SPECIAL REPORTS AND PROJECTS
They should not be called public development banks
Published
5 years agoon

From 9-12 November 2020, 450 finance institutions from around the world will gather for the first international meeting of public development banks, dubbed the “Finance in Common” summit, hosted by the French government. The institutions, which range from the World Bank to the China Development Bank, collectively spend $2 trillion a year on so-called development projects – roads, power plants, agribusiness plantations and more. Much of this spending is financed by the public – us – which is why they called themselves “public development banks”. But our partners on the ground and our experience teach us they are not public and what they fund is not development.
For the most part, these institutions get their money from public coffers, fuelled by people’s labour and taxes. As state-owned institutions, they have the obligation to respect and protect human rights in their policies and operations. And they are supposed to be accountable to the public, through government oversight bodies. But that accountability hardly exists. From Proparco in France, to BIO in Belgium, to DFC in the US, few people have heard of these development banks much less know what they are up to.
In contrast to development cooperation bodies, which provide grants and loans to governments of the global south, development banks invest in the private sector for a financial return. They argue that companies drive growth and jobs, and, for this to happen, financiers have to take risk, for example through debt and private equity. A few million dollars from a development bank gives companies a form of guarantee that they can then use to raise more millions from private lenders or other development banks, often at a cheaper rate. This is how the development banks play such a critical role in enabling corporations operating in the global south to expand further into markets and territories – from polluting coal plants in Bangladesh, to controversial hydroelectric dams in Honduras, to hazardous soybean plantations in Paraguay – in ways they could not otherwise.
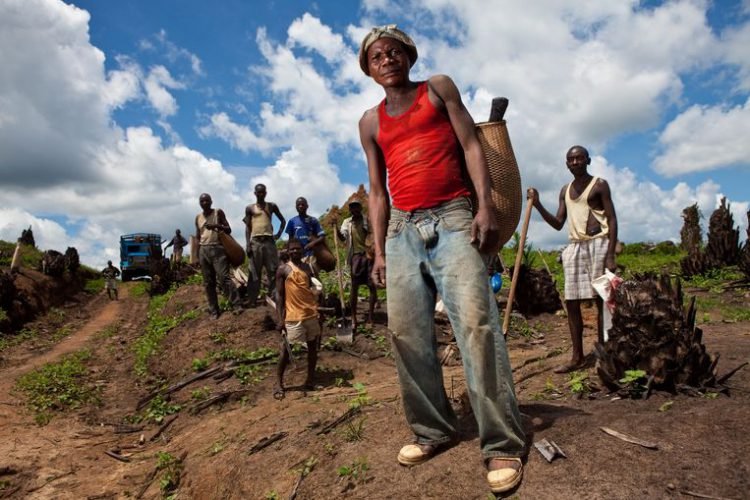
As civil society organisations working closely with partners and communities in the global south, we are most familiar with these institutions’ involvement in agriculture. What they contribute to can hardly be called development. We have witnessed how they invest primarily in agribusiness companies and an industrial model of agriculture that is a main driver of both pandemics and the climate crisis. Development banks have little track record for supporting locally-controlled food systems or peasant-led agroecological farming, which are the real solutions to these two problems.
Over the past five years, for instance, a number of groups have worked together to support communities in the Democratic Republic of the Congo badly affected by a Canadian oil palm plantation company that received more than $140 million in financing from numerous development banks, including approximately $88 million from the UK development bank CDC Group. The company, Feronia Inc, was majority-owned by the development banks until it went bankrupt this year and was handed over to a private equity fund based in the tax haven of Mauritius. Feronia, which never made a profit but paid its expat staff handsomely, would have collapsed years ago had it not been for the intervention of the development banks.
It was argued that the involvement of these institutions would provide leverage for the local communities living in and around the plantations to address their long-standing grievances that have existed ever since the lands were stolen from them at gunpoint over a 100 years ago by the then Anglo-Dutch giant Unilever and colonial Belgium’s King Leopold. They have suffered immensely over the past century, and any sincere commitment to “development” could only be possible if it began by addressing the theft of their lands and forests and led to land restitution and reparations. But the development banks have resisted any meaningful movement down this path. In fact, it’s been quite the opposite.
They have taken no action to address the historic conflicts over the nearly 100,000 hectares of land concessions or the allegations of corruption plaguing the project. Their environmental, social and governance (ESG) plans did nothing to alleviate poverty in the communities. And the involvement of the various banks did not reduce rampant human rights violations against villagers or workers. What’s worse, the banks have acted to undermine the community efforts to use the grievance mechanisms that they themselves established.
