FARM NEWS
Sugarcane farmers abandon fields due to lack of markets
Published
3 years agoon
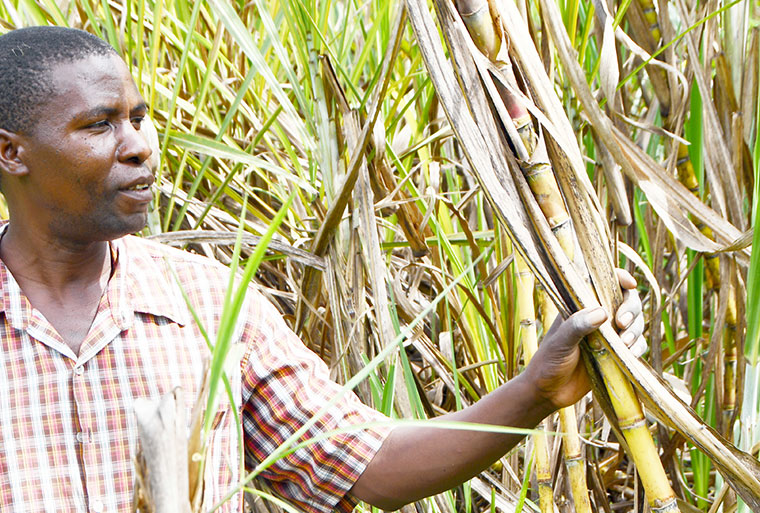

While the sugarcane sector has the potential to empower stakeholders along the value chain, farmers have abandoned their fields for other income-generating activities, writes YUDAYA NANGONZI.
Currently, sugar production has declined amidst increasing demand from consumers and fluctuating prices, with the majority of millers operating below capacity. In a study conducted by the Economic Policy Research Center (EPRC) on the sector, Dr Swaibu Mbowa, the lead researcher, attributed the massive exodus of cane growers to lack of markets and a decline in cane prices while other farmers have already replaced cane with food crops.
The increasing levels of poverty in cane-growing districts have also forced farmers to rethink the crop. In Uganda, about 29,000 farming households engage in cane production with an estimated 640,000 labourers. More households took up the business between 2012 and 2021 with at least 40,000 households, at one point, growing cane between 2005 and 2021.
“By the time we collected data in November-December 2021, this number had declined to about 29,000. This indicates that 28 per cent of out- growers had abandoned cane growing, with the highest attrition rate (33.8%) occurring in the Busoga sub-region,” Mbowa said.
This implies that one in every three cane farmers in Busoga has abandoned the business. Currently, Busoga has 20,474 growers while 10,475 stopped growing cane. In the Buganda region, the research shows that there are 4,394 growers and 522 farmers out of the business. In Bunyoro, 367 farmers joined other activities, leaving 3,801 active growers.
Mbowa presented the daunting figures at the recent 10th national Forum on Agriculture and Food Security held at Sheraton hotel in Kampala. The forum was organized by the EPRC in collaboration with Michigan State University and the International Food Policy Research Institute under the auspices of the Food Security Policy Research, Capacity and Influence.
Themed “Revisiting Policy, Institutional and Regulatory Arrangements in Uganda’s Sugarcane Sector”, the forum intended to stimulate debate on how to strengthen and improve the implementation of the sugarcane policy and regulatory frameworks to foster sustainable transformation in Uganda.
“MILLERS FAILING FARMERS”
Worldwide, sugar factory ownership is a mix between the government and the private sector. For Uganda, ownership is largely private with the government owning a lesser stake in the Atiak Sugar factory after selling its shares in Kinyara Sugar Factory in 2017.
This arrangement, farmers argued, has forced many to collapse as millers suffocate the sector. As of 2020, there were 33 licensed mills, with a combined milling capacity of 71,850 tonnes per day.
However, by December 2021, only 12 mills in the study sub-regions were operational and out-growers sold more cane to mainly established large millers who have disproportionate power over sugarcane price determination.
Mbowa noted that existing millers acquired new licenses in different jurisdictions to forestall other players from establishing milling plants in the same area. This could explain why there are fewer operational mills than those licensed.
The negative free-fall in sugarcane prices worsened the situation. For instance, a tonne of cane that cost Shs 175,000, Shs 162,000, and Shs 135,000 in Buganda, Busoga, and Bunyoro in 2017 has since dropped to Shs 95,282, Shs 92,782, and Shs 97,907 respectively.
Speaking to The Observer on the sidelines of the forum, a cane out-grower and director of the sugarcane value chain at Operation Wealth Creation, Kabakumba Labwoni Masiko, agreed that prices are illogically fixed by millers.
“We may look at millers as competitors in business but it’s not the case during price determination. Unlike in the past when millers would negotiate with farmers or their association, today, you find the price fixed on their notice board. Surprisingly, cane is the only crop where prices don’t vary much across the country. What does that mean?” Kabakumba asked.
Due to the price inconsistencies, some farmers have been forced to cut the cane for other activities since millers were also taking longer to buy it at fair prices.
“Today, there’s scarcity of cane. Millers are looking for cane in vain and that cyclical nature of operation by hurting farmers is catching up with them and the entire sugar sector,” she said.
The farmers also faulted millers for infiltrating their organization to ensure that they remain weak and the introduction of cane harvesting permits has created a black market for them, especially in Buganda to the detriment of farmers.
The manager of Kayunga Sugarcane Outgrowers Cooperative Society, Semeo Mugenyi, urged the government to regulate how far millers can go in expanding their nucleus to reduce competition with farmers.
“The primary role of an investor is to give economic opportunities to the local people. If the investor takes half of the supply, then it limits potential farmers on their supply,” Mugenyi said, adding that without a sugar mill managed by farmers as promised by President Museveni, cane farmers will continue to be exploited or exit the sector.
RECOMMENDATIONS
The study findings call for urgent discussions among government and sector stakeholders on the future of the sugarcane sector. In particular, the study points to the need for the constitution of the sugar board, as recommended by the Sugar Act 2020 to oversee the sector. Mbowa said the inclusion of out-growers in the cane sector is “the primary means by which it can contribute to increases in rural farm household incomes, food security, and rural employment in cane-growing areas.”
To date, the 2010 Sugar Policy and the Sugar Act of 2022 are not operational. David Kiiza, a senior industrial officer at the ministry of Trade, said the government has made strides in organizing the sector but remains constrained by inadequate funds.
“We wrote to stakeholders and they sent us their nominations but the ministry of Finance said it has no money for setting up the board. They [Finance] told us to make a supplementary budget of Shs 2bn [to set up the board] but they have told us to wait. Most likely, the money will be availed in the next financial year,” Kiiza said.
He added: “The ministry of Trade has already held a meeting with millers and we plan to schedule one for the out-growers and later meet them all in one meeting to agree how to set up the board as we await funds from the government. By the end of this year, we expect the Act to be reviewed.”
In the meantime, Kabakumba urged the traditional big millers to graduate into the production of refined industrial sugar as Uganda has brown sugar in surplus. This would provide the much-needed market for the farmers of sugarcane as well as more employment opportunities for small millers dealing in brown sugar.
Source: The Observer
You may like
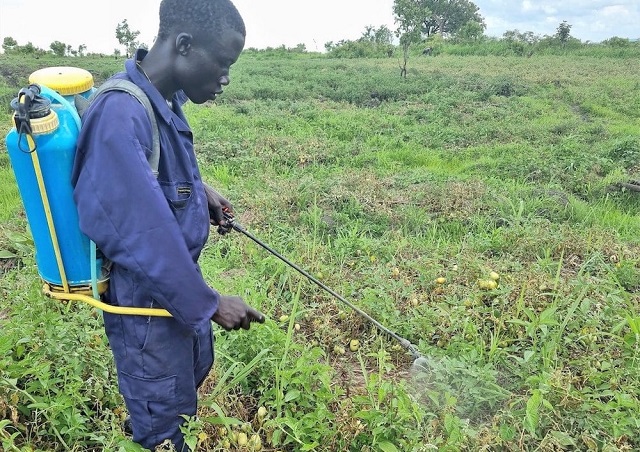

A smallholder tomato farmer in the northwestern Uganda region of West Nile sprays his half-acre tomato garden without adequate protection. Many farmers around the country interact with hazardous agro-chemicals without using adequate PPEs. COURTESY PHOTO/SASAKAWA AFRICA ASSOCIATION.
A consortium of civil society organisations (CSOs) has in a Jan.05 statement shown concern about the continued wrong use of dangerous pesticides in the country.
Members of the concerned CSOs mainly work to promote sustainable agricultural trade, food safety and sovereignty, climate justice, biodiversity restoration, and human and environmental rights.
The activists say there are growing concerns about pesticide misuse, including improper application and storage, counterfeit products, insufficient training in use, and use of poorly maintained or totally inadequate spraying equipment.
The activists insist the agriculture ministry should deregister at least 55 agro-chemicals that it registered in 2023 well-knowing that the same pesticides, herbicides and insecticides are banned by the European Union, a major market of Uganda’s agricultural produce.
Glyphosate-based herbicides, in particular, have raised significant alarm due to their potential environmental and health risks. Globally, they have been linked to contamination of water sources, soil degradation, and potential carcinogenic effects on humans.
In Uganda, glyphosate which appears in brands such as Rounduo and Weed Master, is widely used, especially among large-scale commercial farms and in weed control.
Betty Rose Aguti, the Policy and Advocacy Specialist at Caritas-Uganda who also doubles as the National Coordinator of Uganda Farmers Common Voice Platform says Uganda’s smallholder farmers need to be guided on the danger posed by some agro-chemicals.
“No one is guiding them on what to do with the agro-chemicals. Nobody is telling the farmers which agro-chemicals to use in what type of soils or on which type of crops and thereafter, what period of time they should take before they harvest.
“We have scenarios where some of these farmers apply these agro-chemicals bare-chested with no face masks and other protective gear; these farmers are using agro-chemicals as though they are using ordinary water.”
“They spray their gardens as they converse with their children and wives. In the course of doing this, they are inhaling the chemicals and after some time, they fall victim to the toxicity of these agro-chemicals and end up flooding the Uganda Cancer Institute,” she says.
What are pesticides?
Pesticides are defined by UN agencies; the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), as substances or mixture of substances of chemicals or biological ingredients intended for repelling, destroying or controlling any pest, or regulating plant growth.
These often include ingredients that modify pest behaviour or their physiology (insect repellents) or affect crops during production or storage (herbicide safeners and synergists, germination inhibitors), as well as insecticides, fungicides and herbicides.
However, according to the activists, most of the chemicals on the Ugandan market are quite hazardous to both human health and the environment and yet they continue being used inappropriately by Ugandan smallholder farmers.

“We call upon the government of Uganda to regulate and ban all hazardous pesticides especially glyphosate and chlorpyriphos on the market in Uganda,” said Jane Nalunga, the Executive Director of the Uganda chapter of the Southern and Eastern Africa Trade Information and Negotiations Institute (SEATINI), a regional NGO that promotes pro-development trade, fiscal and investment-related poicies and processes.
Backbone of Uganda’s economy
The activists say Uganda’s agriculture sector is the mainstay of Uganda’s economy as it remains the main source of food, raw materials for industries, and employment of about 70% of Ugandans. The sector contributes about 24% to the country’s GDP.
“We cannot allow people with intellectual dishonesty to continue playing with the sector,” one of the activists said on Jan.5 during a press conference at the SEATINI-Uganda headquarters in Kampala. “We are aware that pesticides are significantly impacting health, biodiversity, socio-economic well-being, trade, and food security,” added Nalunga.
According to a 2020 World Health Organisation report, about 385 million cases of unintentional pesticide poisoning, including 11,000 deaths, mostly in low- and middle-income countries such as Uganda, are registered annually worldwide. According to UNICEF, pregnant and breastfeeding mothers, children under the age of five and the elderly are the most vulnerable to the effects of pesticides.
The activists say increased use of highly hazardous pesticides in Uganda is a threat to the right to adequate food, people’s livelihoods and farmers’ rights. They say pesticide runoff is reducing aquatic species diversity by 42% and threatening pollinators like bees. These insects are particularly critical for 75% of global crop production.
According to the European Environmental Agency, pesticides are intrinsically harmful to living organisms. When used outdoors, they can impact ecosystems even when they are intended to exclusively target a specific pest.
Herbert Kafeero, the Programme Manager at SEATINI-Uganda says the use of hazardous pesticides also has implications for trade. He says, in 2015, the government of Uganda imposed a self-ban on the export of agricultural produce to the EU because agro-chemical residues had been found in Uganda’s agricultural produce. “The self-ban was meant to address the challenges that were cited by the EU,” he says, “So we cannot ignore the fact that hazardous pesticides negatively impact the country’s trade and food security.”
He says, at the time, the government committed to retrain farmers and exporters to the EU regarding the EU’s sanitary and phytosanitary standards. Kafeero says the government must find solutions to the mushrooming agro-chemical dealers on the market.
“In every trading centre, you will not miss finding an agro-chemical shop and the person operating that agro-chemical shop presents himself as an expert when they actually are not.”
The activists want the Agricultural Chemicals Control Board under the Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Industry and Fisheries to quickly profile the various agrochemicals, acaricides and inputs and their various sources that are available on the market in Uganda and ban the highly hazardous ones.
They also want the Department of Crop Inspection and Certification at the agriculture ministry to strengthen the regulation, management, use, handling, storage and trade of agrochemicals in the country.
They also want the government and other stakeholders to purposively plan and budget for education and awareness on the management, use, handling, storage and trade of agrochemicals in Uganda.
Prof. Ogenga Latigo disagrees
The activists were infact responding to Morris Ogenga Latigo, a Ugandan professor of entomology (study of insects) who had written an opinion on December 31, 2024, downplaying civil society’s concerns about hazardous pesticide and insecticide use in Uganda.
Prof. Ogenga Latigo in his article said the issue of agro-chemical use on farm pests and weeds and households was being exaggerated by civil society. He said the targeted agro-chemical inputs (pesticides, insecticides and herbicides) were being used in other countries.
The acrimonious debate has since sucked in the agricuture ministry. Stephen Byantware, the Director in charge of Crop Protection at the agriculture ministry told the media in Kampala recently that Uganda has an Agriculture Police Force and a Department of Inspection and Certification of agriculture inputs that “ensure that only nationally and globally approved agro-chemicals enter the Ugandan market.”
“The chemicals allowed into the country are those that have been approved,” he said, “There are no banned products on sale in Uganda. You cannot find DDT or Endosulfan in Uganda.”

But David Kabanda, the Executive Director of the Centre for Food and Adequate Living Rights, a Kampala-based non-profit, says Ugandans should know that hazardous pesticides have become one of the “loudest killers” and yet Ugandan smallholder farmers continue to associate with these chemicals on the farms, in the food stores, and in the homes.
“It’s only in Uganda where we don’t have a farmgate policy and yet we have scientific reports that have pointed out that the food we buy in markets in Kampala is contaminated.” “Don’t we see tomatoes and broccoli full of Mancozeb fungicide yet this chemical has been banned everywhere including the EU?”
“Pesticides are silent killers of humans, of nature, of our soils that are getting barren, of our water, of our agri-food system. I don’t imagine an agri-food system in Uganda without bees, without butterflies, and above all, without grasshoppers,” said Agnes Kirabo, the Executive Director of Food Rights Alliance (FRA).
Desperate smallholder farmers
According to the activists, Uganda’s agriculture system is by default largely organic but in recent years, pest and disease management has become one of the major production constraints for the country’s millions of subsistence farmers. And in recent years, farmers have turned to pesticides to control the pests.
According to the Food and Agricultural Organisation (FAO) of the United Nations, the number of agricultural pesticides used in Uganda doubled in 12 years (2010 – 2022) from 2,990.23 tonnes to 6,009.78 tonnes.
Similarly, the monetary value of pesticides imported to Uganda more than doubled from US$ 32.57 million to US$75.87 million in 2022 with a peak import value of US$108.57 million reported in 2020. The lucrative agro-chemical business has attracted more than 40 registered pesticide importing companies in the country.
The activists say the increased use of pesticides is attributed to their use for weeding and the increased use of hybrid seeds and livestock. According to the CSOs, equally alarming is that many of these pesticides are “synthetic pesticides” which are persistent organic chemicals.
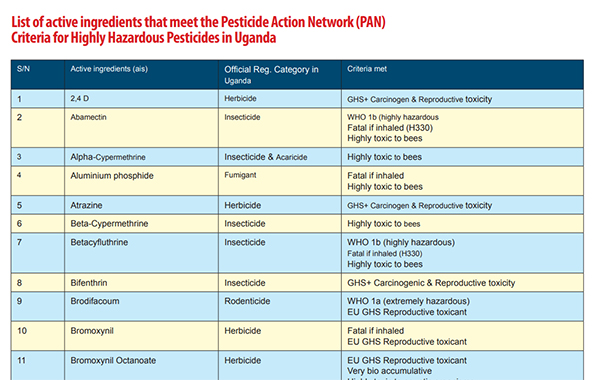
A study published last year by the Food Safety Coalition Uganda (FoSCU) titled: ‘‘Food Safety-Crop Protection Nexus: Insights from the Uganda’s agriculture sector,’’ noted that of the legally registered active ingredients, 47.8% (of the active ingredients) and 68.6% of the brands in Uganda qualified as “Highly Hazardous Pesticides.”
Highly Hazardous Pesticides (HHPs) are classified as “reproductive toxicants” meaning they potentially can negatively affect the human reproductive system and have adverse effects on pregnancy outcomes and reduced fertility.
The same study noted that 15.6% of the registered active ingredients and 19.2% of the registered brands in Uganda qualified as highly hazardous pesticides in accordance with the FAO/WHO-Joint Meeting on Pesticide Management (JMPM) criteria.
According to the activists, by July 2023, over 65% of the 55 flagged active ingredients registered for use in Uganda and yet considered as highly hazardous pesticides according to the Pesticide Action Network (PAN) criteria, were not approved for use in the European Union economic bloc.
The majority (49%) of these pesticides are highly toxic to bees, 20% are carcinogenic and reproductive toxicants while 18% are probable carcinogens, and 9% are highly persistent in water and soil and are highly toxic to aquatic organisms.
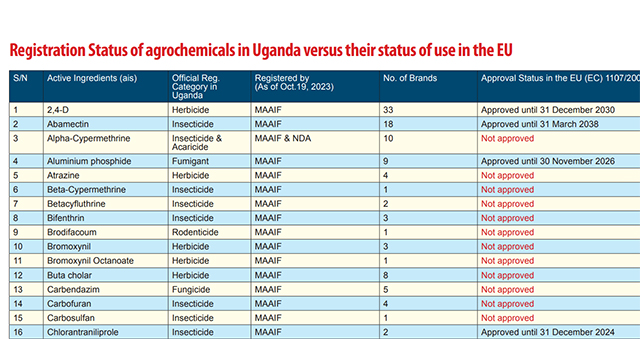
They say that, based on the Uganda agrochemical register at the Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Industry and Fisheries (MAAIF) and the National Drug Authority (NDA), the country had at least 115 active ingredients and 669 brands of synthetic pesticides legally registered for use in Uganda by the end of 2023.
“These are presenting in 459 brands, but all these active ingredients in the 459 brands, according to the PAN, are classified as highly hazardous,” said Bernard Bwambale, the head of programmes at the Global Consumer Centre, or CONSENT, who also coordinates the activities on food safety at the Food Safety Coalition of Uganda.
If it is hazardous in EU, it is hazardous in Uganda
Bwambale says his organisation has found that of the 55 active ingredients registered in Uganda, 65.5% of them cannot be used in their countries of origin. “Now, if a chemical, a highly hazardous chemical, is produced in a particular country and that country cannot use it, who are we to start thinking that we can use it? This is where our concern is.”
“So, whatever is not used in the EU, it means it’s not fit for use for human beings. The human beings in Uganda and the human beings in Europe are all human beings. And we are all sharing the same human rights.” He says some of the highly hazardous pesticides are mutagenic, meaning they can alter one’s DNA or genetic make-up.
“Literally, it would mean that when you consume food consisting of this kind of product, you stand a risk of your DNA or your genetic makeup being altered. And that is why some research is pointing to some of these chemicals being responsible for birth defects.” He says other chemicals are carcinogenic, meaning the chemical has the potential to cause cancer.
But Prof. Ogenga Latigo says some chemicals like Mancozeb the civil society claim are carcinogenic are not. He describes others as ‘probable carcinogens.’ A probable carcinogen is a substance that has a strong but not conclusive amount of evidence that it can cause cancer in humans.
But Bwambale says, “They don’t want people to keep confusing us with science.” He says other chemicals have been considered fatal when inhaled. “Imagine a farmer who doesn’t know these things and is spraying but is carrying a baby. So both the mother and the baby are inhaling this chemical,” he says, “We need to regulate these chemicals as much as we can.”
He says recent studies have indicated that some of these chemicals were found in human bodies –in sweat, urine and blood, in food and in water. “When the Europeans send us, for instance, these chemicals and we buy them, they also have regulations on which kind of food we can sell to them. We all know that.”
He says when farmers use these chemicals in the name of commercialising agriculture, they may produce very big tomatoes that do not rot, for example, but they cannot sell them beyond Uganda.
“You cannot put them on the EU market because they don’t meet the standard of the EU market. So they (agriculture products still remain with us,” he says.
Source: The independent
FARM NEWS
Coffee Leaf Rust disease hits Mbale region farmers
Published
7 months agoon
November 18, 2024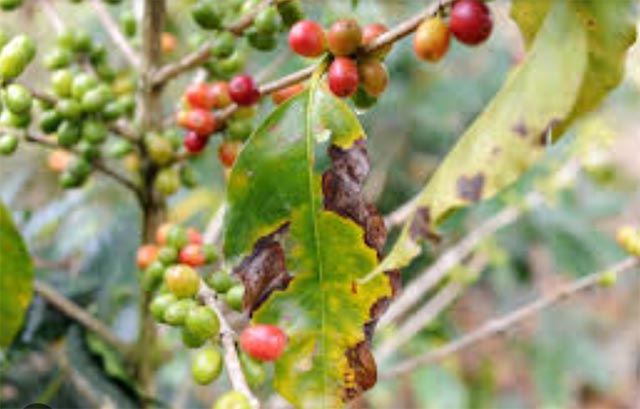
Mbale, Uganda | Coffee farmers from Bulambuli and Sironko districts are counting their losses after being attacked by coffee leaf rust disease. The disease, caused by the rust fungus Hemileia vastatrix, can reduce coffee production by between 30% to 50%.
The most affected sub-counties in Sironko include Buhugu, Masaba, Busulani, Bumasifwa, Bumalimba, and others. In Bulambuli, the hardest-hit areas are Lusha, Bulugeni Town Council, Buginyanya, and Kamu, among others.
In an exclusive interview with our reporter, Francis Nabugodi, the Sironko District Agricultural Officer, spoke about the devastating effects on farmers. “This disease has negatively impacted farmers in terms of production, and since it’s coffee season, they are going to make losses,” Nabugodi said.
He added that he had instructed extension workers to start massive sensitization campaigns in the six affected sub-counties about preventive measures, such as spraying, to curb the spread of the disease.
Nabugodi also urged the Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries, and Animal Husbandry to supply the district with chemicals so they can distribute them to farmers, as many cannot afford to buy them.
Julius Sagaiti, the LCIII Chairperson of Lusha Sub-County in Bulambuli District, stated that his sub-county is the worst affected, with over 100 farmers having all their gardens hit by the disease. He called for urgent action from Bulambuli district leaders, warning that the situation would have severe consequences for farmers.
Timothy Wegoye and Suzan Nanduga, both affected coffee farmers from Bukisa, the worst-affected sub-county, shared their concerns. “The majority of farmers are ignorant about preventive measures and do not know the chemicals for spraying,” they said, urging extension workers to use the media to sensitize them.
Original Source: URN Via The Independent
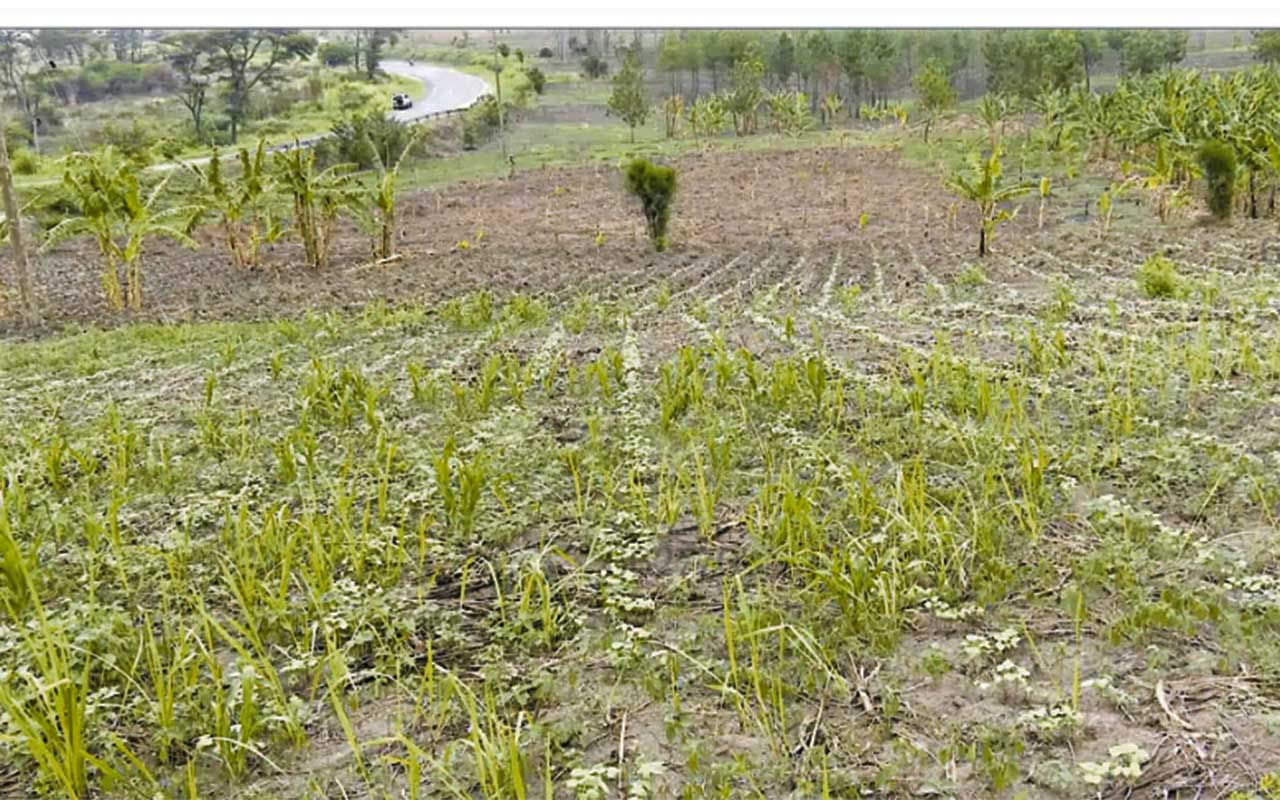

Along Bwera-Mpondwe road, in Kasese district, farmers till the land, with every hoe raising more dust than dirt, a testament of how hard the sun has scorched the ground. Located at the slopes of the Rwenzori Mountains, the low altitude leads to high temperatures as the district also sits on the Equator. In January this year, the average temperatures were 25.1 °C

Gideon Bwambale walks through drying maize garden.
Today, the temperature is 28.6 °C. The most affected areas are low-lying sub-counties like Kahokya, Nyakatonzi and Muhokya.

A decade of displacement: How Uganda’s Oil refinery victims are dying before realizing justice as EACOP secures financial backing to further significant environmental harm.

Carbon Markets Are Not the Solution: The Failed Relaunch of Emission Trading and the Clean Development Mechanism

Govt launches Central Account for Busuulu to protect tenants from evictions

Top 10 agribusiness giants: corporate concentration in food & farming in 2025

Uganda’s top Lands Ministry official has been arrested and charged with Corruption and Abuse of Office, a significant event that will have far-reaching implications for land governance in the country.

A decade of displacement: How Uganda’s Oil refinery victims are dying before realizing justice as EACOP secures financial backing to further significant environmental harm.

Govt launches Central Account for Busuulu to protect tenants from evictions

Environmentalists raise red flags over plan to expand oil palm fields in Kalangala

Innovative Finance from Canada projects positive impact on local communities.
Over 5000 Indigenous Communities evicted in Kiryandongo District
Petition To Land Inquiry Commission Over Human Rights In Kiryandongo District
Invisible victims of Uganda Land Grabs
Resource Center
- LAND GRABS AT GUNPOINT REPORT IN KIRYANDONGO DISTRICT
- RESEARCH BRIEF -TOURISM POTENTIAL OF GREATER MASAKA -MARCH 2025
- The Mouila Declaration of the Informal Alliance against the Expansion of Industrial Monocultures
- FORCED LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA TRENDS RIGHTS OF DEFENDERS IMPACT AND CALL FOR ACTION
- 12 KEY DEMANDS FROM CSOS TO WORLD LEADERS AT THE OPENING OF COP16 IN SAUDI ARABIA
- PRESENDIANTIAL DIRECTIVE BANNING ALL LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA
- FROM LAND GRABBERS TO CARBON COWBOYS A NEW SCRAMBLE FOR COMMUNITY LANDS TAKES OFF
- African Faith Leaders Demand Reparations From The Gates Foundation.
Legal Framework
READ BY CATEGORY
Newsletter
Trending
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week agoA decade of displacement: How Uganda’s Oil refinery victims are dying before realizing justice as EACOP secures financial backing to further significant environmental harm.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week agoGovt launches Central Account for Busuulu to protect tenants from evictions
-

 WITNESS RADIO MILESTONES2 weeks ago
WITNESS RADIO MILESTONES2 weeks agoTop 10 agribusiness giants: corporate concentration in food & farming in 2025
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week agoCarbon Markets Are Not the Solution: The Failed Relaunch of Emission Trading and the Clean Development Mechanism






















