MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
Well connected: The resistance against the fossil industry in East Africa.
Published
1 year agoon

Uganda and Tanzania have created facts about the promotion of the fossil industry by launch on the construction of the East African crude oil pipeline. At the same time, the internationally networked resistance of civilian actors towards the booming oil production in East Africa is growing. Judicial complaints are a central element in their fight to uphold the rule of law, human rights and environmental protection.
Last year, the beginning of the end of the fossil era was ushered in at the world climate conference in Dubai. Some countries interpret this as follows: it is necessary to get the last fossil fuels out of the ground. This means drilling, dredging, pumping – to earn crude oil, gas and coal once again.
One example is the fossil industry in Uganda, which is trying to feed its last fossil occurrences from the ground into the global economy. It wants to pump the petroleum down there to the surface and through a heated pipeline into a deep-sea port into the Tanzanian tanga. From there, it, together with the French energy giant TotalEnergies and Chinese participation, is being shipped for the global oil industry.
The oil project called the East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP) with a targeted running time of 25 years has been under construction since this April. In Tanzania and Uganda, the scope of civilian actors who are fighting against land seizures for the 1,443-kilometre-long pipeline corridor and defending human rights is severely restricted. In Uganda, the police have arrested farmers, journalists, human rights and environmental defenders who have spoken out against the oil projects. Reporters Without Borders once again stated in May that freedom of the press and civil say are strictly curtailed. At the end of May, eight environmental activists were arrested when a letter of protest to the Chinese Embassy was arrested by Ugandan security forces. Obviously, governments sacrifice freedom of expression, human rights and livelihoods for their fossil utopianism.
Bizarre oil shops
Uganda’s government is not only pursuing an export strategy for its crude oil, which is stored in the Albertgraben on the border with the DR Congo. It also wants to modify its own oil import infrastructure. For this purpose, Ugandan President Yoweri Museveni initiated an old oil dispute with Kenya: In February, the neighbouring countries decided to resume the plan to expand the Mombasa-Eldoret-Kampala pipeline. This pipeline originates in the port of Mombasa/Kenya, on the Indian Ocean and currently leads via Nairobi to Eldoret in West Kenya. This part has been in operation since May 2014. For many years, plans to extend the pipeline have been circulating, first to Kampala on Lake Victoria, Ugandan, then on to Rwanda’s capital Kigali, possibly even to Lake Bujumbura Burundi around Lake Tanganyika.
This would mean that on the one hand, the export of crude oil is being produced, while at the same time the import of refined oil will be extended. This contradicts any economic logic that the finishing of a product is not outsourced as far as possible. While Uganda wants to transport its crude oil via the East African crude pipeleline EACOP to the port to Tanga and sell it from there on the world market, from Mombasa, 130 kilometres north of Tanga, refined oil via the Mombasa Eldoret pipeline to Kampala is to be pumped at the same time.
On the one hand, crude oil transport for the world market, on the other hand, import of refined oil – that is, of fishing-for fuels – for one’s own energy needs: this is an old pattern for asymmetric trade relations – or, as the Kenyan climate activist Omar Elawi said: business colonialism. Others will benefit from the refinement of the crude oil and transport. The oil, transported twice over thousands of kilometres, puts a heavy impact on the environment and undermines the social development of the adjacent municipalities. The economic dependence of the Global South is simply reproduced in terms of trade policy. And climate policy, the EACOP is also a disaster that undermines the fair energy transition in Uganda.
Problems and protest on the spot …
It is therefore not surprising that the sharpest critics of EACOP include many regional environmental and human rights defenders as well as initiatives affected. For example, Witness Radio Uganda documents land veins on an interactive map and has been providing legal assistance to people in rural areas affected by land expulsion for years. Tonny Katende from Witness Radio says: “We combine legal assistance and media work to mobilize the rural population. This is the only way she can protest with a strong voice against the injustices in land use and environmental destruction and advocate for equal access to resources in our country.”
Another activist is Christopher Opio, founder of the Oil Refinery Residents Association (ORRA). The NGO with over 7,000 members recently protested before the Court in Hoima in Western Uganda. This is where the pipeline is to start, and 42 households have recently been sued by the government, because they refused to accept compensation for their country: “This means that these people are now being driven out of their country,” said Opio. At the protest on the 15th April the landowners moved through the city towards court. They hold signs high with messages such as “Do not attach our rights” and “do not self-elige us for oil”.
TotalEnergies has been drilling in Tilenga on the northern shore of Lake Albert on Lake Albert since June 2023. Four hundred holes are planned, one third of which are in a natural park. In the Kingfisher area further south of the lake, the Chinese company CNCOOC is taking hold to light since January 2023. Fishing communities of both places turn to the companies with a protest letter in April 2024: the light from the drilling rigs violates and distributes the fish, and nitrogen- and phosphorous-containing wastewater is burdening the water quality. The risks documented by international environmental organizations such as Les Amis de la Terre, Natural Justice and Greenpeace, as well as Human Rights Watch and BankTrack, are concerned about water and the health of over eleven million residents at Lake Albert: 426 wells ensure that water is pumped from Lake Lake Lake. The water is then heavily heavy metal and poses a threat to the population as wastewater. A leak would be a disaster for which no one is sufficiently prepared.
… and anti-imperial rhetoric of the revolt
Local civilian actors in Tanzania and Uganda, including lawyers, students and stakeholders, are often discredited by their own governments as an extended arm of imperial Western environmental extremists. An environmental journalist and a community worker temporarily left the country for persecution and intimidation.
Governments sacrifice the environment for their fossil utopianism
Activism does not arise from a capitalist lobby, but scientifically proven risks to the environment, dangers to the health of neighbouring communities, concrete human rights violations such as land displacements and expropriations, and de facto violent attacks by the police and the military – including rape and massive bodily injury to the rural population. On the basis of research and witness reports, problems are combated, such as the inadequate compensation of the oil lobby or the authoritarian behavior of the project operators. Here the anti-imperial rhetoric of the government side is like a diversionary manoeuvre.
The Chinese CNCOOC and TotalEnergies are now feeling resistance from all over the world in addition to the local protest. This is the international (instead of imperial) dimension of the debate. More than 260 civil society organisations are demanding a stop from EACOP. The political forms of action and protest of the well-connected movement against the construction of the EACOP are manifold: an important lever is legal complaints against violations by companies and governments. Another strategy is divestment. Potential investors or insurance companies should be persuaded not to invest in environmentally harmful and anti-social projects, or to deduct their capital from such projects.
Complained, divestment and political pressure
In November 2020, four East African civil society organisations, including AFIEGO, Natural Justice Kenya and the Tanzanian Strategic Litigation Centre (SLC), filed a complaint against EACOP at the East African Court (EACJ). After an initial dismissal, the Appeals Division of the East African Court requested the plaintiffs at the beginning of the year, until 22. March submit written comments. By the end of April, the defendants were again allowed to react to them in writing. The civilian plaintiffs see legal principles violated by the state, including the environmental and human rights standards enshrined in the Treaty of East African Community for the benefit of current and future generations, as well as compliance with international treaties.
The consortium of lawsuits is an expression of a regionally and internationally well-connected NGO community, which takes legal action against the fossil fuels, including its financial and reinsurance companies, through legal action. This means that among the global civilian NGO networks is growing know-how to strategies for how to take several tracks against the land grabbing of the climate-damaging fossil industry. With the worldwide campaign “StopEACOP, 29 investors have now been discouraged to be part of the pipeline project, including the second largest German insurance group Talanx.
In the fight against the large-scale fossil-fuel project EACOP, the strategy of divestment is considered promising, especially in Europe: Public pressure on the suppliers from the construction, insurance, logistics and credit institutions sectors is to prevent the cash flow for the project, which is still not financially secured. Another great success of the international campaign alliance “StopEACOP” was the withdrawal of the Japanese Sumitomo Mitsui Financial Group over a year ago. Meanwhile, 27 banks and 23 reinsurers as well as four export credit agencies have announced that they will not support EACOP. Therefore the mood on the Instagram account of the campaign alliance is sometimes euphoric.
The political pressure was also some success. International alliances confront politicians with studies such as “A Disaster in the Making” by Les Amis de la Terre or “Our Trust is Broken” by Human Rights Watch 2023. The European Parliament called on the governments of Uganda and Tanzania to comply with human rights standards in September 2022. In a decision on the COP27 climate conference, the German Bundestag spoke out against the financing of the EACOP in 2022.
Do the climate complain?
Lucien Limacher from the organisation Natural Justice from South Africa, one of the members of the plaintiffs against the EACOP before the East African Court, generally likes the effects of climate lawsuits. On the one hand, climate lawsuits are also increasing on the African continent. However, Limacher also says: “In the global North there is a misunderstanding about how we define climate processes. Africa will suffer massively from the consequences when global warming of more than 2.5 degrees is suffering.” In addition, in view of the 400 to 600 fossil projects that are up to 400 to 600, the climate cannot be saved solely through the route of the process. “So we need to think about how we proceed in legal disputes. A new way of thinking is emerging on the African continent: local climate lawsuits are no longer just about emissions, but about much more comprehensive risk factors such as access to food and water or land, because these areas that will be most severely affected.”
Despite the manifold resistance, the further construction of the EACOP is also progressing – and thus Uganda’s desire to become part of the ranks of the petrostate, half of which cover their economy from oil business. After the exit of European and Japanese banks from EACOP financing, the French energy giant TotalEnergies has signed a contract with China Petroleum Pipeline Engineering (CPP) for the construction and supply of line pipes. This means that the cross-border project has been relocated to Beijing, from where most of the still missing loans are likely to come from. During the recent visit of China’s head of state Xi Jinping to France in early May, there was no public talk of the oil shipping in Uganda. It is hardly conceivable that Macron and Xi of all people can silence the issue, because the resistance against the EACOP is great, especially in France.
The struggles for oil production in Uganda, with the words of the Ugandan anthropologist Paddy Kinyeras 1, show that pipelines as critical infrastructures represent physical manifestations of power geometry. The realization of the pipeline requires governmental power and strengthens it at the same time. Since the Paris Climate Agreement, the World Climate Summits have been a place to publicly confront this government and corporate power and to create political back pressure against the fossil industry. They also serve as an international networking area for the civilian actors.
At the end of 2024, after the United Arab Emirates in 2023, a fossil heavyweight will once again host the World Climate Summit: Azerbaijan. And thus for the third time in a row a country that plans to rely on fossil resources and revive oil and gas production before the agreed phasing-out. Once again, the summit will be headed by a long-standing employee of an oil company, Muchtar Babaiev. He is the Minister for the Environment of a host country that has little understanding for civilian engagement. It is not very promising to take place against the charged fossil lobby. This is one reason upon all, internationally networked environmental, research and human rights initiatives in the fossil industry. They are essential to open the oil business with protests, climate lawsuits, divestment campaigns and political pressure.
Source: www.iz3w.org
Related posts:

 East African Court of Justice is to decide whether it has jurisdiction to try the EACOP case filed by Four East African NGOs today.
East African Court of Justice is to decide whether it has jurisdiction to try the EACOP case filed by Four East African NGOs today.
 A reference filed by CSOs against the planned construction of the East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP) is set for hearing.
A reference filed by CSOs against the planned construction of the East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP) is set for hearing.
 The East African Court of Justice fixes the ruling date for a petition challenging the EACOP project.
The East African Court of Justice fixes the ruling date for a petition challenging the EACOP project.
 Appellate Division of the East African Court of Justice (EACJ) to hear an Appeal filed by CSOs which seeks to reinstate a petition against the construction of the EACOP project tomorrow.
Appellate Division of the East African Court of Justice (EACJ) to hear an Appeal filed by CSOs which seeks to reinstate a petition against the construction of the EACOP project tomorrow.

You may like
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
“Vacant Land” Narrative Fuels Dispossession and Ecological Crisis in Africa – New report.
Published
2 days agoon
November 13, 2025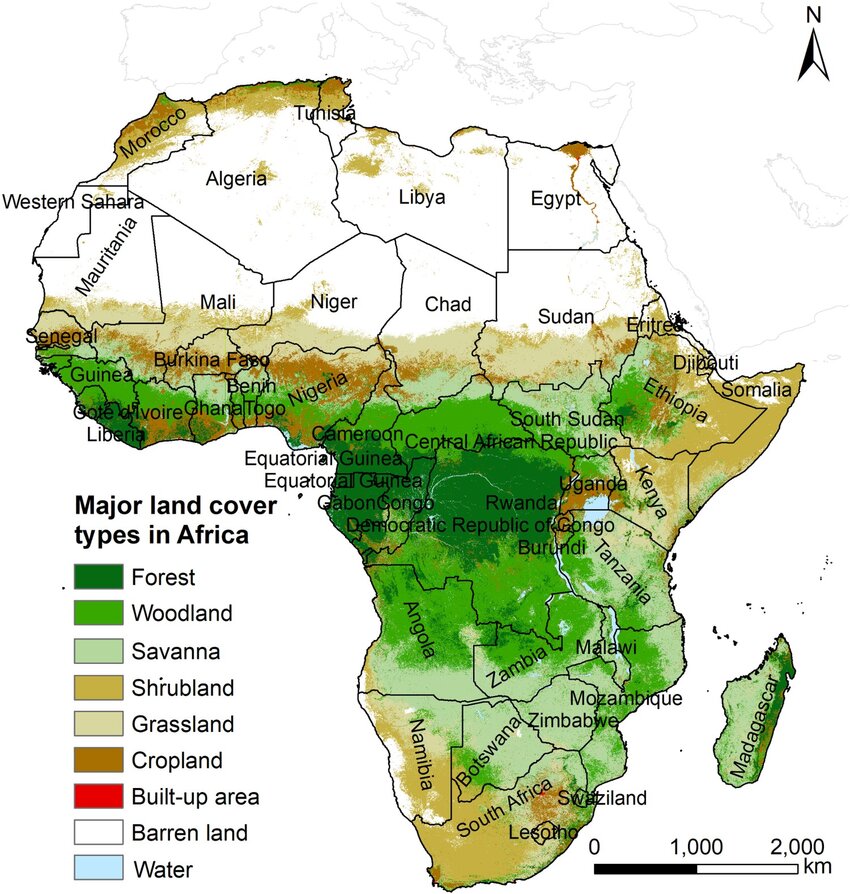
By Witness Radio team.
Over the years, the African continent has been damaged by the notion that it has vast and vacant land that is unused or underutilised, waiting to be transformed into industrial farms or profitable carbon markets. This myth, typical of the colonial era ideologies, has justified land grabs, mass displacements, and environmental destruction in the name of development and modernisation.
A new report by the Alliance for Food Sovereignty in Africa (AFSA) titled “Land Availability and Land-Use Changes in Africa (2025)” dismisses this narrative as misleading. Drawing on satellite data, field research, and interviews with farmers across Africa, including Zambia, Mozambique, South Africa, and Zimbabwe, the study reveals that far from being empty, Africa’s landscapes are multifunctional systems that sustain millions of lives.
“Much of the land labelled as “underutilised” is, in fact, used for grazing, shifting cultivation, gathering wild foods, spiritual practices, or is part of ecologically significant systems such as forests, wetlands, or savannahs. These uses are often invisible in formal land registries or economic metrics but are essential for local livelihoods and biodiversity. Moreover, the land often carries layered customary claims and is far from being available for simple expropriation,” says the report.
“Africa has seen three waves of dispossession, and we are in the midst of the third. The first was the alienation of land through conquest and annexation in the colonial period. In some parts of the continent, there have been reversals as part of national liberation struggles and the early independence era. But state developmentalism through the post-colonial period also brought about a second wave of state-driven land dispossession.” This historical context is crucial to understanding the current state of land rights and development in Africa. Said Ruth Hall, a professor at the Institute for Poverty, Land and Agrarian Studies (PLAS), at the University of the Western Cape in Cape Town, South Africa, during the official launch of the report.
The report further underestimates the assumption that smallholder farmers are unproductive and should be replaced with mechanised large-scale farming, leading to a loss of food sovereignty.
“The claim that small-scale farmers are incapable of feeding Africa is not supported by evidence. Africa has an estimated 33 million smallholder farmers, who manage 80% of the continent’s farmland and produce up to 80% of its food. Rather than being inefficient, small-scale agro-ecological farming offers numerous advantages: it is more labour-intensive, resilient to shocks, adaptable to local environments, and embedded in cultural and social life. Dismissing this sector in favour of large-scale, mechanised monocultures undermines food sovereignty, biodiversity, and rural employment.” Reads the Report.
The idea that industrial agriculture will lift millions out of poverty has not materialised. Instead, large-scale agribusiness projects have often concentrated land and wealth in the hands of elites and foreign investors. Job creation has been minimal, as modern farms rely heavily on machinery rather than human labour. Moreover, export-oriented agriculture prioritises global markets over local food security, leaving communities vulnerable to price fluctuations and shortages.
“The promise that agro-industrial expansion will create millions of decent jobs is historically and economically questionable. Agro-industrial models tend to displace labour through mechanisation and concentrate benefits in the hands of large companies. Most industrial agriculture jobs are seasonal, poorly paid, and insecure. In contrast, smallholder farming remains the primary source of employment across Africa, particularly for young people and women. The idea that technology-intensive farming will be a panacea for unemployment ignores the structural realities of African economies and the failures of previous industrialisation efforts.”
Additionally, the assumption that increasing yields and expanding markets will automatically improve food access overlooks the structural causes of food insecurity. People’s ability, particularly that of the poor and marginalised, to access nutritious food depends on land rights, income distribution, gender equity, and the functioning of political systems. In many countries, high agricultural productivity coexists with hunger and malnutrition because food systems are oriented towards export and profit rather than equitable distribution and local nourishment. It highlights the urgent need for equitable food distribution, making the audience more empathetic and aware of the issue.
Furthermore, technological fixes such as improved seeds, synthetic fertilizers, and irrigation are being promoted as solutions to Africa’s food insecurity, but evidence suggests otherwise. The Alliance for a Green Revolution in Africa (AGRA) spent over a decade pushing such technologies with little success; hunger actually increased in its target countries.
These high-input models overlook local ecological realities and structural inequalities, while increasing dependence on costly external inputs. As a result, smallholders often fall into debt and lose control over their own seeds and farming systems. It underscores the importance of understanding and respecting local ecological realities, making the audience feel more connected and responsible.
Africa is already experiencing an increased and accelerating squeeze on land due to competing demands including rapid population growth and urbanisation, Expansion of mining operations, especially for critical minerals like cobalt, lithium, and rare-earth elements, which are central to the global green transition, The proliferation of carbon-offset projects, often requiring vast tracts of land for afforestation or reforestation schemes that displace existing land users, Rising global demand for timber, which is increasing deforestation and land competition as well as Agricultural expansion for commodity crops, including large-scale plantations of palm oil, sugarcane, tobacco, and rubber.
“In East Africa, we see mass evictions, like the Maasai of Burunguru, forced from their ancestral territories in the name of conservation and tourism. In Central Africa, forests are cleared for mining of transitional minerals, destroying ecosystems and livelihoods. Women, a backbone of Africa’s food production, remain the most affected, and least consulted in decisions over land and resources and things that affect them.” Said Mariam Bassi Olsen from Friends of the Earth Nigeria, and a representative of the Alliance for Food Sovereignty in Africa.
The report urges a shift away from Africa’s high-tech, market-driven, land-intensive development model toward a just, sustainable, and locally grounded vision by promoting agroecology for food sovereignty, ecological renewal, and rural livelihoods, while reducing the need for land expansion through improved productivity, equitable food distribution, and reduced waste.
Additionally, a call is made for responsible urban planning, sustainable timber management, and reduced mineral demand through circular economies, as well as the legal recognition of customary land rights, especially for women and Indigenous peoples, and adherence to the principle of Free, Prior, and Informed Consent (FPIC) for all land investments.
Related posts:

 AGRA’s Silent Takeover: The Hidden Impact on Africa’s Agricultural Policies.
AGRA’s Silent Takeover: The Hidden Impact on Africa’s Agricultural Policies.
 63 million people food insecure in Horn of Africa: report
63 million people food insecure in Horn of Africa: report
 African Food Systems Summit 2024: Do not use it to promote failed agricultural models – African Faith Leaders.
African Food Systems Summit 2024: Do not use it to promote failed agricultural models – African Faith Leaders.
 Carbon offset projects exacerbate land grabbing and undermine small farmers’ independence – GRAIN report
Carbon offset projects exacerbate land grabbing and undermine small farmers’ independence – GRAIN report
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
Uganda’s Army is on the spot for forcibly grabbing land for families in Pangero Chiefdom in Nebbi district.
Published
2 days agoon
November 13, 2025
By the Witness Radio team.
Despite the challenges, the community in Koch Parish, Nebbi Sub-County, in Nebbi District, near the Congolese border, has shown remarkable resilience. The Army seized approximately 100 acres of land, including private buildings, that members of the local Koch community had used for over 150 years to establish an Army barracks. Their resilience in the face of such a significant loss is genuinely inspiring.
The UPDF, as described on its website, is a nonpartisan force, national in character, patriotic, professional, disciplined, productive, and subordinate to the civilian authority as established under the constitution. Furthermore, it states that its primary interest is to protect Uganda and Africa at large, providing a safe and secure environment in which all Ugandan citizens can live and prosper.
However, according to a whistleblower, when the UPDF seized their land, no military chiefs offered prior communication, consultation, compensation, or resettlement. Instead, Uganda’s national Army only occupied people’s land forcefully, and not even the section commanders offered an official explanation.
“Citizens just woke up to a massive Army deployment in their fields,” wrote a whistleblower in an exchange with Witness Radio.
The occupied area in Koch Parish is not just a piece of land, but a home to the members of the Pangero chiefdom. This community belongs to the Alur kingdom, which spans north-western Congo and western Uganda, north of Lake Albert.
The reality and daily life of the Pangero community, which typically lives in a closely connected and communal manner, have been significantly impacted by the loss of both private and communal land. Not only is the cultural identity associated with land and community life at risk, but access to cultural sites, such as the graves of ancestors, is now denied.
Members of the local community who resisted the unlawful seizure of their land were reported to have been harassed and defamed. Despite these challenges, they continue to fight for their rights, making negotiations with the UPDF significantly more challenging.
Beyond the human suffering, the takeover also raises serious legal questions under Ugandan land law. Under Ugandan law, this action by the UPDF constitutes an illegal act. In principle, the government and, by extension, the Army are entitled to take over land if it is in the public interest, and are subject to fairly compensating the landowners.
However, this is subject to the condition that their intention is clearly communicated in advance and that negotiations take place with the previous residents, resulting in a mutual agreement on the necessary and appropriate compensation.
When faced with community resistance, the Army was compelled to conduct a survey and valuation of the land occupied by the UPDF in 2023 and 2024. However, land defenders in the area claim that the process was marred by irregularities in some cases, against the will and in the absence of many landowners.
“The community was also pressured by the Koch Land Committee responsible for the review. Despite that it was supposed to represent the local population, it was not democratically elected by consensus, as is tradition in Alur communities, and was comprised of an imposed elite.” A local defender told Witness Radio
At an announcement meeting facilitated by officials from the UPDF Land Board, their national surveyor, and the Commander of Koch Army Barracks on September 19, 2025, community members were compelled to sign documents for meager compensation for land that had been seized five years prior.
“Residents whose land was surveyed before were given two choices: To sell their land to the Army by accepting the offered compensation, or to refuse the UPDF’s offer. In the latter case, however, it would be necessary to contact the Army headquarters in Mbuya, which is far away, to assert one’s claims or submit a petition.” Says another defender. Despite signing for this money, as of the writing of this article, the community claims it had never received it, almost two months later.
Mr Opio Okech, who attended the meeting himself, disapproves that this equates to a forced decision to sell, as the further necessary measures seem almost impossible for those affected without legal knowledge or external support.
“The problem here from the government was to enter upon the land, stay for long without adequate awareness creation, then decide we are going nowhere. Come for compensation. This looks, smells, and walks like a forceful eviction, “he mentions.
The effects of forced land acquisition by the UPDF in Koch Parish pose a high risk of home and landlessness, rises in youth criminality, and recurring poverty, primarily affecting women and children. Furthermore, the dispersal of the traditional community of the Pangero chiefdom is most likely to result in a severe loss of cultural heritage.
The Ugandan government has a duty here to look after the needs of this traditional community beyond compensation. This could include providing alternative land on which the traditional communal way of life could continue.
Witness Radio had not received a response from Army spokesperson Mr. Felix Kulayigye regarding the land grab, despite several attempts. However, since the initial takeover in 2020, another land grab by the same agency is looming in the same Kochi community for the expansion of the Army barracks.
According to sources, the UPDF intends to acquire more than 1,000 acres in total, nearly half of Koch Parish, leaving residents in fear and uncertainty.
“People are now panicking because they have heard speculations that more land is being
targeted for expansion. They are concerned about the impunity of the national Army, since the land that was grabbed five years ago has not been paid for, and now there are reports that more than 1,000 acres of community land are being targeted.” Mr. Okello further revealed.
The fate of the Pangero chiefdom is not an isolated case. Across Uganda, communal lands belonging to traditional clans and kingdoms continue to face similar threats from investors and state actors. Although Ugandan law recognizes customary ownership, enforcement often remains weak, and those affected rarely have access to the information or resources needed to defend their rights.
Related posts:

 Church of Uganda’s call to end land grabbing is timely and re-enforces earlier calls to investigate quack investors and their agents fueling the problem.
Church of Uganda’s call to end land grabbing is timely and re-enforces earlier calls to investigate quack investors and their agents fueling the problem.
 Ugandan army to punish soldiers for torturing Journalist in Kampala
Ugandan army to punish soldiers for torturing Journalist in Kampala
 Mubende district police are aiding land grabbing and committing crimes against locals they are obliged to protect.
Mubende district police are aiding land grabbing and committing crimes against locals they are obliged to protect.
 Uganda: World Bank financing is violently forcing thousands of local families off their land for large-scale cereal growing.
Uganda: World Bank financing is violently forcing thousands of local families off their land for large-scale cereal growing.
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
Seed Sovereignty: Most existing and emerging laws and policies on seeds are endangering seed saving and conservation on the African continent.
Published
4 days agoon
November 11, 2025
By the Witness Radio team
In Africa, farmers and civil society organizations are urgently warning about the adverse effects of existing policies on agrobiodiversity. These policies aim to erode centuries-old traditions of seed saving and exchange, effectively undermining seed sovereignty and intensifying dependency on commercial seed companies.
The struggle over seed sovereignty, particularly the rights of smallholder farmers, has become one of the most pressing issues for the continent’s agricultural future. As governments introduce new seed laws, such as the proposed East African Seed and Plant Varieties Act Bill of 2024, the preservation of cultural seeds and the rights of smallholder farmers are at stake.
The Communications and Advocacy Officer at Kenya’s Seed Savers Network, Tabitha Munyeri, notes that this has heightened monoculture, thereby significantly reducing the focus on indigenous plant varieties.
“There’s a lot of loss of agrobiodiversity with people focussing on a few foods, a few crops, leaving out so many other essential crops that have sustained humankind for generations and it is also important because it is coming at a time where we are having a lot of also conversations around different seed laws that are coming up for example within the EAC we see that there is the seed and plant varieties bill of 2024 and we are looking at it as a huge setback and there is need for us to create awareness around even the policies that exist.”
She further argues that there is a need to raise awareness and sensitise farmers to the existing policies so that they can understand their effects on agrobiodiversity.
“Even for Kenya we have been having punitive seed laws for the longest time but now we are happy that courts of law are reviewing the law, but we still think that there is need to create a lot of advocacy around the seed laws and what they really mean to farmers because some of them do not understand, some of them are not even interested but once they get to know what it means and the impacts that the laws have on them then they are also able to become more vocal and more involved in the process.” She says.
Farmers in Africa have been the custodians of agricultural biodiversity, developing and maintaining numerous varieties of crops that are suited to local soils and climates. However, over the last few decades, the focus on farming has drastically declined to a handful of “high-yield” crops and imported hybrid varieties, leaving out the diverse indigenous seeds that have sustained communities through droughts, pests, and diseases.
Munyeri warns that this decline in agrobiodiversity is accelerating, driven not merely by market pressures, but by restrictive laws that criminalise and discourage traditional seed-saving practices.
In Kenya, where smallholder farmers supply more than 80 percent of the country’s food, seed systems have long depended on the informal exchange of seeds within communities. Small-hold farmers have relied on these systems to share, adapt, and innovate with seeds suited to their local conditions. However, existing laws have tended to favour the formal sector, requiring seed certification, variety registration, and compliance with intellectual property protections that most small-scale farmers cannot afford.
The 2024 Seed and Plant Varieties Act Bill, currently under discussion in several East African countries, has sparked significant controversy. It seeks to modernize agriculture and align national systems with international standards. However, smallholder farmers and critics contend that it allows corporate control over genetic resources, limiting farmers’ autonomy and threatening biodiversity. Under such a framework, only registered seed varieties can be legally traded or exchanged, effectively outlawing the informal seed networks that have sustained rural communities for centuries.
If smallholder farmers lose their rights to exchange and cultivate indigenous varieties, they may also lose control over their food systems. Dependence on improved seeds necessitates purchasing new stock each planting season, eroding self-reliance and increasing vulnerability to market fluctuations.
This awareness gap is what the Seed Savers Network hopes to address. Through training programs and advocacy initiatives, including its recently concluded regional boot camp, the organization equips participants from across Africa with knowledge about seed laws, biodiversity, and policy engagement.
Related posts:

 Seed Boot Camp: A struggle to conserve local and indigenous seeds from extinction.
Seed Boot Camp: A struggle to conserve local and indigenous seeds from extinction.
 The EAC Seed & Plant Varieties Bill, 2025, is a potential threat to smallholder farmers, as it aims to disengage them from the agriculture business, according to experts.
The EAC Seed & Plant Varieties Bill, 2025, is a potential threat to smallholder farmers, as it aims to disengage them from the agriculture business, according to experts.
 CSOs and Smallholder farmers are urgently convening to scrutinize the EAC Seed & Plant Varieties Bill, 2025.
CSOs and Smallholder farmers are urgently convening to scrutinize the EAC Seed & Plant Varieties Bill, 2025.
 African governments are giving in to corporate pressure and undermining local seed systems – report
African governments are giving in to corporate pressure and undermining local seed systems – report
“Vacant Land” Narrative Fuels Dispossession and Ecological Crisis in Africa – New report.

Uganda’s Army is on the spot for forcibly grabbing land for families in Pangero Chiefdom in Nebbi district.

Climate wash: The World Bank’s Fresh Offensive on Land Rights

Africa’s Land Is Not Empty: New Report Debunks the Myth of “Unused Land” and Calls for a Just Future for the Continent’s Farmland

StopEACOP Coalition warns TotalEnergies and CNOOC investors of escalating ‘financial and reputational’ Risks

Seed Boot Camp: A struggle to conserve local and indigenous seeds from extinction.

Know Your Land rights and environmental protection laws: a case of a refreshed radio program transferring legal knowledge to local and indigenous communities to protect their land and the environment at Witness Radio.

Failed US-Brokered “Peace” Deal Was Never About Peace in DRC

Innovative Finance from Canada projects positive impact on local communities.
Over 5000 Indigenous Communities evicted in Kiryandongo District
Petition To Land Inquiry Commission Over Human Rights In Kiryandongo District
Invisible victims of Uganda Land Grabs
Resource Center
- REPARATORY AND CLIMATE JUSTICE MUST BE AT THE CORE OF COP30, SAY GLOBAL LEADERS AND MOVEMENTS
- LAND GRABS AT GUNPOINT REPORT IN KIRYANDONGO DISTRICT
- THOSE OIL LIARS! THEY DESTROYED MY BUSINESS!
- RESEARCH BRIEF -TOURISM POTENTIAL OF GREATER MASAKA -MARCH 2025
- The Mouila Declaration of the Informal Alliance against the Expansion of Industrial Monocultures
- FORCED LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA TRENDS RIGHTS OF DEFENDERS IMPACT AND CALL FOR ACTION
- 12 KEY DEMANDS FROM CSOS TO WORLD LEADERS AT THE OPENING OF COP16 IN SAUDI ARABIA
- PRESENDIANTIAL DIRECTIVE BANNING ALL LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA
Legal Framework
READ BY CATEGORY
Newsletter
Trending
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks agoReport reveals ongoing Human Rights Abuses and environmental destruction by the Chinese oil company CNOOC
-

 SPECIAL REPORTS AND PROJECTS2 weeks ago
SPECIAL REPORTS AND PROJECTS2 weeks agoThe Environmental Crisis Is a Capitalist Crisis
-
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 days ago“Vacant Land” Narrative Fuels Dispossession and Ecological Crisis in Africa – New report.
-

 SPECIAL REPORTS AND PROJECTS2 weeks ago
SPECIAL REPORTS AND PROJECTS2 weeks agoGlobal use of coal hit record high in 2024
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week agoLands ministry rejects call to save over 300 Masaka residents facing eviction
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK4 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK4 days agoSeed Sovereignty: Most existing and emerging laws and policies on seeds are endangering seed saving and conservation on the African continent.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 days agoUganda’s Army is on the spot for forcibly grabbing land for families in Pangero Chiefdom in Nebbi district.
-

 NGO WORK4 days ago
NGO WORK4 days agoDiscover How Foreign Interests and Resource Extraction Continue to Drive Congo’s Crisis