The reality is that no matter the ESG guidelines or codes of conduct against land grabbing, there is no way that development bank investments in industrial plantations can contribute to “sustainable development”. These plantations are colonial relics, designed purely to extract profits for their owners and to produce commodities for foreign buyers. They require stolen lands, exploited labour and armed violence to keep distraught villagers and workers from rising up. The creation of “jobs” and social projects, like poorly equipped schools and health clinics, that the development banks use to justify their presence is merely the theft and destruction of lands and resources that the villagers once had to sustain themselves.
Let us be clear: public development banks are disconnected from any sense of what “public” means and any argument about what “development” should look like. In food and farming, the backbone of our very existence, they finance corporate agribusiness. They were not set up to support any other model and have no real capacity to do so. As industrial agriculture is responsible for up to 37% of the world’s annual greenhouse gas emissions, the case to dismiss development banks is clear. We need a very different approach to international finance that supports communities rather than companies, and food systems free of corporate control.
Signed by
Alliance for Food Sovereignty in Africa – Africa
WoMin African Alliance – Africa
Entraide & Fraternité – Belgium
FIAN Belgium – Belgium
CIDSE – Belgium
Friends of the Earth Europe – Belgium
Associação Brasileira de Reforma Agrária – Brazil
SOS Chapada dos Veadeiros – Brazil
Movimento Ciencia Cidadã – Brazil
CAPINA – Cooperação e Apoio a Projetos de Inspiração Alternativa – Brazil
Terra de Direitos – Brazil
Comissão Pastoral da Terra – Brazil
Amigos da Terra Brasil – Brazil
FAOR – Fórum da Amazônia Oriental – Brazil
FASE – Solidariedade e Educação – Brazil
IPDMS – Instituto de Pesquisa, Direitos e Movimentos Sociais – Brazil
Rede Jubileu Sul – Brazil
Via Campesina – Brazil
Emater – Brazil
Campaign in Defense of the Cerrado – Brazil
Réseau des acteurs du développement durable (RADD) – Cameroon
Synaparcam – Cameroon
REFEB – Côte d’Ivoire
DIOBASS Platform – Democratic Republic of Congo
Réseau d’information et d’appuis aux ONG en République démocratique du Congo (RIAO-RDC) – Democratic Republic of Congo
Acción Ecológica – Ecuador
Confédération paysanne – France
CCFD-Terre Solidaire – France
Les Amis de la Terre – France
Attac France – France
Survie – France
Muyissi Environnement – Gabon
FIAN Germany – Germany
APVVU – India
Indian Social Action Forum – India
Growthwatch – India
Karavali Karnataka Janabhivriddhi Vedike – India
Sahanivasa – India
Bina Desa – Indonesia
KRuHA – Indonesia
SNI – Indonesia Fisherfolk Union – Indonesia
Suluh Muda Inspirasi – Indonesia
GERAK LAWAN – Indonesia
Serikat Tani Merdeka (SETAM) – Indonesia
Front Perjuangan Pemuda Indonesia (FPPI) – Indonesia
Indonesia for Global Justice – Indonesia
Koalisi Rakyat Untuk Keadilan Perikanan (KIARA) – Indonesia
Solidaritas Perempuan – Indonesia
Global Legal Action Network – Ireland
Trócaire – Ireland
SONIA for a Just New World – Italy
Africa Japan Forum – Japan
Africa Rikai Project – Japan
Eriko Yano – Japan
Network between Village and Town – Japan
Japan International Volunteer Center (JVC) – Japan
Friends of the Earth Japan – Japan
Missionary Society of Saint Columban – Japan
WE21 Japan – Japan
Indigenous Strategy & Institution for Development – Kenya
SOS FAIM- Luxembourg
Collectif pour la défense des terres malgaches – TANY – Madagascar/France
Milieudefensie – Netherlands
Pakistan Kissan Rabita Committee – Pakistan
Kilusang Magbubukid ng Pilipinas – Philippines
Organización Boricuá de Agricultura Ecológica de Puerto Rico, CLOC-LVC – Puerto Rico
Kamara Organic Promoter – Rwanda
La Via Campesina South Asia – South Asia
Korea Women Peasants’ Association – South Korea
Bread for all – Switzerland
Generation Engage Network – Uganda
Corner House – United Kingdom
Global Justice Now – United Kingdom
Friends of the Earth United States – United States
The Oakland Institute – United States
Thousand Currents – United States
Grassroots International – United States
Family Farm Defenders – United States
National Family Farm Coalition – United States
Association for Women’s Rights in Development (AWID) – International
GRAIN – International
Biofuelwatch – International
World Rainforest Movement – International
Original source: Collective statement
Related posts:
You may like
SPECIAL REPORTS AND PROJECTS
‘Food and fossil fuel production causing $5bn of environmental damage an hour’
Published
2 weeks agoon
December 22, 2025
UN GEO report says ending this harm key to global transformation required ‘before collapse becomes inevitable’.
Related posts:

