SPECIAL REPORTS AND PROJECTS
Banks opt out of oil pipeline funding
Published
5 years agoon
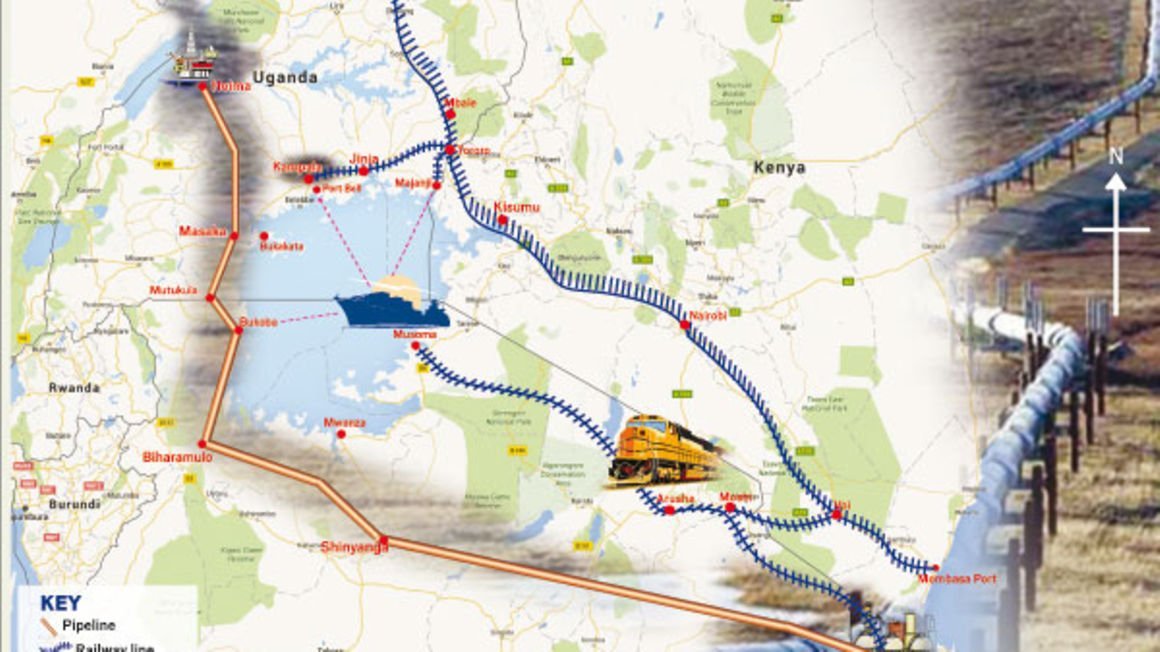
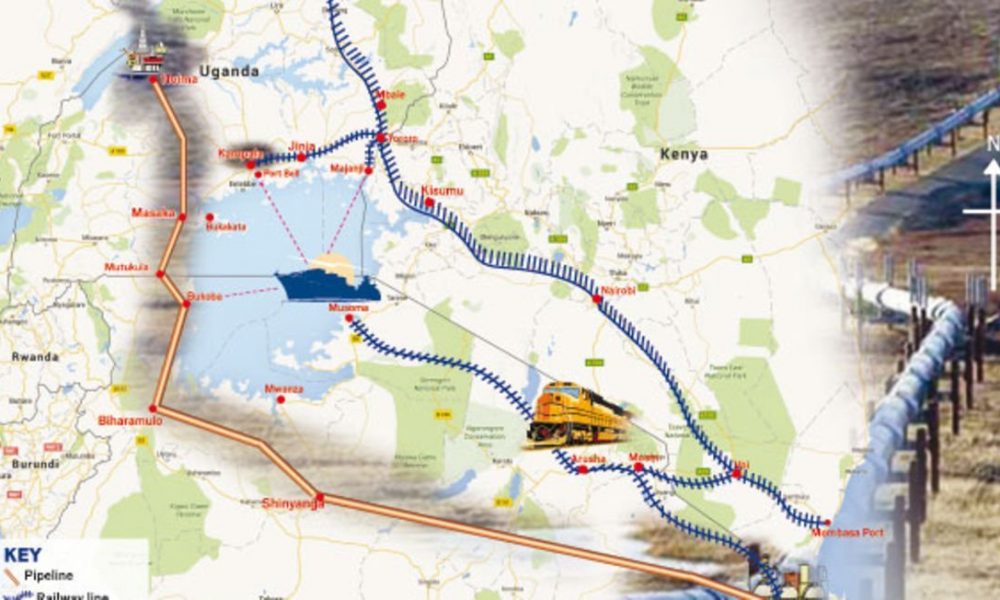
A map showing the Hoima-Tanga oil pipeline route.
The $3.5b East Africa Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP) project could run into trouble after some international commercial banks withdrew from funding the construction of the world’s longest heated crude oil pipeline proposed by French Oil Company Total and the China National Offshore Oil Corporation (CNOOC).
“The banks provided statements making it clear they will not support the East Africa Crude Oil Pipeline [EACOP]after an open letter endorsed by 263 organisations from around the world was sent to 25 banks considered most likely to be approached for financing,” a March 18 press release from Inclusive Development International, read in part.
“Barclays does not intend to participate in the financing of the East African Crude Oil Pipeline project,” it further read.
Credit Suisse is also said to share the same position with Barclays.
On this, an alliance of African and international environmental and human rights organisations have claimed another win in their campaign to stop the construction of the oil pipeline.
Bank Track, which is among these organisations, raised the red flag over alleged ignored social and environmental concerns along with the project.
“The EACOP is manifestly incompatible with global efforts to reduce our carbon emissions. Banks simply can’t have it both ways – you can’t claim to be serious about climate change and support climate-destroying projects like the EACOP,” Mr Ryan Brightwell, the Researcher and Editor at BankTrack, said.
When Daily Monitor asked Mr Brightwell about the authenticity of the quoted bank statements in their release, responded in an email, “the banks provided the statements to us, with permission for us to publish them on the stopeacop.net website: https://www.stopeacop.net/banks-checklist. If you wish to confirm these statements with the banks themselves or seek further comment from them, may I suggest you contact their press offices.”
Daily Monitor sought confirmation from Credit Suisse through the Media Relations, Credit Suisse Group in Zurich, Switzerland, both on email and phone calls. “Thanks for reaching out. I can confirm: Credit Suisse is not considering participating in the EACOP project. Kind regards,” Mr Yannick Orto, the Credit Suisse Services Ag Group External Communications in Zürich, responded.
Mr Orto said as a bank policy, they will not give the reason why they are not supporting the EACOP and advised everyone to only use their “public statement” .
Daily Monitor could not reach Barclays Bank through its corporate and investment contacts as provided on the bank’s website for press and media. Our calls could not be answered by the bank and the voice mail message left was not returned.
However, the bank is quoted on the #STOPEACOP campaign: “Barclays does not intend to participate in the financing of the East African Crude Oil Pipeline project” as its public statement.
“Besides climate and environmental risks, our field investigations reveal serious human rights violations already caused by EACOP, with tens of thousands of people deprived of their livelihoods before having received any compensation. We call on French banks to commit themselves quickly and publicly not to finance this project,” Juliette Renaud, the senior campaigner at Friends of the Earth France, said.
