply abandoned.
Farmers’ voices
Mr Peter Mwigala, a 73-year-old farmer from Bubulanga Village, recalls with nostalgia: “I grew matooke for 30 years. But now my plantation is less than half what it used to be. The pests are too many, the prices are too low, and the rains are no longer reliable.” His story echoes across villages, evidence of a slow, steady decline in matooke production. This decline has unfolded over two to three decades, rather than as a sudden collapse. Agricultural researchers point to several reasons. Among them, banana bacterial wilt (BBW), banana weevils, and nematodes that have devastated plantations in major banana-growing areas. These pests cause premature ripening, rotting, and eventual uprooting of infected plants.
“When wilt enters your plantation, you can lose everything in one season,” says Mr Abner Botiri, an agriculture officer in Budaka. He further explains that erratic rainfall and prolonged dry spells also take a toll. Matooke thrives in consistent moisture, but under drought stress it yields smaller bunches. Repeated losses have led some farmers to abandon the crop entirely. Continuous cultivation without soil management has also depleted many banana-growing soils. Beyond agronomic challenges, the economics of matooke farming have shifted dramatically. Local market prices fluctuate widely depending on supply, while transport costs have risen sharply.
Mr John Gwanyi, a 71-year-old farmer, recalls: “In the 1980s and 1990s, matooke farmers could educate children through primary, secondary, and tertiary levels, and still cover basic needs. Today, a whole plantation might not pay for one term’s school fees.” Urbanisation has worsened the trend. Younger generations moving to towns now eat rice, spaghetti, and bread more frequently.
The once sacred matooke meal is no longer the undisputed centrepiece of Ugandan dining tables. Meanwhile, land fragmentation leaves families with smaller plots, unable to sustain large banana plantations. In some areas, higher-value or quicker-return crops like coffee, passion fruit, or maize dominate. As one agricultural economist notes: “A bunch of matooke takes nine months to mature, but maize can be ready in three months. For cash-strapped farmers, that difference matters.
Government interventions
Government and research institutions have made several attempts to address the situation. The National Agricultural Research Organisation (NARO) has introduced resistant banana varieties and promoted good agronomic practices. NGOs are training farmers in mulching, proper spacing, and integrated pest management. Still, the decline carries a cultural weight. In Buganda, for instance, matooke is central to marriage ceremonies, community gatherings, and daily life.
“When you serve matooke at a function, it shows respect,” explains Mr Badiru Kirya, a cultural leader in Obwa Ikumbania bwa Bugwere. Yet, Mr Kirya attributes part of the decline to newer banana varieties introduced by research agencies. “The old varieties planted by our grandparents could withstand weather changes better. These new varieties are weaker against climate volatility,” he says. He also notes that soil infertility and population pressure have accelerated the decline, as families squeeze more onto smaller pieces of land.
National standing
Uganda remains one of the world’s largest banana consumers, with per capita consumption estimated at 250–300 kg annually in some regions. Yet, national banana production has generally declined. According to the Uganda Bureau of Statistics (UBOS) 2024 census, only 27.1 percent of households participate in banana cultivation. Dr Sadik Kassim, the NARO deputy director general in-charge of agricultural promotion, highlights several factors. “Soil fertility has gone low, while pests and disease build-up have grossly affected matooke gardens. Erratic rainfall and climate change further reduce yields.
Poor agricultural practices have made the decline worse,” he says. However, Dr Kassim dismisses the claim that new technologies are to blame. Similarly, Dr Rabooni Tumuhimbise, the director of research at Rwebitaba Zonal Agricultural Research and Development Institute, said: “As of now, I am not aware that Bukedi has registered a decline in banana production. This needs verification before conclusions.” But farmers and local leaders insist the reality is clear: matooke is disappearing from Bukedi. Mr Arthur Wako Mboizi, a seasoned politician and opinion leader, argues: “Bukedi has drastically registered a total decline in banana production due to various factors, including soil infertility, diseases, and erratic rainfall.”
Efforts are underway to add value. Under the Presidential Initiative on Banana, NARO and Kilimo Trust have developed matooke-based products such as flour, bread, and cakes. More than 13 million Ugandans consume bananas as their staple, and 75 percent of farmers grow them, contributing nearly $440 million annually to the economy. Yet, for Bukedi, the reality is sobering. The once proud producer of matooke is a shadow of its former self. As Mr Nanghejje, the Kibuku elder, put it: “We are losing more than a crop. We are losing a piece of who we are.”
Background
In 2024, national banana production was estimated at 6 million tonnes annually, 70 percent of which was consumed at household level and 30 percent sold.
The Banana Merchandise Trade Statistics Bulletin (2024) shows export earnings rose from $2.1 million in June 2023 to $2.4 million in June 2024. Still, yields remain below potential—currently 5–30 tonnes per hectare compared to an attainable 60–70 tonnes. Uganda’s banana losses to wilt disease are massive, with officials estimating a 71.4 percent loss of potential harvest annually, worth nearly $300 million.
Source: Monitor
Related posts:

 Govt injects Shs47b into cassava growing in Bukedi
Govt injects Shs47b into cassava growing in Bukedi
 Uganda’s natives are becoming more powerless; losing land everyday, says a New Research Report
Uganda’s natives are becoming more powerless; losing land everyday, says a New Research Report
 Omoro farmers task Naro on crop varieties
Omoro farmers task Naro on crop varieties
 Uganda losing agricultural advantage to neighbours – UN.
Uganda losing agricultural advantage to neighbours – UN.
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
Cases against anti-EACOP activism are skyrocketing in Uganda. Witness Radio has documented close to 60 cases in the last eight months.
Published
4 months agoon
August 7, 2025
By the dedicated efforts of the Witness Radio team.
The Witness Radio team has documented nearly 60 cases of arrest, detention, and prosecution targeting activists protesting the East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP) since January 2025.
The $5 billion EACOP project, led by TotalEnergies and its partners, involves the construction of a 1,444km heated pipeline from Hoima in Uganda to Tanga in Tanzania. This pipeline, which will transport crude oil from the Tilenga and Kingfisher fields, has been a subject of controversy due to its potential environmental and social impacts.
As activism against the EACOP Project grows in Uganda, youth activists leading the cause face strong resistance from the government and its agents, who are pushing for the development of oil activities, including EACOP. Their bravery in the face of such adversity is truly inspiring.
The activists have continuously been suppressed and weakened with torture, unlawful arrests, and prolonged detentions accompanied by unscrupulous charges. The injustice they face is a call for empathy from all who hear their story.
The latest incident happened on Friday, August 1, 2025, when the police brutally arrested 12 environmental activists at Stanbic Bank Headquarters in Kampala. The urgency of the situation is apparent, as the activists were protesting against the bank’s financing of the EACOP project.
On March 26, 2025, EACOP Ltd., the company in charge of the construction and future operation of the EACOP project, announced new project financing from regional banks such as Stanbic Bank Uganda Limited, KCB Bank Uganda, African Export-Import Bank (Afreximbank), the Standard Bank of South Africa Limited, and the Islamic Corporation for the Development of the Private Sector (ICD). The announcement sparked widespread alarm and outcry, with activists urging the banks to immediately withdraw their support and halt the financing of the project.
These activists, individuals from Civil Society Organisations (CSOs) and environmental enthusiasts, strongly oppose the implementation of the EACOP project. They cite its harmful effects, including the displacement of thousands of people, damage to sensitive ecosystems, a threat to water resources, and exacerbating climate change mainly through carbon emissions. They argue that the short-term economic benefits do not justify these long-term consequences.
In doing their work, they have ended up in the hands of the authorities with numerous charges slapped against them. The latest remandees include Teopista Nakyambade, Shammy Nalwadda, Dorothy Asio, Shafik Kalyango, Habibu Nalungu, Noah Kafiiti, Ismael Zziwa, Ivan Wamboga, Akram Katende, Baker Tamale, Keisha Ali, and Mark Makobe.
On the same day of their arrest, the victims were arraigned before the Buganda Road Chief Magistrate Winnie Nankya, who charged them with common nuisance. She later remanded them to Luzira prison until August 18, 2025.
Section 160 of the Penal Code Act, Cap 120 states that a person convicted of common nuisance faces a one-year imprisonment.
In response, the Stanbic Bank manager for corporate communications, Mr. Kenneth Agutamba, confirmed that the bank is financing the EACOP project, justifying that it aligns with and balances environmental sustainability and economic development in the country.
Ever since this year started, Witness Radio has documented 56 cases of arrests and illegal detentions of EACOP activists, with most of them being charged with common nuisance. Below is a chronology of these incidents as they happened.
| Date | Incident | Charge |
| 26th Feb. 2025 | 11 activists were arrested while marching to the European Union offices deliver a petition concerning TotalEnergies’ involvement in harmful fossil fuels in Uganda. | Common nuisance |
| 19th Mar. 2025 | 4 activists were arrested while marching to the Parliament of Uganda to deliver a petition to the speaker, Anita Annet Among, in protest of the ongoing construction of the EACOP Project. | Common nuisance |
| 2nd April, 2025 | 9 activists were arrested while marching to Stanbic bank offices. | Common nuisance |
| 23rd of April, 2025 | A group of 11 activists were arrested as peacefully went to deliver a petition to KCB Uganda offices challenging its will to fund the EACOP project. | Criminal trespass. |
| 21 May 2025 | 9 activists arrested while protesting KCB financing of the EACOP | Common nuisance. |
| 1 Aug. 2025. | 12 activists arrested for protesting the Stanbic bank funding. | common nuisance |
According to Witness Radio’s special report, “Activism on Trial: Despite the increasing repressive measures, Uganda’s EACOP Protesters are achieving unexpected victories in the country’s justice systems,” released last month, a case review revealed that while Uganda’s justice system is being used to suppress the activities of youth activists opposing the EACOP project, many of these cases have lacked merit and were ultimately dismissed.
The report found that none of the activists had been convicted, though they continue to face prolonged court processes marked by repeated adjournments. “Of a sample of 20 documented cases since 2022 involving the arrest of over 180 activists, 9 case files have either been dismissed by the courts or closed by the police due to lack of prosecution, another signal indicating the relevance and legitimacy of their work, while 11 cases remain ongoing,” the report noted.
Related posts:

 EACOP activism under Siege: Activists are reportedly criminalized for opposing oil pipeline project in Uganda.
EACOP activism under Siege: Activists are reportedly criminalized for opposing oil pipeline project in Uganda.
 Breaking: over 350,000 acres of land were grabbed during Witness Radio – Uganda’s seven months ban.
Breaking: over 350,000 acres of land were grabbed during Witness Radio – Uganda’s seven months ban.
 EACOP: The number of activists arrested for opposing the project is already soaring in just a few months of 2025
EACOP: The number of activists arrested for opposing the project is already soaring in just a few months of 2025
 Crackdown on EACOP protesters intensifies: 35 Activists arrested in just four months.
Crackdown on EACOP protesters intensifies: 35 Activists arrested in just four months.

Activists storm TotalEnergies’ office ahead of G20 Summit, demand end to fossil fuel expansion in Africa

Environmentalists reject TFFF, warning it will deepen forest destruction.
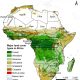
“Vacant Land” Narrative Fuels Dispossession and Ecological Crisis in Africa – New report.

Uganda’s Army is on the spot for forcibly grabbing land for families in Pangero Chiefdom in Nebbi district.

Seed Boot Camp: A struggle to conserve local and indigenous seeds from extinction.

REC25 & EXPO Ends with a call on Uganda to balance conservation and livelihood

“Vacant Land” Narrative Fuels Dispossession and Ecological Crisis in Africa – New report.

Report reveals ongoing Human Rights Abuses and environmental destruction by the Chinese oil company CNOOC

Innovative Finance from Canada projects positive impact on local communities.
Over 5000 Indigenous Communities evicted in Kiryandongo District
Petition To Land Inquiry Commission Over Human Rights In Kiryandongo District
Invisible victims of Uganda Land Grabs
Resource Center
- REPARATORY AND CLIMATE JUSTICE MUST BE AT THE CORE OF COP30, SAY GLOBAL LEADERS AND MOVEMENTS
- LAND GRABS AT GUNPOINT REPORT IN KIRYANDONGO DISTRICT
- THOSE OIL LIARS! THEY DESTROYED MY BUSINESS!
- RESEARCH BRIEF -TOURISM POTENTIAL OF GREATER MASAKA -MARCH 2025
- The Mouila Declaration of the Informal Alliance against the Expansion of Industrial Monocultures
- FORCED LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA TRENDS RIGHTS OF DEFENDERS IMPACT AND CALL FOR ACTION
- 12 KEY DEMANDS FROM CSOS TO WORLD LEADERS AT THE OPENING OF COP16 IN SAUDI ARABIA
- PRESENDIANTIAL DIRECTIVE BANNING ALL LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA
Legal Framework
READ BY CATEGORY
Newsletter
Trending
-
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago“Vacant Land” Narrative Fuels Dispossession and Ecological Crisis in Africa – New report.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK3 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK3 days agoActivists storm TotalEnergies’ office ahead of G20 Summit, demand end to fossil fuel expansion in Africa
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks agoUganda’s Army is on the spot for forcibly grabbing land for families in Pangero Chiefdom in Nebbi district.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks agoSeed Sovereignty: Most existing and emerging laws and policies on seeds are endangering seed saving and conservation on the African continent.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK4 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK4 days agoEnvironmentalists reject TFFF, warning it will deepen forest destruction.
-

 NGO WORK2 weeks ago
NGO WORK2 weeks agoDiscover How Foreign Interests and Resource Extraction Continue to Drive Congo’s Crisis
-

 NGO WORK2 weeks ago
NGO WORK2 weeks agoAfrica’s Land Is Not Empty: New Report Debunks the Myth of “Unused Land” and Calls for a Just Future for the Continent’s Farmland
-

 NGO WORK2 weeks ago
NGO WORK2 weeks agoClimate wash: The World Bank’s Fresh Offensive on Land Rights