 Activists storm TotalEnergies’ office ahead of G20 Summit, demand end to fossil fuel expansion in Africa
Activists storm TotalEnergies’ office ahead of G20 Summit, demand end to fossil fuel expansion in Africa
 New billion-dollar loans to fossil fuel companies from SEB, Nordea and Danske Bank.
New billion-dollar loans to fossil fuel companies from SEB, Nordea and Danske Bank.
 Fossil fuel opponents lobby Africans for support
Fossil fuel opponents lobby Africans for support
 Ecological land grab: food vs fuel vs forests
Ecological land grab: food vs fuel vs forests
SPECIAL REPORTS AND PROJECTS
Britain, Netherlands withdraw $2.2 billion backing for Total-led Mozambique LNG
Published
3 weeks agoon
December 17, 2025
CONSTRUCTION HALTED IN 2021, BUT DUE TO RESTART
PROJECT CAN PROCEED WITHOUT UK, DUTCH FINANCING, TOTAL HAS SAID
CRITICISM FROM ENVIRONMENTAL, HUMAN RIGHTS GROUPS
Related posts:

 Uganda, Total sign crude oil pipeline deal
Uganda, Total sign crude oil pipeline deal
 Witness Radio – Uganda, Community members from Mozambique and other organizations around the world say NO to more industrial tree plantations
Witness Radio – Uganda, Community members from Mozambique and other organizations around the world say NO to more industrial tree plantations
 NGOs file suit against Total over Uganda oil project
NGOs file suit against Total over Uganda oil project
 Agribusiness Company with financial support from UK, US and Netherlands is dispossessing thousands.
Agribusiness Company with financial support from UK, US and Netherlands is dispossessing thousands.
SPECIAL REPORTS AND PROJECTS
The secretive cabal of US polluters that is rewriting the EU’s human rights and climate law
Published
1 month agoon
December 5, 2025
Leaked documents reveal how a secretive alliance of eleven large multinational enterprises has worked to tear down the EU’s flagship human rights and climate law, the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD). The mostly US-based coalition, which calls itself the Competitiveness Roundtable, has targeted all EU institutions, governments in Europe’s capitals, as well as the Trump administration and other non-EU governments to serve its own interests. With European lawmakers soon moving ahead to completely dilute the CSDDD at the expense of human rights and the climate, this research exposes the fragility of Europe’s democracy.
Key findings
- Leaked documents reveal how a secretive alliance of eleven companies, including Chevron, ExxonMobil, and Koch, Inc., has worked under the guise of a “Competitiveness Roundtable” to get the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD) either scrapped or massively diluted.
- The companies, most of which are headquartered in the US and operate in the fossil fuel sector, aimed to “divide and conquer in the Council”, sideline “stubborn” European Commission departments, and push the European People’s Party (EPP) in the European Parliament “to side with the right-wing parties as much as possible”.
- Chevron and ExxonMobil were in charge of mobilising pressure against the CSDDD from non-EU countries. The Roundtable companies endeavoured to get the CSDDD high on the agenda of the US-EU trade negotiations and also worked on mobilising other countries against the CSDDD, in order to disguise the US influence.
- Roundtable companies paid the TEHA Group – a think tank – to write a research report and organise an event on EU competitiveness, which echoed the Roundtable’s position and cast doubt on the European Commission’s assessment of the economic impact of the CSDDD.
While Europeans were told that their governments were negotiating a landmark law to hold corporations accountable for human rights abuses and climate damage, a secretive alliance of US fossil fuel giants was working behind the scenes to destroy it. Collaborating under the innocent-sounding name ‘Competitiveness Roundtable’, eleven multinational enterprises have worked closely to eviscerate several EU sustainability laws, including the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD) and the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD). This Competitiveness Roundtable may be unknown, but its members are a who’s-who of polluting, mainly US, multinationals, including Chevron, ExxonMobil, and Dow. The group seems to have run rings around all branches of the EU and the Trump administration to get what they want: scrapping, or at least hugely diluting, the CSDDD.