It is, however, not clear whether the banks’ refusal to finance the project is related to the environment. Mr Samuel Okulony, the chief executive officer of the Uganda-based Environment Governance Institute, said the next 10 years will be critical for efforts to mitigate the severity of climate change and that the pipeline will generate an additional 34 million tonnes of carbon emissions each year, which is disastrous.
Mr David Pred, the executive director of Inclusive Development International, said it would be a significant blow to the project if Standard Bank was to walk away, given the key role it has played as a financial advisor in arranging the $2.5 billion project loan that is required to finance construction.
“Any credible assessment would find that this project is too risky for the millions of people whose water resources it would jeopardise and for our rapidly warming climate, which simply cannot afford another massive oil project,” Mr Pred said.
Affected persons
The environmental and rights activists say the project stretching nearly 1,445 kms threatens to displace families and farmers and would pose risk to water resources and wetlands – including the Lake Victoria basin, which more than 40 million people rely on.
According to a report released by Oxfam International in September 2020 titled ‘‘empty promises down the line’’ a human rights impact assessment on the EACOP, approximately 200 households will be relocated.
The report adds that an estimated 3,200 to 3,500 households will be economically displaced, meaning they will lose land whereas in Tanzania, 391 households will lose land as part of the priority areas and 9,122 will lose land for the pipeline right of way.
Oil companies, govt respond
Both the oil companies and government have been slow to comment.
Ms Linda Nabirye, the external communications coordinator for Total E&P Uganda, referred us to their March 8 press release that responds to some issues raised by the banks and the NGOs.
The release titled: “Uganda and Tanzania: Total acts in transparency on social and environmental stakes of the Lake Albert resources development project,” said the projects Tilenga in Uganda and the EACOP in Uganda and Tanzania “are undertaken in a sensitive environmental context and require the implementation of land acquisition programmes with a specific attention to respecting the rights of the communities concerned.”
Total says environmental and social impact assessment (ESIA) studies have been conducted and approved by the Ugandan and Tanzanian authorities for both projects, which are carried out in compliance with the stringent performance standards of the International Finance Corporation (IFC).
Total also said it would work closely with Uganda Wildlife Authority and with IUCN experts to integrate the best practices for the protection of chimpanzees, particularly by promoting the conservation of forest habitats.
Ms Amina Bukenya, the spokesperson for CNOOC, asked us to send questions on her email which she had not responded to by press time.
On the government side, Ms Stella Amony, the communications lead for EACOP, replied: “The matter is sensitive and needs a collective response from the joint venture members.”
Ms Angella Karisa Ambaho, the communications Officer of Uganda National Oil Company (UNOC) said: “I am still waiting for approval of my response to your questions you raised on email, which I shared with my superiors”.
Established in 2013, UNOC is mandated to hold 15 per cent of Uganda’s petroleum licences on behalf of the government.
Local NGOs take on the issue
Africa Institute for Energy Governance (AFIEGO), a registered public policy research and advocacy organisation whose main objectives is to promote environmental conservation and community rights in the extractives sector, said the banks turning down requests to finance CNOOC and Total is a signal to other financiers to consider their .
“….Climate change, environmental and social risks of the project are immense and when banks see other financial institutions taking a step back and refusing to finance the project, they also re-assess their participation,” Ms Diana Nabiruma, the senior communications officer at AFIEGO, said.
Mr Brian Nahamya, a programmes associate at Global Rights Alert, an NGO involved in advocacy for the oil pipeline PAPs, said the land acquisition was done but no project affected person has received compensation since the end of the valuation process in 2018/2019.
‘‘…Every person affected by this project from Hoima to Rakai, no one has received compensation up to date,” he said.
Holes poked on EACOP Environmental remedies
Despite the National Environment Management Authority (Nema) issuing a certificate of approval to Total East Africa for an Environmental and Social Impact Assessment (ESIA) as required by law on such a project in 2019, other international environmentalists have poked holes in it.
Section 3.3 of the Netherlands Commission for Environmental Assessment (NCEA) report on water and wetlands crossings and water use contends that “The ESIA does not make clear why open trench river crossings are chosen as the way to go. This is critical as major rivers typically come together with wide wetlands.”
The oil pipeline route
In Uganda, the oil pipeline will traverse through Hoima, Kikuube, Kakumiro, Mubende, Kyankwanzi, Gomba, Rakai, Lwengo, Kyotera, and Sembabule districts.
According to the East Africa Crude Oil Pipeline Environment and Impact Assessment Report 2019, the pipeline will originate from Kabaale, Hoima District and snake through different communities for a distance of 296km before it approaches the Uganda-Tanzanian border.
About the project
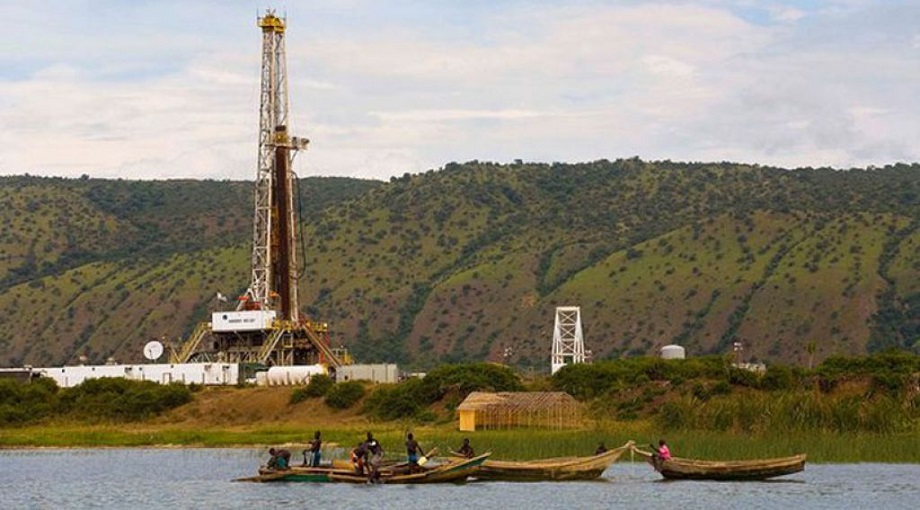
The East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP) is a proposed 1,445km-pipeline that will transport oil from Hoima in Uganda to Tanga port in Tanzania.
About 1.7 billion barrels of recoverable oil have been discovered in the Albertine Graben, the basin of Lake Albert, on the border between Uganda and DR Congo. The extraction will take place at two oil fields: the Kingfisher field, operated by China National Offshore Oil Corporation (CNOOC) and the Tilenga field, operated by Total S.A.
In September 2020 both Tanzania and Uganda agreed on the $3.5b oil pipeline project after years of discussing the relative merits of different routes out to the Indian Ocean.
Work was scheduled to start by the end of 2020 but the Covid-19 pandemic delayed the project. Tanzania says the project will create 10,000 jobs and that more than 90,000 people would be compensated to pave the way for the pipeline.
The oil will be partly refined in Uganda to supply the local market and partly exported to the international market via the EACOP. The project is being implemented by a joint venture of oil companies operating in the Albertine Graben including CNOOC and Total and Uganda government through the Uganda National Oil Company and Tanzania Petroleum Development Corporation.
Original Source: Daily monitor
Related posts:

 ‘We cannot drink oil’: campaigners condemn east African pipeline project.
‘We cannot drink oil’: campaigners condemn east African pipeline project.
 Put people above profits – Climate Activists urge Total to defund EACOP
Put people above profits – Climate Activists urge Total to defund EACOP
 Rights Groups Say Villagers Not Compensated for East Africa Oil Pipeline
Rights Groups Say Villagers Not Compensated for East Africa Oil Pipeline
 CSOs urge banks and other IFIs not to finance E.Africa oil pipeline project…
CSOs urge banks and other IFIs not to finance E.Africa oil pipeline project…
You may like
-


‘We cannot drink oil’: campaigners condemn east African pipeline project.
-


Rights Groups Say Villagers Not Compensated for East Africa Oil Pipeline
-
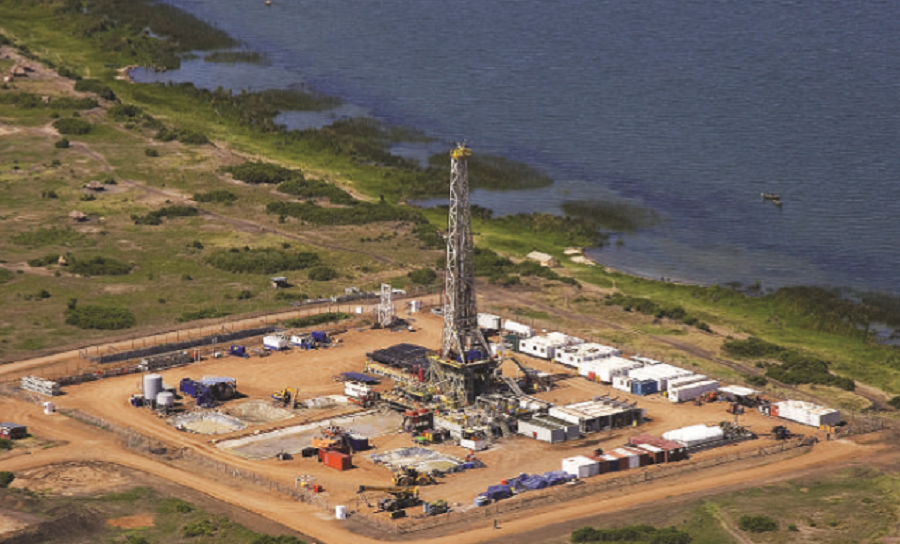


Govt pushes for compulsory land acquisition in Buliisa
-
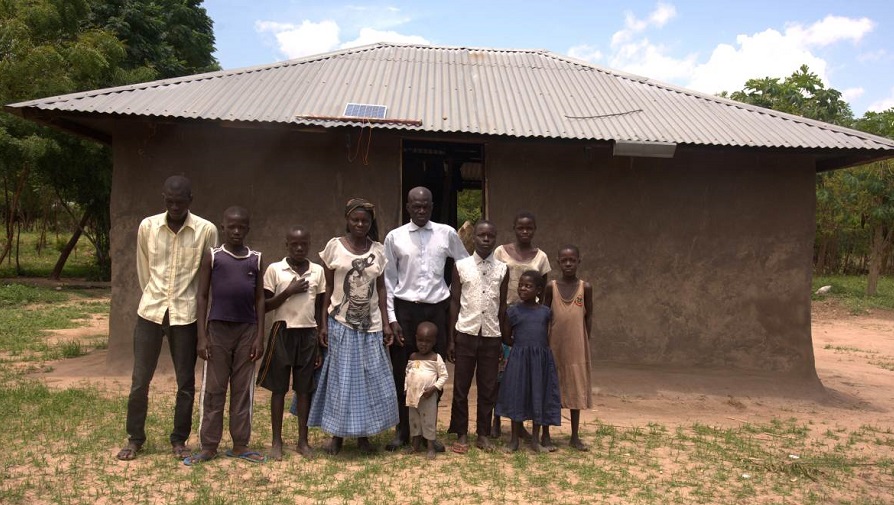


Families left in limbo as Uganda oil project earmarks land
-


Transparency: Uganda is the newest member of EITI
-


NGOs file suit against Total over Uganda oil project
SPECIAL REPORTS AND PROJECTS
‘Food and fossil fuel production causing $5bn of environmental damage an hour’
Published
2 weeks agoon
December 22, 2025
UN GEO report says ending this harm key to global transformation required ‘before collapse becomes inevitable’.
Related posts:

 Activists storm TotalEnergies’ office ahead of G20 Summit, demand end to fossil fuel expansion in Africa
Activists storm TotalEnergies’ office ahead of G20 Summit, demand end to fossil fuel expansion in Africa
 New billion-dollar loans to fossil fuel companies from SEB, Nordea and Danske Bank.
New billion-dollar loans to fossil fuel companies from SEB, Nordea and Danske Bank.
 Fossil fuel opponents lobby Africans for support
Fossil fuel opponents lobby Africans for support
 Ecological land grab: food vs fuel vs forests
Ecological land grab: food vs fuel vs forests
SPECIAL REPORTS AND PROJECTS
Britain, Netherlands withdraw $2.2 billion backing for Total-led Mozambique LNG
Published
3 weeks agoon
December 17, 2025
CONSTRUCTION HALTED IN 2021, BUT DUE TO RESTART
PROJECT CAN PROCEED WITHOUT UK, DUTCH FINANCING, TOTAL HAS SAID
CRITICISM FROM ENVIRONMENTAL, HUMAN RIGHTS GROUPS
Related posts:

 Uganda, Total sign crude oil pipeline deal
Uganda, Total sign crude oil pipeline deal
 Witness Radio – Uganda, Community members from Mozambique and other organizations around the world say NO to more industrial tree plantations
Witness Radio – Uganda, Community members from Mozambique and other organizations around the world say NO to more industrial tree plantations
 NGOs file suit against Total over Uganda oil project
NGOs file suit against Total over Uganda oil project
 Agribusiness Company with financial support from UK, US and Netherlands is dispossessing thousands.
Agribusiness Company with financial support from UK, US and Netherlands is dispossessing thousands.
SPECIAL REPORTS AND PROJECTS
The secretive cabal of US polluters that is rewriting the EU’s human rights and climate law
Published
1 month agoon
December 5, 2025
Leaked documents reveal how a secretive alliance of eleven large multinational enterprises has worked to tear down the EU’s flagship human rights and climate law, the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD). The mostly US-based coalition, which calls itself the Competitiveness Roundtable, has targeted all EU institutions, governments in Europe’s capitals, as well as the Trump administration and other non-EU governments to serve its own interests. With European lawmakers soon moving ahead to completely dilute the CSDDD at the expense of human rights and the climate, this research exposes the fragility of Europe’s democracy.
Key findings
- Leaked documents reveal how a secretive alliance of eleven companies, including Chevron, ExxonMobil, and Koch, Inc., has worked under the guise of a “Competitiveness Roundtable” to get the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD) either scrapped or massively diluted.
- The companies, most of which are headquartered in the US and operate in the fossil fuel sector, aimed to “divide and conquer in the Council”, sideline “stubborn” European Commission departments, and push the European People’s Party (EPP) in the European Parliament “to side with the right-wing parties as much as possible”.
- Chevron and ExxonMobil were in charge of mobilising pressure against the CSDDD from non-EU countries. The Roundtable companies endeavoured to get the CSDDD high on the agenda of the US-EU trade negotiations and also worked on mobilising other countries against the CSDDD, in order to disguise the US influence.
- Roundtable companies paid the TEHA Group – a think tank – to write a research report and organise an event on EU competitiveness, which echoed the Roundtable’s position and cast doubt on the European Commission’s assessment of the economic impact of the CSDDD.
While Europeans were told that their governments were negotiating a landmark law to hold corporations accountable for human rights abuses and climate damage, a secretive alliance of US fossil fuel giants was working behind the scenes to destroy it. Collaborating under the innocent-sounding name ‘Competitiveness Roundtable’, eleven multinational enterprises have worked closely to eviscerate several EU sustainability laws, including the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD) and the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD). This Competitiveness Roundtable may be unknown, but its members are a who’s-who of polluting, mainly US, multinationals, including Chevron, ExxonMobil, and Dow. The group seems to have run rings around all branches of the EU and the Trump administration to get what they want: scrapping, or at least hugely diluting, the CSDDD.

Leaked documents obtained by SOMO reveal how, under the pretext of the now-near-magical concept of ‘competitiveness’, these companies plotted to hijack democratically adopted EU laws and strip them of all meaningful provisions, including those on climate transition plans, civil liability, and the scope of supply chains. EU officials appear not to have known who they were up against. But the documents obtained by SOMO show a high level of organisation and strategising with a clear facilitator: Teneo, a US public relations and consultancy company.
The documents indicate that many of the companies involved wanted to stay hidden from view. After all, if it were widely known that a secretive group of mostly American fossil fuel companies like Chevron, ExxonMobil, and Koch, Inc. was working as a coordinated organisation to dilute an EU climate and human rights law, that might raise questions and serious concern among the public and the policymakers they were targeting. Many of the companies in the Roundtable have never publicly spoken out against the CSDDD.
Big Oil’s ‘Competitiveness Roundtable’
The Competitiveness Roundtable is dominated by fossil fuel companies, including three Big Oil companies (ExxonMobil, Chevron, TotalEnergies) and three other companies with activities in the oil and gas sector (Koch, Inc., Honeywell, and Baker Hughes). Other members are Nyrstar (minerals and metals, a subsidiary of Trafigura Group); Dow, Inc. (chemicals); Enterprise Mobility (car rentals); and JPMorgan Chase (finance).
Teneo, the Roundtable’s coordinator, has a track record(opens in new window) of working with fossil fuel companies, including Chevron, Shell, and Trafigura, and was hired by the government of Azerbaijan to handle public relations(opens in new window) when it hosted the COP29 climate conference.
In February 2025, the European Commission published the Omnibus I proposal(opens in new window), which aims to “simplify” several EU sustainability laws, including the CSDDD. The documents obtained by SOMO reveal that the Roundtable companies, which have been meeting weekly since at least March 2025, worked on deep interventions within each of the three EU institutions to get the Omnibus I package to align exactly with their views. The EU institutions are expected to reach a final agreement on Omnibus I by the end of 2025.
The documents reveal that the Roundtable companies’ activities in the Parliament are far more significant than what is visible in the EU Transparency Register(opens in new window). Eight of the Roundtable’s lobbying meetings during the Strasbourg plenary sessions of May and June 2025, listed in the Transparency Register, show Teneo as the only attendee, thereby failing to disclose the names of other Roundtable companies that participated in these meetings. Another three meetings the Roundtable held were not found in the EU Transparency Register(opens in new window) at all.
“Divide and conquer” the Council
In the European Council, the Roundtable plotted to “divide and conquer” EU governments to get the climate article in the CSDDD deleted. In June 2025, during the final weeks of negotiations in the Council on the Omnibus I proposal, the Roundtable discussed lobbying EU government leaders to “intervene politically” to ensure its priorities were included in the Council’s negotiation mandate. Subsequently, German Chancellor Merz and French President Macron reportedly(opens in new window) personally intervened(opens in new window) in the Council’s political process, leading to a dramatic dilution(opens in new window) of the texts(opens in new window) negotiated in the months before the intervention. Several of the changes made to the texts strongly align with the Roundtable’s demands, including delaying and substantially weakening the climate obligations, scrapping EU civil liability provisions, and limiting the responsibility of companies to take responsibility for their supply chains (the ‘Tier 1’ restriction).

Competitiveness Roundtable meeting document, 11 July 2025.
Additionally, the documents reveal that the Roundtable is still aiming to drum up a “blocking minority” to overturn the Council’s negotiation mandate during the trilogue negotiations, which started in November 2025. By “tak[ing] advantage of the ‘weak’ Council negotiating mandate” and disagreements between EU Member States on “contentious articles”, the Competitiveness Roundtable companies hope to force the Danish Council presidency to give up on including any form of climate obligations in the CSDDD – despite EU Member States’ agreement on this in the June 2025 Council mandate(opens in new window) .
To implement the divide-and-conquer strategy, the Roundtable assigned specific companies to “establish rapporteurships” with different EU governments. TotalEnergies would target the French, Belgian, and Danish governments, and ExxonMobil would target Germany, Hungary, the Czech Republic, and Romania.



Circumventing “stubborn” European Commission departments
The Roundtable also discussed working on “circumvent[ing]” two “stubborn” European Commission departments involved in the Omnibus political process, DG JUST and DG FISMA, which, in their view, were “unlikely to be willing to see our side of the story”. According to the documents, DG JUST opposed deleting the climate article and restricting the Directive’s scope to only very large enterprises. The Roundtable aimed to diminish the role of these departments by pressuring President Von der Leyen and Commissioners McGrath (DG JUST) and Albuquerque (DG FISMA) by “organising letters from Irish and German business groups” and using an event held by the European Roundtable for Industry to “target” Von der Leyen and McGrath.
Read full report: Somo.nl
Source: Somo
Related posts:

 Victims of human rights violations in Uganda still waiting for redress
Victims of human rights violations in Uganda still waiting for redress
 UN Human Rights Chief urges EU leaders to approve key business and human rights legislation
UN Human Rights Chief urges EU leaders to approve key business and human rights legislation
 Business, UN, Govt & Civil Society urge EU to protect sustainability due diligence framework
Business, UN, Govt & Civil Society urge EU to protect sustainability due diligence framework
 Development financiers fuel human rights abuses – New Report
Development financiers fuel human rights abuses – New Report

COP30 : a further step towards a Just Transition in Africa

‘Food and fossil fuel production causing $5bn of environmental damage an hour’

Four hundred fifty victim families of the Oil Palm project in Buvuma are to receive compensation by this Friday – Witness Radio

Britain, Netherlands withdraw $2.2 billion backing for Total-led Mozambique LNG

Four hundred fifty victim families of the Oil Palm project in Buvuma are to receive compensation by this Friday – Witness Radio

Women’s groups demand equality in land tenure security to boost food production.

Tension as Project-Affected Persons demand to meet Uganda’s President over Oil Palm growing on their grabbed land.

Land commission starts updating govt land countrywide.

Innovative Finance from Canada projects positive impact on local communities.
Over 5000 Indigenous Communities evicted in Kiryandongo District
Petition To Land Inquiry Commission Over Human Rights In Kiryandongo District
Invisible victims of Uganda Land Grabs
Resource Center
- REPARATORY AND CLIMATE JUSTICE MUST BE AT THE CORE OF COP30, SAY GLOBAL LEADERS AND MOVEMENTS
- LAND GRABS AT GUNPOINT REPORT IN KIRYANDONGO DISTRICT
- THOSE OIL LIARS! THEY DESTROYED MY BUSINESS!
- RESEARCH BRIEF -TOURISM POTENTIAL OF GREATER MASAKA -MARCH 2025
- The Mouila Declaration of the Informal Alliance against the Expansion of Industrial Monocultures
- FORCED LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA TRENDS RIGHTS OF DEFENDERS IMPACT AND CALL FOR ACTION
- 12 KEY DEMANDS FROM CSOS TO WORLD LEADERS AT THE OPENING OF COP16 IN SAUDI ARABIA
- PRESENDIANTIAL DIRECTIVE BANNING ALL LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA