MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
Monoculture tree plantations are a false climate solution
Published
5 years agoon
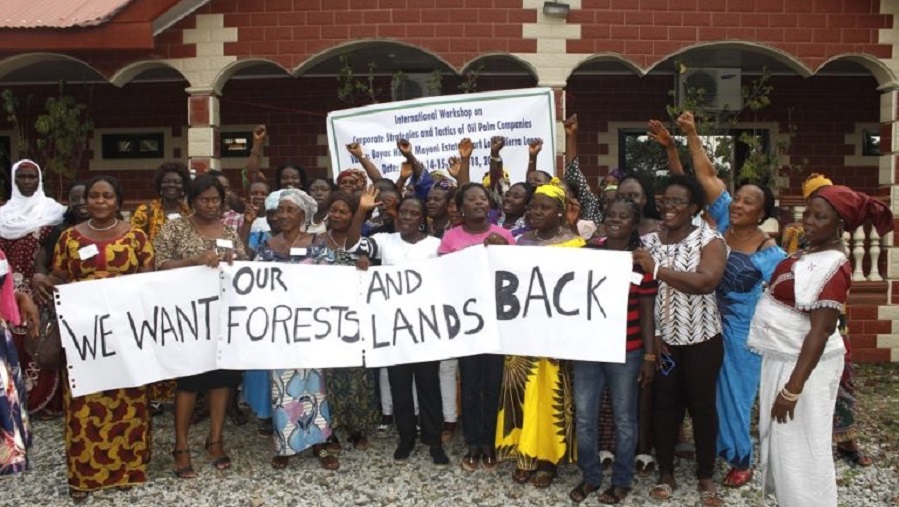

Yesterday was the 16th International Day of Struggle against Monoculture Tree Plantations. In 2004, rural communities in Brazil declared the day to commemorate the resistance against the expansion of monoculture tree plantations in Brazil. Through solidarity statements and actions around the world the day has evolved to become an International Day of Struggle.
This year, a group of organisations from African countries, together with the World Rainforest Movement, has issued an open letter about investments in monoculture tree plantations in the global South, particularly in Africa.
The letter is a response and critique of a June 2019 report titled, “Towards Large-Scale Commercial Investment in African Forestry”. The report was prepared by an outfit called Acacia Sustainable Business Advisors, which was set up by Martin Poulsen, a development banker. One of his co-authors for the study was Mads Asprem, the ex-CEO of Green Resources, a Norwegian industrial tree plantation and carbon offsets company. Green Resources’ land grabs in Mozambique, Tanzania, and Uganda have resulted in loss of land, evictions, loss of livelihoods and increased hunger for local communities.
The study was produced for the African Development Bank and WWF Kenya, with funding from the World Bank’s Climate Investment Funds.
The Open Letter (signed by 117 organisations and people) is posted here in full:
International Day of Struggle against Monoculture Tree Plantations
Open Letter about investments in monoculture tree plantations in the global South, especially in Africa, and in solidarity with communities resisting the occupation of their territories.
September 21st is the International Day of Struggle against Monoculture Tree Plantations. Unlike others, this Day was not created by the United Nations (UN) or by governments. The Day was created in 2004 by rural communities, gathered in the Brazilian hinterland, to denounce and shed light on the impacts of monoculture tree plantations on their territories, and affirm their determination to resist such plantations and take back their territories from the hands of corporations.
16 years later, the Day remains as relevant as ever: there is a real danger of a gigantic, worldwide expansion of monoculture tree plantation. This is promoted as a solution to prevent climate chaos and to the industrialized world’s dependence on oil, gas and coal. A group of governments, corporations, consultants, investors and major conservationist NGOs have come together to put their mega-plans[1] for tree plantation expansions on the table.
Although highly questioned, a forest as defined by the FAO (UN Food and Agriculture Organization) and several national governments mistakenly includes monoculture tree plantations. In their eyes, plantations are “planted forests”. This definition favours only the plantation corporations, thus guaranteeing their main objective: generating profits.
Africa is the continent with “the most profitable afforestation potential worldwide”, according to a report produced in 2019 by consultants for the African Development Bank (AfDB) and the conservationist NGO WWF-Kenya. “The study has identified around 500,000 ha of viable plantation land in ten countries: Angola, Republic of Congo, Ghana, Mozambique, Malawi, South Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia and Zimbabwe.” The study proposes the speedy creation of a Fund, headquartered in a tax haven (Mauritius), to finance the planting of the first 100,000 hectares of trees.
In order for these plantations to generate profits for private investors, the study claims that aid will be necessary from European public international cooperation agencies, i.e., taxpayers’ money from Northern European countries, namely, Finland, Sweden, Norway, Denmark, Iceland, the United Kingdom and The Netherlands, as well as from the World Bank via the International Finance Corporation (IFC), which makes loans to private companies.
The study and its recommendations leave us perplexed and indignant, given the false assumptions and inconsistencies on which it is based (see Annex I for a more detailed description). Below, we present a summary of our main criticism.
The study repeats the same treacherous and false promises that corporations and their advocates always make. It states that plantations improve communities’ living conditions, create jobs, improve the soil and the quality and quantity of water. The corporations’ ‘social’ projects would be attractive to the communities. However, plantations lead to a large number of violations of rights, create very few poorly-paid and dangerous jobs, destroy forests and savannas, degrade soils, contaminate and dry up water sources and destroy communities’ way of life. With the plantations, guards arrive who will restrict communities’ freedom of movement; cases of abuse, sexual violence against women and HIV/AIDS infections increase in number. The promise of ‘social’ projects, often not fulfilled, is the main bargaining chip for corporations to gain access to communities’ lands.
The study refers to land conflicts only as “challenges” and the proposed solution is to “follow FSC and other best practises”. Firstly, the 500,000 hectares that the study suggests corporations should plant as monoculture tree plantations are not abandoned or degraded lands. Corporations always want fertile lands, usually flat and with availability of water – in other words, lands that tend to be used by communities. By recommending the FSC, the study ignores ample documentation that proves that the FSC does not solve plantations’ structural problems, and land conflicts even less. The FSC deceives consumers by considering the model of large-scale monoculture plantations “sustainable”, for it always leads to large tracts of land being controlled by corporations and to the intensive use of agro-chemicals and synthetic fertilizers. So far, compensation for the populations that have lost their lands and means of subsistence has always been derisory or inexistent. Meanwhile, the social, environmental, economic and cultural damage caused by monoculture tree plantations in rural areas of African countries has never been compensated by corporations. There exists no way to calculate the damage and much of the harm done is irreparable.
The study references a World Bank/IFC project in Mozambique, stressing that “one important element of the IFC approach will be to define and register land rights”. In fact, the World Bank, as well as financing plantations, has a policy of encouraging governments in countries of the South to speed up the granting of individual deeds and, therefore, the privatization of land, in an attempt to prevent its collective recognition as community land. The World Bank has been promoting the handing over of community lands to private capital all over the world. It is important to highlight the fact that in recent years, the government of Mozambique has put in place a number of reforms in the forestry sector. These include a review of the Forestry Policy and its Implementation Strategy and, very recently, a public consultation process with a view to also reviewing the National Land Policy. In all of these processes the World Bank is the common denominator in terms of promotion and financial “support”. This review is taking place under the pretext of improving transparency and efficacy in land management and policies, and will inevitably force an alteration of the Land Law and respective Regulation, thus legitimizing the occupation of community lands which provide living conditions for communities and peoples.
The study states that the tree plantations would be “a stable, long-term carbon sink”, and result in “substantial adaptation benefits” vis-à-vis climate change at the local level. By stating this, the study ignores a growing body of scientific work showing that monoculture tree plantations are a false climate solution. The experiences of communities all over the world with monoculture tree plantations show that they create a local environment even less prepared for responding to the ever more perceptible impacts of climate change.
The study states that “Global oil and industrial companies” want to “become part of the solution rather than a major part of the problem. They are beginning to see the potential of forestry investments.” Oil and gas companies are an integral part of the climate crisis, regardless of such proclamations. They have not shown any interest in solving it; on the contrary, they intend to invest first and foremost in false solutions – after all, profits are above all else.
Other false statements include: “the world will need the type of intensive afforestation (…) that the Brazilian forestry industry is implementing”; and that Brazil’s neighbour, Uruguay, is “the world’s most recently developed forestry country”. The truth is that the Brazilian experience with industrial tree plantations over the course of the last few decades has led to numerous land conflicts and environmental degradation. Municipalities with the highest concentrations of plantations are among the poorest, compared with those with diversified agriculture based on smallholders. In Uruguay, the same negative impacts occur. Rural areas have seen a massive exodus of people, with the rural population reduced by half. Furthermore, citizens of Uruguay have taken on an enormous debt, owing to a recent contract between its government and Finnish multinational UPM. According to this contract, the government agreed to carry out multi-million dollar infrastructure works to service UPM and the export plans of its second pulp factory.
The study also states that “The main barrier to successful investments in African greenfield planting is low historic returns. New planting by private companies has ground to a halt in recent years.” This not only reveals that profits are what really matters to private investors, but also that the authors of the study deliberately ignore the main reason why the expansion of industrial plantations has been impeded in various African countries: the resistance of communities against such monoculture plantations.
The study also seeks to attract investors, suggesting “the possibility of planting [trees] at significantly lower costs (…), more or less half of 10 years ago (…)”. Promising companies that they will have to spend less means that the weight of the industrial plantation projects from the proposed fund will fall even more upon already indebted African countries and, consequently, on their populations, particularly rural communities that run the risk of losing their most fertile lands.
It is important to stress that a “conservationist” NGO is a co-producer of this study that promotes investments that will benefit first and foremost private companies. The study itself reveals how NGOs like WWF should no longer be considered NGOs since they function and act as the ‘right hand of the plantation industry’.
The report refers to a non-public version of the study which has not been disclosed to the public as far as we are aware. The report also notes that “(…) there is a clear coalition of DFIs [development finance institutions] interested in further discussion on this topic [creation of the Fund], including: CDC [United Kingdom], Finnfund [Finland], IFC [World Bank], NDF [Nordic countries: Finland, Norway, Sweden, Denmark, Iceland] and FMO [The Netherlands]”. This demonstrates that decisions about investments are being made without the participation of the communities and other civil society organizations and social movements from the regions in question, i.e., the parties most affected. How can it still be acceptable in the 21st century that public international cooperation agencies use money from their taxpayers in this way? Hiding their decisions from their own citizens and from the populations that will be affected? When plantation corporations and their investors, after everything has been decided, state that they are applying the principle of communities’ “free, prior and informed consent”, does this merit any credibility?
We demand that the non-public version of this study be published immediately by the AfdB and WWF-Kenya, so that its content may be known to the communities and organized civil society in the countries where they intend to implement their plans.
We reiterate our indignation with regard to the channelling of public resources towards private investments, through tax havens, to be invested in highly damaging activities, such as large-scale monoculture plantations.
We further demand a wide-ranging review of the process of allocation of land to plantation corporations, ensuring the return of land to the communities that depend on this land, today and in the future. In Mozambique, for example, peasant agriculture constitutes the main guarantee of subsistence for more than 80% of the population, and the land is the only thing to which communities can resort to ensure food safety and sovereignty.
We reiterate our solidarity on this September 21st with the legitimate and just struggles of communities around the world that resist the advance of plantations and strive to take back their lost lands. They must be remembered and made visible every day. And they will certainly resist this new and insane expansion plan proposed in the AfDB and WWF-Kenya study and commented on in this Open Letter.
We appeal to the solidarity and unity, so that together we may demand the immediate abandonment of any and every afforestation programme based on large-scale monoculture plantation.
The Struggle Continues!
Plantations Are Not Forests!
Signed by:
- ADECRU (Mozambique)
- Justiça Ambiental (Mozambique)
- Missão Tabita (Mozambique)
- SUHODE Foundation (Tanzania)
- WRM (International)
Related posts:

 The African Development Bank and the Tree Plantations Industry
The African Development Bank and the Tree Plantations Industry
 MONOCULTURE TREE PLANTATIONS – Uganda – Promotion of plantation agriculture – a disgrace to human kind and environment
MONOCULTURE TREE PLANTATIONS – Uganda – Promotion of plantation agriculture – a disgrace to human kind and environment
 12 Replies to 12 Lies about Industrial Tree Plantations: New edition of a WRM briefing paper
12 Replies to 12 Lies about Industrial Tree Plantations: New edition of a WRM briefing paper
 Colonization and Monoculture Plantations: Histories of Large-Scale ‘Grabbings’
Colonization and Monoculture Plantations: Histories of Large-Scale ‘Grabbings’
You may like
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
USA, Israel, and Iran War effects: Why the world cannot afford to delay the renewable energy transition?
Published
4 days agoon
March 5, 2026
By the Witness Radio team.
When conflict erupted in the Middle East, oil and gas prices surged within hours. Insurance premiums increased, shipping routes became uncertain, and inflation followed. The 2024 World Energy Investment report notes that the Middle East accounts for about 30% of global oil production.
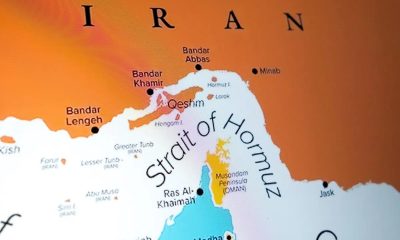
Now, with the ongoing conflict between the USA, Israel, and Iran, the Strait of Hormuz is closed, and any ship attempting to pass will be fired upon by Iran, according to a senior Iranian Revolutionary Guards official on Monday.
“The Strait (of Hormuz) is closed. If anyone tries to pass, the heroes of the Revolutionary Guards and the regular navy will set those ships ablaze,” Ebrahim Jabari, a senior adviser to the Guards commander-in-chief, said in remarks carried by state media.
The Strait is the world’s most vital oil export route, connecting the largest Gulf oil producers, such as Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, and the United Arab Emirates, with the Gulf of Oman and the Arabian Sea.
The closure came after Israeli and American strikes on Iran on February 28, with the intention of weakening its government. Iran retaliated by firing missiles at the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, and Oman in addition to launching missile barrages toward Gulf nations that house American military installations, such as Qatar, Kuwait, and Bahrain.
These developments demonstrate the extent to which fossil fuel geopolitics continue to influence the world economy.
For energy policy expert Sandrine Dixson-Declève, these recurring shocks expose a structural weakness in the global economy.
“Energy is not just about electricity. It is about geopolitical power. As long as we remain dependent on fossil fuels, we will remain vulnerable to conflict, price volatility, and political leverage.” Sandrine says in an exclusive interview with the Witness Radio team.
The global push toward renewable energy, she argues, is not driven solely by environmental idealism. It is rooted in security, sovereignty, and economic resilience.
Energy dependence has always had a geopolitical component. Experts say the oil crises of the 1970s revealed how exposed industrialized nations were to supply disruptions in the Middle East. Decades later, similar dynamics re-emerged when Europe relied heavily on Russian gas delivered through projects like Nord Stream 2 before the invasion of Ukraine.
“We have known since the 1970s that dependency on fossil fuels creates political fragility. And yet we failed to reduce that dependency structurally.” Sandrine Dixson-Declève maintains.
The war in Ukraine, alongside renewed tensions involving Israel and Iran, underscores the same vulnerability. Energy-importing nations find their foreign policy constrained by supply risks.
“The only way to break that cycle is to shift the demand side of the equation. We need to reduce dependence on fossil fuel supply altogether and think of alternatives, such as the transition to renewable energy.” The expert adds.
Geopolitical tensions alone make a strong case for accelerating the energy transition. However, climate science makes the need even more urgent. The planet has already temporarily exceeded 1.5°C of warming above pre-industrial levels — the limit governments committed to avoid under the Paris Agreement.
“We are already seeing the consequences: floods, desertification, water stress, extreme storms, Tornados. So, the weather and people’s lives and livelihoods will be increasingly affected. And the number one source of greenhouse gas emissions is the burning of fossil fuels. So, it is that dual reason, both the geopolitical dependency, but also the need to shift towards renewables, that is really driving this transition.” Adds Sandrine.
She warns that the economic consequences of inaction are mounting. “The cost of climate inaction is already estimated at around 3 percent of global GDP annually. At higher levels of warming, that figure could rise dramatically. Governments that think delay is cheaper are fundamentally mistaken. So, if governments really want to buffer GDP and ensure they preserve and build more resilient economies for the future, they have to move towards decarbonized energy. We have to reduce our impact on climate change.”
The primary source of greenhouse gas emissions remains the combustion of fossil fuels. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), fossil fuels — coal, oil, and natural gas — account for roughly three-quarters of global greenhouse gas emissions and nearly 90 percent of carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions. The energy sector alone, including electricity, heat production, transport, and industry, is responsible for the largest share of global emissions. Coal-fired power plants remain the single biggest contributor, while oil dominates transport emissions, and gas is playing an increasingly important role in power generation and industry.
“This is a dual crisis: it’s geopolitical dependency, and it’s climate destabilization, and both point in the same direction: transition. Globally, we continue to subsidize fossil energy at enormous levels. At the same time, oil and gas companies have made extraordinary windfall profits.” Sandrine says.
For Dixson-Declève, this reflects a structural distortion in the market. “We have created a perverse system where fossil fuels are artificially cheaper than renewables because of subsidies and the absence of proper taxation.” She maintains.
Attempts to secure a global commitment to phase out fossil fuels have repeatedly encountered political resistance. At the 2023 climate Summit, COP28 — held under the framework of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change — governments agreed for the first time to “transition away from fossil fuels in energy systems.
“There are countries that continue to block progress. Without stronger financial and regulatory pressure, change remains slower than it should be.” She adds.
The Secretary-General of the United Nations, António Guterres, recently accused world leaders of slowing the transition at COP30 in Belém, Brazil, citing nations’ inaction and lack of commitment to ending fossil fuels.
“Fossil fuels still receive huge public subsidies, spending billions on lobbying, deceiving the public, and hindering progress. Too many corporations are making record profits from the climate devastation they cause. Too many leaders remain hostage to fossil fuel interests,” Mr. Guterres stressed.
But Dixson argues that eliminating fossil subsidies and taxing windfall profits would significantly accelerate the shift. “If we correct the economic signals, the transition speeds up. Beyond national-level commitments, we need commitments at the corporate, business, and industrial levels to reduce the impact of emissions from their production processes. This really calls for transitioning away from fossil fuels and energy systems and tripling global renewable energy capacity by 2030.” Sandrine advises.
Despite political resistance, economic trends suggest that renewables are gaining momentum.
“Solar and wind are now cheaper than new fossil fuel projects in most parts of the world. The market fundamentals are increasingly in favor of renewables.” Sandrine notes.
Related posts:

 New! The Eyes on a Just Energy Transition in Africa Program is now live on Witness Radio.
New! The Eyes on a Just Energy Transition in Africa Program is now live on Witness Radio.
 30 civil society organizations have written to the World Bank Group demanding to publicly disclose the Africa Energy Approach paper.
30 civil society organizations have written to the World Bank Group demanding to publicly disclose the Africa Energy Approach paper.
 Over 600 million Africans lack electricity despite huge renewable energy potential
Over 600 million Africans lack electricity despite huge renewable energy potential
 Statement: The Energy Sector Strategy 2024–2028 Must Mark the End of the EBRD’s Support to Fossil Fuels
Statement: The Energy Sector Strategy 2024–2028 Must Mark the End of the EBRD’s Support to Fossil Fuels
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
COVID-19 unending effects: Demand for land to host refugees in Uganda caused forced land displacement and pushed the refugee-hosting community into Internally Displaced Camps (IDPs).
Published
5 days agoon
March 4, 2026
By Witness Radio Team
As the world was grappling with a global pandemic (COVID-19), which was accompanied by impromptu lockdowns and economic uncertainty. For the residents who lived around the Kyangwali Refugee Settlement, the crisis was far more severe than the effects of the lockdown; the second phase of the lockdown was taken advantage of to carry out a massive and illegal land eviction by a Ugandan government Ministry.
According to affected residents, Uganda’s Office of the Prime Minister (OPM) used the 2020 COVID-19 lockdown to illegally evict more than 20,000 people from Kyangwali Sub-county in what many describe as a calculated operation carried out under the cover of pandemic restrictions.
The Prime Minister’s Office had previously displaced thousands during a 2013 eviction that affected over 60,000 people. At the time, the OPM claimed the residents were unlawfully occupying land designated for refugees. Some residents later returned after government officials reportedly acknowledged irregularities in the earlier eviction.
“After three weeks, the government responded with a delegation from the Prime Minister’s office led by Minister Hillary Onek, who then said that the exercise was not right, it was a wrong one, and that they are sorry for the actions of OPM individuals and that we should return to our land,” Ampumbuza explained.
However, in 2020, residents described what they called a “second phase” of evictions targeting more than 35 villages in Bukinda and Katikala in Kyangwali. According to testimonies gathered by Witness Radio, security forces, including the Uganda People’s Defence Force (UPDF), were deployed along key roads and trading centers, effectively sealing off the settlement and surrounding communities.
Residents say that COVID-19 control measures were manipulated to facilitate illegal evictions, while security personnel enforced movement restrictions that barred journalists, politicians, and civil society actors from accessing the area.
“During 2020, they announced that there was a high outbreak of COVID-19 in Kyangwali Refugee Camp, and people are dying at a high rate, like flies. And so, they slammed us with a total lockdown, and there was no journalist or political leader allowed in the area. The announcement was made on all local radio stations in the area, and the whole place was deployed by the UPDF, so that no movement of people was seen.” Mr. Ahumuze Busingye, a leader of the affected group, told Witness in an exclusive interview.
Busingye further revealed that the officials acted smartly and evicted the community with no interference, “Now what is shocking here is that the security intentionally acted smartly and took advantage of the 2020 COVID-19 outbreak to cordon off the whole refugee settlement land and made false announcements that the area had rampant death in the zone and so no movements were allowed.”
Mbambali Fred, another affected resident, claims the lockdown created an environment where security personnel operated with impunity.
“Residents were rounded up, beaten, and ordered to vacate land described as government property designated for refugees,” he said. “When we asked why they were beating us, they replied that they wanted us to leave because the land was not ours.”
Residents named OPM officials, including Bafaki Charles and Kebirungi Joy, as leading the eviction efforts. According to the evictees, officials maintained that the land was reserved for refugees and that occupants were unlawful settlers.
During the height of the pandemic, the Ugandan government imposed strict restrictions to curb the spread of COVID-19, including bans on movement, public gatherings, and rallies. At the same time, the Ministry of Lands, Housing, and Urban Development issued directives halting evictions nationwide. Yet residents say these safeguards were disregarded in Kyangwali.
This was the second eviction. Earlier, in 2012, more than 60,000 people had been evicted by the same office without compensation. The OPM claimed the evictees were occupying refugee land, but some later returned.
In 2016, President Yoweri Museveni issued a directive to reopen and verify the 1998 land boundaries and compensate individuals affected by prior demarcations. An implementation team reportedly visited the area in 2018 but did not immediately displace the residents.
“And then in 2018, we saw a team coming to implement the president’s directive. They did all they could and left without touching us, and some of our colleagues had stayed at the sub-county camp.” Busingye further added.
It was not only the displaced residents who faced injustice after being uprooted from their land. Mr. Mbambali, a landowner before the 2020 evictions, was not spared. He, too, was evicted by the Office of the Prime Minister (OPM).
He says the deepest injustice lies in the fact that the land in Kyeya, which he acquired through years of hard work, was later used to resettle people displaced from Bukinda and Katikala, without his consent and without compensation.
“Five people, including me, hold land measuring 778.570 hectares. But the OPM grabbed it and settled people in. Personally, I was tortured and evicted without compensation despite holding a land title for the said land.” He added.
During an interview with Witness Radio, the middle-aged, brown, and slim defender broke into tears, displaying big scars all over his body, which he says emerged as a result of beatings and torture during the evictions.
“They named me a land grabber who was resisting vacating land, which they called government land. They beat and tortured me.” The defender told Witness Radio
“I hold scars, and I have a lot of pain that those people caused me. My family is currently suffering because of greed from the big shots.” He added.
Whereas some of the evictees were eventually resettled, leaders of the affected communities reveal that serious injustices marred the process. Local land rights defenders, including Ahumuza, say the resettlement exercise was riddled with irregularities. They claim it triggered yet another violent eviction, as the land onto which the government relocated residents had itself been irregularly and allegedly illegally acquired.
“The process was not fair at all. The government never settled many of us, which is why we are now camping in an internally displaced camp. Some people were settled on land belonging to private individuals like Mbambali.” Ahumuza added.
Uganda has long been praised for its progressive refugee policies, including land allocation and freedom of movement, yet behind this lies evictions of nationals, which raises concern about balancing refugee resettlement with the land rights of host communities.
While refugees in Kyangwali remain settled and supported under national and international protection frameworks, many evicted host community members say they now live in informal, unrecognized settlements without compensation or redress.
Like the thousands of evictees who remain without justice and are now confined to an informal camp in Kiziranfumbi, Mr. Mbambali — himself a lawful landowner — has endured repeated dispossession alongside many others.
Despite repeated appeals, residents say government authorities have remained hesitant to address the dispute, leaving thousands in protracted uncertainty.
Related posts:

 13 years after the refugee host community was forcefully evicted to expand a refugee settlement, thousands remain unsettled.
13 years after the refugee host community was forcefully evicted to expand a refugee settlement, thousands remain unsettled.
 Covid-19 effects: More than half of Ugandan households ate less food in June- Twaweza findings
Covid-19 effects: More than half of Ugandan households ate less food in June- Twaweza findings
 Breaking Alert! A community fighting forced eviction during COVID-19 lockdown, Witness Radio-Uganda together with Accountability Counsel file a complaint before the World Bank’s Inspection Panel…
Breaking Alert! A community fighting forced eviction during COVID-19 lockdown, Witness Radio-Uganda together with Accountability Counsel file a complaint before the World Bank’s Inspection Panel…
 COVID-19 Lockdown: Lawyers demand for court’s immediate intervention into the land grab violence meted out to communities by multinational companies in Kiryandongo
COVID-19 Lockdown: Lawyers demand for court’s immediate intervention into the land grab violence meted out to communities by multinational companies in Kiryandongo
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
StopEACOP raises alarm over €1.5bn back door funding for TotalEnergies
Published
7 days agoon
March 2, 2026
- StopEACOP coalition says €1.5bn bond creates “back door” funding channel for EACOP and Mozambique LNG.
- Over 40 global banks previously declined direct EACOP financing on ESG and climate grounds.
- Coalition calls for shift from project exclusions to client based exclusions.
The StopEACOP coalition has raised alarm over a €1.5bn bond issued by TotalEnergies this week, arguing that the transaction exposes a critical gap in global banks’ ESG and climate commitments.
According to the coalition, several international banks that had publicly distanced themselves from the controversial East African Crude Oil Pipeline project participated in underwriting the bond. While more than 40 global banks have declined to directly finance EACOP, campaigners argue that facilitating corporate bond issuances for TotalEnergies effectively provides the company with unrestricted capital that can be allocated to any of its projects.
These include both EACOP and the Mozambique LNG development in Mozambique, another project facing sustained international scrutiny.
Among the banks that had previously announced they would not support EACOP are Société Générale in 2021, followed in 2022 by HSBC, Intesa Sanpaolo, J.P. Morgan and Mizuho. BBVA made a similar announcement in 2025.
Campaigners argue that although these institutions avoided direct project finance exposure, their participation in corporate level fundraising undermines the intent of those commitments. Bond proceeds are typically unrestricted, enabling companies to allocate capital internally, including to subsidiaries such as EACOP Ltd.
Zaki Mamdoo, StopEACOP Campaign Coordinator, said banks were seeking reputational protection while maintaining financial relationships that sustain fossil fuel expansion. He argued that bond underwriting allows lenders to benefit from fees and returns while distancing themselves from direct project finance scrutiny.
The coalition maintains that the €1.5bn raised strengthens TotalEnergies’ ability to internally finance projects that have struggled to attract external lenders due to environmental and social risk concerns. Recent risk briefings from BankTrack noted that public pressure has made it increasingly difficult for EACOP sponsors to secure conventional project finance.
EACOP, a planned 1 443 km heated crude oil pipeline linking oilfields in western Uganda to the Tanzanian coast, has faced sustained opposition over land acquisition, biodiversity risks and human rights concerns. Project affected communities in Uganda have reported land disputes and delayed compensation, while activists allege judicial and security pressures against opponents of the development.
Rachael Tugume, a project affected person from Hoima, said that once TotalEnergies channels internal funding to EACOP Ltd, the capital raised through bonds becomes directly linked to on the ground impacts, including land loss and livelihood disruption.
The coalition has called on banks to move beyond project specific exclusions and adopt client based exclusions. Under such a framework, financial institutions would decline to finance companies pursuing projects deemed incompatible with climate and human rights commitments, rather than simply avoiding individual transactions.
As TotalEnergies, alongside project partners including CNOOC and host governments in Uganda and Tanzania, continues to target first oil by July 2026, the financing structure behind the project is drawing renewed scrutiny from civil society.
Diana Nabiruma of the Africa Institute for Energy Governance said banks must align their financing practices with stated commitments to human rights, biodiversity protection and climate leadership. She argued that continued capital market support for companies expanding fossil fuel infrastructure erodes public confidence in ESG frameworks.
The controversy highlights a broader debate within global finance over the effectiveness of project level exclusions in driving climate aligned capital allocation. For African energy markets seeking to balance development priorities with environmental safeguards, the outcome of this debate will carry significant implications for future upstream oil and gas financing across the continent.
Source: greenbuildingafrica.co.za
Related posts:

 #StopEACOP campaign calls on Standard Bank to come clean about its funding of the East African Crude Oil Pipeline
#StopEACOP campaign calls on Standard Bank to come clean about its funding of the East African Crude Oil Pipeline
 Swedish pension fund drops TotalEnergies amid rising EACOP risks
Swedish pension fund drops TotalEnergies amid rising EACOP risks
 Activists storm TotalEnergies’ office ahead of G20 Summit, demand end to fossil fuel expansion in Africa
Activists storm TotalEnergies’ office ahead of G20 Summit, demand end to fossil fuel expansion in Africa
 Uganda: StopEACOP Campaign Condemns Standard Bank’s Decision to Fund EACOP
Uganda: StopEACOP Campaign Condemns Standard Bank’s Decision to Fund EACOP

Statement by Witness Radio- Legal Aid Clinic on International Women’s Day 2026; Scaling Up Investment to Accelerate Access to Justice for Women and Girls Defending Land and Environmental Rights

USA, Israel, and Iran War effects: Why the world cannot afford to delay the renewable energy transition?

COVID-19 unending effects: Demand for land to host refugees in Uganda caused forced land displacement and pushed the refugee-hosting community into Internally Displaced Camps (IDPs).

StopEACOP raises alarm over €1.5bn back door funding for TotalEnergies

Small-scale fishers and coastal communities are pushing to testify before a human rights commission investigating the causes of food inequality in South Africa.

USA, Israel, and Iran War effects: Why the world cannot afford to delay the renewable energy transition?

The Kenyan government insists on maintaining provisions of the Seed Act that the court nullified: farmers and legal experts question the motive.

COVID-19 unending effects: Demand for land to host refugees in Uganda caused forced land displacement and pushed the refugee-hosting community into Internally Displaced Camps (IDPs).

Innovative Finance from Canada projects positive impact on local communities.
Over 5000 Indigenous Communities evicted in Kiryandongo District
Petition To Land Inquiry Commission Over Human Rights In Kiryandongo District
Invisible victims of Uganda Land Grabs
Resource Center
- Land And Environment Rights In Uganda Experiences From Karamoja And Mid Western Sub Regions
- REPARATORY AND CLIMATE JUSTICE MUST BE AT THE CORE OF COP30, SAY GLOBAL LEADERS AND MOVEMENTS
- LAND GRABS AT GUNPOINT REPORT IN KIRYANDONGO DISTRICT
- THOSE OIL LIARS! THEY DESTROYED MY BUSINESS!
- RESEARCH BRIEF -TOURISM POTENTIAL OF GREATER MASAKA -MARCH 2025
- The Mouila Declaration of the Informal Alliance against the Expansion of Industrial Monocultures
- FORCED LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA TRENDS RIGHTS OF DEFENDERS IMPACT AND CALL FOR ACTION
- 12 KEY DEMANDS FROM CSOS TO WORLD LEADERS AT THE OPENING OF COP16 IN SAUDI ARABIA
Legal Framework
READ BY CATEGORY
Newsletter
Trending
-
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK4 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK4 days agoUSA, Israel, and Iran War effects: Why the world cannot afford to delay the renewable energy transition?
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK5 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK5 days agoCOVID-19 unending effects: Demand for land to host refugees in Uganda caused forced land displacement and pushed the refugee-hosting community into Internally Displaced Camps (IDPs).
-

 STATEMENTS22 hours ago
STATEMENTS22 hours agoStatement by Witness Radio- Legal Aid Clinic on International Women’s Day 2026; Scaling Up Investment to Accelerate Access to Justice for Women and Girls Defending Land and Environmental Rights
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago85-year-old widow recovers her grabbed land after daughter-in-law convicted
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks agoCSOs push for reforms at the KFW Accountability Mechanism after experts discovered that it has weak remedies in addressing grievous harms caused by its investments.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK7 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK7 days agoStopEACOP raises alarm over €1.5bn back door funding for TotalEnergies