Leaked documents obtained by SOMO reveal how, under the pretext of the now-near-magical concept of ‘competitiveness’, these companies plotted to hijack democratically adopted EU laws and strip them of all meaningful provisions, including those on climate transition plans, civil liability, and the scope of supply chains. EU officials appear not to have known who they were up against. But the documents obtained by SOMO show a high level of organisation and strategising with a clear facilitator: Teneo, a US public relations and consultancy company.
The documents indicate that many of the companies involved wanted to stay hidden from view. After all, if it were widely known that a secretive group of mostly American fossil fuel companies like Chevron, ExxonMobil, and Koch, Inc. was working as a coordinated organisation to dilute an EU climate and human rights law, that might raise questions and serious concern among the public and the policymakers they were targeting. Many of the companies in the Roundtable have never publicly spoken out against the CSDDD.
Big Oil’s ‘Competitiveness Roundtable’
The Competitiveness Roundtable is dominated by fossil fuel companies, including three Big Oil companies (ExxonMobil, Chevron, TotalEnergies) and three other companies with activities in the oil and gas sector (Koch, Inc., Honeywell, and Baker Hughes). Other members are Nyrstar (minerals and metals, a subsidiary of Trafigura Group); Dow, Inc. (chemicals); Enterprise Mobility (car rentals); and JPMorgan Chase (finance).
Teneo, the Roundtable’s coordinator, has a track record(opens in new window) of working with fossil fuel companies, including Chevron, Shell, and Trafigura, and was hired by the government of Azerbaijan to handle public relations(opens in new window) when it hosted the COP29 climate conference.
In February 2025, the European Commission published the Omnibus I proposal(opens in new window), which aims to “simplify” several EU sustainability laws, including the CSDDD. The documents obtained by SOMO reveal that the Roundtable companies, which have been meeting weekly since at least March 2025, worked on deep interventions within each of the three EU institutions to get the Omnibus I package to align exactly with their views. The EU institutions are expected to reach a final agreement on Omnibus I by the end of 2025.
The documents reveal that the Roundtable companies’ activities in the Parliament are far more significant than what is visible in the EU Transparency Register(opens in new window). Eight of the Roundtable’s lobbying meetings during the Strasbourg plenary sessions of May and June 2025, listed in the Transparency Register, show Teneo as the only attendee, thereby failing to disclose the names of other Roundtable companies that participated in these meetings. Another three meetings the Roundtable held were not found in the EU Transparency Register(opens in new window) at all.
“Divide and conquer” the Council
In the European Council, the Roundtable plotted to “divide and conquer” EU governments to get the climate article in the CSDDD deleted. In June 2025, during the final weeks of negotiations in the Council on the Omnibus I proposal, the Roundtable discussed lobbying EU government leaders to “intervene politically” to ensure its priorities were included in the Council’s negotiation mandate. Subsequently, German Chancellor Merz and French President Macron reportedly(opens in new window) personally intervened(opens in new window) in the Council’s political process, leading to a dramatic dilution(opens in new window) of the texts(opens in new window) negotiated in the months before the intervention. Several of the changes made to the texts strongly align with the Roundtable’s demands, including delaying and substantially weakening the climate obligations, scrapping EU civil liability provisions, and limiting the responsibility of companies to take responsibility for their supply chains (the ‘Tier 1’ restriction).

Competitiveness Roundtable meeting document, 11 July 2025.
Additionally, the documents reveal that the Roundtable is still aiming to drum up a “blocking minority” to overturn the Council’s negotiation mandate during the trilogue negotiations, which started in November 2025. By “tak[ing] advantage of the ‘weak’ Council negotiating mandate” and disagreements between EU Member States on “contentious articles”, the Competitiveness Roundtable companies hope to force the Danish Council presidency to give up on including any form of climate obligations in the CSDDD – despite EU Member States’ agreement on this in the June 2025 Council mandate(opens in new window) .
To implement the divide-and-conquer strategy, the Roundtable assigned specific companies to “establish rapporteurships” with different EU governments. TotalEnergies would target the French, Belgian, and Danish governments, and ExxonMobil would target Germany, Hungary, the Czech Republic, and Romania.



Circumventing “stubborn” European Commission departments
The Roundtable also discussed working on “circumvent[ing]” two “stubborn” European Commission departments involved in the Omnibus political process, DG JUST and DG FISMA, which, in their view, were “unlikely to be willing to see our side of the story”. According to the documents, DG JUST opposed deleting the climate article and restricting the Directive’s scope to only very large enterprises. The Roundtable aimed to diminish the role of these departments by pressuring President Von der Leyen and Commissioners McGrath (DG JUST) and Albuquerque (DG FISMA) by “organising letters from Irish and German business groups” and using an event held by the European Roundtable for Industry to “target” Von der Leyen and McGrath.
Read full report: Somo.nl
Source: Somo
Related posts:

 Victims of human rights violations in Uganda still waiting for redress
Victims of human rights violations in Uganda still waiting for redress
 UN Human Rights Chief urges EU leaders to approve key business and human rights legislation
UN Human Rights Chief urges EU leaders to approve key business and human rights legislation
 Business, UN, Govt & Civil Society urge EU to protect sustainability due diligence framework
Business, UN, Govt & Civil Society urge EU to protect sustainability due diligence framework
 Development financiers fuel human rights abuses – New Report
Development financiers fuel human rights abuses – New Report

COP30 : a further step towards a Just Transition in Africa

‘Food and fossil fuel production causing $5bn of environmental damage an hour’

Four hundred fifty victim families of the Oil Palm project in Buvuma are to receive compensation by this Friday – Witness Radio

Britain, Netherlands withdraw $2.2 billion backing for Total-led Mozambique LNG

Four hundred fifty victim families of the Oil Palm project in Buvuma are to receive compensation by this Friday – Witness Radio

Women’s groups demand equality in land tenure security to boost food production.

Tension as Project-Affected Persons demand to meet Uganda’s President over Oil Palm growing on their grabbed land.

Land commission starts updating govt land countrywide.

Innovative Finance from Canada projects positive impact on local communities.
Over 5000 Indigenous Communities evicted in Kiryandongo District
Petition To Land Inquiry Commission Over Human Rights In Kiryandongo District
Invisible victims of Uganda Land Grabs
Resource Center
- REPARATORY AND CLIMATE JUSTICE MUST BE AT THE CORE OF COP30, SAY GLOBAL LEADERS AND MOVEMENTS
- LAND GRABS AT GUNPOINT REPORT IN KIRYANDONGO DISTRICT
- THOSE OIL LIARS! THEY DESTROYED MY BUSINESS!
- RESEARCH BRIEF -TOURISM POTENTIAL OF GREATER MASAKA -MARCH 2025
- The Mouila Declaration of the Informal Alliance against the Expansion of Industrial Monocultures
- FORCED LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA TRENDS RIGHTS OF DEFENDERS IMPACT AND CALL FOR ACTION
- 12 KEY DEMANDS FROM CSOS TO WORLD LEADERS AT THE OPENING OF COP16 IN SAUDI ARABIA
- PRESENDIANTIAL DIRECTIVE BANNING ALL LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA