NGO WORK
Development banks have no business financing agribusiness
Published
3 years agoon

On the eve of an annual gathering of public development banks in Rome, 280 groups from 70 countries have signed a letter slamming them for bankrolling the expansion of industrial agriculture, environmental destruction and corporate control of the food system. The signatories affirm only fully public and accountable funding mechanisms based on people’s actual needs can achieve real solutions to the global food crisis.
Over 450 Public Development Banks (PDBs) from around the world are gathering in Rome from 19 to 20 October 2021 for a second international summit, dubbed Finance in Common. During the first summit in Paris in 2020, over 80 civil-society organizations published a joint statement demanding that the PDBs stop funding agribusiness companies and projects that take land and natural resources away from local communities. This year, however, PDBs have made agriculture and agribusiness the priority of their second summit. This is of serious concern for the undersigned groups as PDBs have a long track-record of making investments in agriculture that benefit private interests and agribusiness corporations at the expense of farmers, herders, fishers, food workers and Indigenous Peoples, undermining their food sovereignty, ecosystems and human rights.
Our concerns
PDBs are public institutions established by national governments or multilateral agencies to finance government programs and private companies whose activities are said to contribute to the improvement of people’s lives in the places where they operate, particularly in the Global South. Many multilateral development banks, a significant sub-group of PDBs, also provide technical and policy advice to governments to change their laws and policies to attract foreign investment.
As public institutions, PDBs are bound to respect, protect and fulfil human rights and are supposed to be accountable to the public for their actions. Today, development banks collectively spend over US$2 trillion a year financing public and private companies to build roads, power plants, factory farms, agribusiness plantations and more in the name of “development” – an estimated US$1.4 trillion goes into the sole agriculture and food sector. Their financing of private companies, whether through debt or the purchase of shares, is supposed to be done for a profit, but much of their spending is backed and financed by the public – by people’s labor and taxes.
The number of PDBs and the funding they receive is growing.The reach of these banks is also growing as they are increasingly channeling public funds through private equity, “green finance” and other financial schemes to deliver the intended solutions instead of more traditional support to government programs or non-profit projects. Money from a development bank provides a sort of guarantee for companies expanding into so-called high-risk countries or industries. These guarantees enable companies to raise more funds from private lenders or other development banks, often at favorable rates. Development banks thus play a critical role in enabling multinational corporations to expand further into markets and territories around the world – from gold mines in Armenia, to controversial hydroelectric dams in Colombia, to disastrous natural gas projects in Mozambique – in ways they could not do otherwise.
Additionally, many multilateral development banks work to explicitly shape national level law and policy through their technical advice to governments and ranking systems such as the Enabling the Business of Agriculture of the World Bank. The policies they support in key sectors — including health, water, education, energy, food security and agriculture — tend to advance the role of big corporations and elites. And when affected local communities, including Indigenous Peoples and small farmers protest, they are often not heard or face reprisals. For example, in India, the World Bank advised the government to deregulate the agricultural marketing system, and when the government implemented this advice without consulting with farmers and their organisations, it led to massive protests.
Public Development Banks claim that they only invest in “sustainable” and “responsible” companies and that their involvement improves corporate behavior. But these banks have a heavy legacy of investing in companies involved in land grabbing, corruption, violence, environmental destruction and other severe human rights violations, from which they have escaped any meaningful accountability. The increasing reliance of development banks on offshore private equity funds and complex investment webs, including so called financial intermediaries, to channel their investments makes accountability even more evasive and enables a small and powerful financial elite to capture the benefits.
It is alarming that Public Development Banks are now taking on more of a coordinated and central role when it comes to food and agriculture. They are a part of the global financial architecture that is driving dispossession and ecological destruction, much of which is caused by agribusiness. Over the years, their investment in agriculture has almost exclusively gone to companies engaged in monoculture plantations, contract growing schemes, animal factory farms, sales of hybrid and genetically modified seeds and pesticides, and digital agriculture platforms dominated by Big Tech. They have shown zero interest in or capacity to invest in the farm, fisher and forest communities that currently produce the majority of the world’s food. Instead, they are bankrolling land grabbers and corporate agribusinesses and destroying local food systems.
Painful examples
Important examples of the pattern we see Public Development Banks engaging in:
-
The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development and the European Investment Bank have provided generous financing to the agribusiness companies of some of Ukraine’s richest oligarchs, who control hundreds of thousands of hectares of land.
-
SOCFIN of Luxembourg and SIAT of Belgium, the two largest oil palm and rubber plantation owners in Africa, have received numerous financial loans from development banks, despite their subsidiaries being mired in land grabbing, corruption scandals and human rights violations.
-
Multiple development banks (including Swedfund, BIO, FMO and the DEG) financed the failed sugarcane plantation of Addax Bioenergy in Sierra Leone that has left a trail of devastation for local communities after the company’s exit.
-
The UK’s CDC Group and other European development banks (including BIO, DEG, FMO and Proparco) poured over $150 million into the now bankrupt Feronia Inc’s oil palm plantations in the DR Congo, despite long-standing conflicts with local communities over land and working conditions, allegations of corruption and serious human rights violations against villagers.
-
The United Nations’ Common Fund for Commodities invested in Agilis Partners, a US-owned company, which is involved in the violent eviction of thousands of villagers in Uganda for a large-scale grain farm.
-
Norfund and Finnfund own Green Resources, a Norwegian forestry company planting pine trees in Uganda on land taken from thousands of local farmers, with devastating effects on their livelihoods.
-
The Japan Bank for International Cooperation and the African Development Bank invested in a railway and port infrastructure project to enable Mitsui of Japan and Vale of Brazil to export coal from their mining operations in northern Mozambique. The project, connected to the controversial ProSavana agribusiness project, has led to land grabbing, forced relocations, fatal accidents and the detention and torture of project opponents.
-
The China Development Bank financed the ecologically and socially disastrous Gibe III dam in Ethiopia. Designed for electricity generation and to irrigate large-scale sugar, cotton and palm oil plantations such as the gargantuan Kuraz Sugar Development Project, it has cut off the river flow that the indigenous people of the Lower Omo Valley relied on for flood retreat agriculture.
-
In Nicaragua, FMO and Finnfund financed MLR Forestal, a company managing cocoa and teak plantations, which is controlled by gold mining interests responsible for displacement of Afro-descendant and Indigenous communities and environmental degradation.
-
The International Finance Corporation and the Inter-American Development Bank Invest have recently approved loans to Pronaca, Ecuador’s 4th largest corporation, to expand intensive pig and poultry production despite opposition from international and Ecuadorian groups, including local indigenous communities whose water and lands have been polluted by the company’s expansive operations.
-
The Inter-American Development Bank Invest is considering a new $43 million loan for Marfrig Global Foods, the world’s 2nd largest beef company, under the guise of promoting “sustainable beef.” Numerous reports have found Marfrig’s supply chain directly linked to illegal deforestation in the Amazon and Cerrado and human rights violations. The company has also faced corruption charges. A global campaign is now calling for PDBs to immediately divest from all industrial livestock operations.
We need better mechanisms to build food sovereignty
Governments and multilateral agencies are finally beginning to acknowledge that today’s global food system has failed to address hunger and is a key driver of multiple crises, from pandemics to biodiversity collapse to the climate emergency. But they are doing nothing to challenge the corporations who dominate the industrial food system and its model of production, trade and consumption. To the contrary, they are pushing for more corporate investment, more public private partnerships and more handouts to agribusiness.
This year’s summit of the development banks was deliberately chosen to follow on the heels of the UN Food Systems Summit. It was advertised as a global forum to find solutions to problems afflicting the global food system but was hijacked by corporate interests and became little more than a space for corporate greenwashing and showcasing industrial agriculture. The event was protested and boycotted by social movements and civil society, including through the Global People´s Summit and the Autonomous People´s response to the UN Food Systems Summit, as well as by academics from across the world.
The Finance in Common summit, with its focus on agriculture and agribusiness, will follow the same script. Financiers overseeing our public funds and mandates will gather with elites and corporate representatives to strategize on how to keep the money flowing into a model of food and agriculture that is leading to climate breakdown, increasing poverty and exacerbating all forms of malnutrition. Few if any representatives from the communities affected by the investments of the development banks, people who are on the frontlines trying to produce food for their communities, will be invited in or listened to. PDBs are not interested. They seek to fund agribusinesses, which produce commodities for trade and financial schemes for profits rather than food for nutrition.
Last year, a large coalition of civil-society organizations made a huge effort just to get the development banks to agree to commit to a human rights approach and community-led development. The result was only some limited language in the final declaration, which has not been translated into action.
We do not want any more of our public money, public mandates and public resources to be wasted on agribusiness companies that take land, natural resources and livelihoods away from local communities. Therefore:
We call for an immediate end to the financing of corporate agribusiness operations and speculative investments by public development banks.
We call for the creation of fully public and accountable funding mechanisms that support peoples’ efforts to build food sovereignty, realize the human right to food, protect and restore ecosystems, and address the climate emergency.
We call for the implementation of strong and effective mechanisms that provide communities with access to justice in case of adverse human rights impacts or social and environmental damages caused by PDB investments.
Fundación Plurales – Argentina
Fundación Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (FARN) – Argentina
Foro Ambiental Santiagueño – Argentina
Armenian Women For Health &Healthy Environment NGO /AWHHE/ – Armenia
Australian Food Sovereignty Alliance – Australia
SunGem – Australia
Welthaus Diözese Graz-Seckau – Austria
Turkmen Initiative for Human Rights – Austria
FIAN Austria – Austria
Oil Workers’ Rights Protection Organization Public Union – Azerbaijan
Initiative for Right View – Bangladesh
Right to Food South Asia – Bangladesh
IRV – Bangladesh
Bangladesh Agricultural Farm Labour Federation [BAFLF] – Bangladesh
NGO “Ecohome” – Belarus
Eclosio – Belgium
AEFJN – Belgium
FIAN Belgium – Belgium
Entraide et Fraternité – Belgium
Africa Europe Faith & Justice Network (AEFJN) – Belgium
Coalition for Fair Fisheries Arrangements – Belgium
Eurodad – Belgium
Friends of the Earth Europe – Belgium
Alianza Animalista La Paz – Bolivia
Instituto de Estudos Socioeconômicos (Inesc) – Brazil
Centro Ecologico – Brazil
FAOR Fórum da Amazônia Oriental – Brazil
Articulação Agro é Fogo – Brazil
Campanha Nacional de Combate e Prevenção ao Trabalho Escravo – Comissão Pastoral da Terra/CPT – Brazil
Clínica de Direitos Humanos da Amazônia -PPGD/UFPA – Brazil
Universidade Federal Fluminense IPsi – Brazil
Associação Brasileira de Reforma Agrária – Brazil
Rede Jubileu Sul Brasil – Brazil
Alternativas para pequena agricultura no Tocantins APATO – Brazil
CAPINA Cooperação e Apoio a Projetos de Inspiração Alternativa – Brazil
Marcha Mundial por Justiça Climática / Marcha Mundial do Clima – Brazil
MNCCD – Movimento Nacional Contra Corrupção e pela Democracia – Brazil
Marcha Mundial por Justiça Climática/Marcha Mundial do Clima – Brazil
Support Group for Indigenous Youth – Brazil
Comissão Pastoral da Terra -CPT – Brazil
Equitable Cambodia – Cambodia
Coalition of Cambodian Farmers Community – Cambodia
Struggle to Economize Future Environment (SEFE) – Cameroon
Synaparcam – Cameroon
APDDH -ASSISTANCE – Cameroon
Inter Pares – Canada
Vigilance OGM – Canada
National Farmers Union – Canada
SeedChange – Canada
Place de la Dignité – Canada
Corporación para la Protección y Desarrollo de Territorios Rurales- PRODETER – Colombia
Grupo Semillas – Colombia
Groupe de Recherche et de Plaidoyer sur les Industries Extractives (GRPIE) – Côte d’Ivoire
Réseau des Femmes Braves (REFEB) – Côte d’Ivoire
CLDA – Côte d’Ivoire
Counter Balance – Czech Republic
AfrosRD – Dominican Republic
Conseil Régional des Organisations Non gouvernementales de Développement – DR Congo
Construisons Ensemble le MONDE – DR Congo
Synergie Agir Contre la Faim et le Réchauffement Climatique , SACFRC. – DR Congo
COPACO-PRP – DR Congo
AICED – DR Congo
Réseaux d’informations et d’appui aux ONG en République Démocratique du Congo ( RIAO – RDC) – DR Congo
Latinoamérica Sustentable – Ecuador
Housing and Land Rights Network – Habitat International Coalition – Egypt
Pacific Islands Association of Non-Governmental Organisations (PIANGO) – Fiji
Internationale Situationniste – France
Pouvoir d’Agir – France
Europe solidaire sans frontières (ESSF) – France
Amis de la Terre France – France
Médias Sociaux pour un Autre Monde – France
ReAct Transnational – France
CCFD-Terre Solidaire – France
CADTM France – France
Coordination SUD – France
Движение Зеленных Грузии – Georgia
NGO “GAMARJOBA” – Georgia
StrongGogo – Georgia
FIAN Deutschland – Germany
Rettet den Regenwald – Germany
Angela Jost Translations – Germany
urgewald e.V. – Germany
Abibinsroma Foundation – Ghana
Alliance for Empowering Rural Communities – Ghana
Organización de Mujeres Tierra Viva – Guatemala
Campaña Guatemala sin hambre – Guatemala
PAPDA – Haïti
Centre de Recherche et d’Action pour le Developpement (CRAD) – Haiti
Ambiente, Desarrollo y Capacitación (ADC ) – Honduras
Rashtriya Raithu Seva Samithi – India
All India Union of Forest Working People AIUFWP – India
Centre for Financial Accountability – India
People First – India
Environics Trust – India
ToxicsWatch Alliance – India
Food Sovereignty Alliance – India
Indonesia for Global Justice (IGJ) – Indonesia
kruha – Indonesia
Wahana Lingkungan Hidup Indonesia (WALHI) – Indonesia
JPIC Kalimantan – Indonesia
تانيا جمعه /منظمه شؤون المراه والطفل – Iraq
ICW-CIF – Italy
PEAH – Policies for Equitable Access to Health – Italy
Focsiv Italian federation christian NGOs – Italy
Schola Campesina APS – Italy
Casa Congo- Italy
ReCommon – Italy
Japan International Volunteer Center (JVC) – Japan
Team OKADA – Japan
taneomamorukai – Japan
VoiceForAnimalsJapan – Japan
Keisen University – Japan
000 PAF NPO – Japan
Missionary Society of Saint Columban, Japan – Japan
Migrants around 60 – Japan
Mura-Machi Net (Network between Villages and Towns) – Japan
Japan Family Farmers Movement (Nouminren) – Japan
Pacific Asia Resorce Center(PARC) – Japan
A Quater Acre Farm-Jinendo – Japan
Friends of the Earth Japan – Japan
Alternative People’s Linkage in Asia (APLA) – Japan
Mekong Watch – Japan
Family Farming Platform Japan – Japan
Africa Japan Forum – Japan
ATTAC Kansai – Japan
ATTAC Japan – Japan
Association of Western Japan Agroecology (AWJA) – Japan
Mennovillage Naganuma – Japan
Phenix Center – Jordan
Mazingira Institute – Kenya
Dan Owala – Kenya
Jamaa Resource Initiatives – Kenya
Kenya Debt Abolition Network – Kenya
Haki Nawiri Afrika – Kenya
Euphrates Institute-Liberia – Liberia
Green Advocates International (Liberia) – Liberia
Sustainable Development Institute (SDI) – Liberia
Alliance for Rural Democracy (ARD) – Liberia
Frères des Hommes – Luxembourg
SOS FAIM – Luxembourg
Collectif pour la défense des terres malgaches – TANY – Madagascar
Third World Network – Malaysia
Appui Solidaire pour le Développement de l’Aide au Développement – Mali
Réseau CADTM Afrique – Mali
Lalo – Mexico
Tosepanpajt A.C – Mexico
Maya sin Fronteras – Mexico
Centro de Educación en Apoyo a la Producción y al Medio Ambiente, A.C. – Mexico
Mujeres Libres COLEM AC – México
Grupo de Mujeres de San Cristóbal Las Casas AC – México
Colectivo Educación para la Paaz y los Derechos Humanos A.C. (CEPAZDH) – México
Red Nacional de Promotoras Rurales – México
Dinamismo Juvenil A.C – México
Cultura Ambiental en Expansión AC – México
Observatorio Universitario de Seguridad Alimentaria y Nutricional del Estado de Guanajuato – México
Centro Interdisciplinario de Investigación y Desarrollo Alternativo U Yich Lu’um AC – México
The Hunger Project México – México
Americas Program/Americas.Org – México
Association Talassemtane pour l’Environnement et Développement (ATED) – Morocco
Espace de Solidarité et de Coopération de l’Oriental – Morocco
LVC Maroc – Morocco
EJNA – Morocco
NAFSN – Morocco
Fédération nationale du secteur agricole – Morocco
Association jeunes pour jeunes – Morocco
Plataforma Mocambicana da Mulher e Rapariga Cooperativistas/AMPCM – MOZAMBIQUE – Mozambique
Justica Ambiental – JA! – Mozambique
Community Empowerment and Social Justice Network (CEMSOJ) – Nepal
WILPF NL – Netherlands
Milieudefensie – Netherlands
Platform Aarde Boer Consument – Netherlands
Both ENDS – Netherlands
Foundation for the Conservation of the Earth,FOCONE – Nigeria
Lekeh Development Foundation (LEDEF) – Nigeria
Nigeria Coal Network – Nigeria
Spire – Norway
Pakistan Fisherfolk Forum – Pakistan
Gaza Urban Agriculture Platform (GUPAP) – Palestine
Union of Agricultural Work Committees – Palestine
WomanHealth Philippines – Philippines
Agroecology X – Philippines
SEARICE – Philippines
Alter Trade Foundation for Food Sovereignty, Inc – Philippines
Association pour la défense des droits à l’eau et à l’assainissement – Sénégal
Biotech Services Sénégal – Sénégal
Association Sénégalaise des Amis de la Nature – Sénégal
Alliance Sénégalaise Contre la Faim et la Malnutrition – Sénégal
Association Sénégalaise des Amis de la Nature – Sénégal
Alliance Sénégalaise Contre la Faim et la Malnutrition – Sénégal
Green Scenery – Sierra Leone
Land for Life – Sierra Leone
JendaGbeni Centre for Social Change Communications – Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone Land Alliance – Sierra Leone
African Centre for Biodiversity – South Africa
African Children Empowerment – South Africa
Cooperative and Policy Alternative Centre – South Africa
Fish Hoek Valley Ratepayers and Residents Association – South Africa
Consciously Organic – South Africa
Wana Johnson Learning Centre – South Africa
Aha Properties – South Africa
Sacred Earth & Storm School – South Africa
Earth Magic – South Africa
Oasis – South Africa
Envirosense – South Africa
Greenstuff – South Africa
WoMin African Alliance – South Africa
Seonae Eco Centre – South Africa
Eco Hope – South Africa
Kos en Fynbos – South Africa
Ghostwriter Grant – South Africa
Mariann Coordinating Committee – South Africa
Khanyisa Education and Development Trust – South Africa
LAMOSA – South Africa
Ferndale Food Forest and Worm Farm – South Africa
Mxumbu Youth Agricultural Coop – South Africa
PHA Food & Farming Campaign – South Africa
SOLdePAZ.Pachakuti – Spain
Amigos de la Tierra – Spain
Sindicato Andaluz de Trabajadores/AS – Spain
Salva la Selva – Spain
Loco Matrifoco – Spain
National Fisheries Solidarity(NAFSO) – Sri Lanka
Movement for Land and Agricultural Reform (MONLAR) – Sri Lanka
Agr. Graduates Cooperatives Union – Sudan
FIAN Sweden – Sweden
FIAN Suisse – Switzerland
Bread for all – Switzerland
Foundation for Environmental Management and Campaign Against Poverty – Tanzania
World Animal Protection – Thailand
Asia Indigenous Peoples Pact – Thailand
PERMATIL – Timor-Leste
Afrique Eco 2100 – Togo
AJECC – Togo
ATGF – Tunisia
Forum Tunisien des Droits Economiques et Sociaux – Tunisia
Agora Association – Turkey
Uganda Land Rights Defenders – Uganda
Hopes for youth development Association – Uganda
Uganda Consortium on Corporate Accountability – Uganda
Centre for Citizens Conserving Environment &Management (CECIC) – Uganda
Buliisa Initiative for Rural Development Organisation (BIRUDO)) – Uganda
Twerwaneho Listeners Club – Uganda
Alliance for Food Soverignity in Africa – Uganda
Global Justice Now – UK
Friends of the Earth International – UK
Compassion in World Farming – UK
Environmental Justice Foundation – UK
Fresh Eyes – UK
War on Want – UK
Friends of the Earth US – US
A Growing Culture – US
Center for Political Innovation – US
GMO/Toxin Free USA – US
Friends of the Earth US – US
Thousand Currents – US
Local Futures – US
National Family Farm Coalition – US
Community Alliance for Global Justice/AGRA Watch – US
Bank Information Center – US
Seeding Sovereignty – US
Yemeni Observatory for Human Rights – Yemen
Zambia Alliance for Agroecology and Biodiversity – Zambia
Zambian Governance Foundation for Civil Society – Zambia
Urban Farming Zimbabwe – Zimbabwe
Centre for Alternative Development – Zimbabwe
FACHIG Trust – Zimbabwe
Red Latinoamericana por Justicia Económica y Social – Latindadd – América Latina
European Coordination Via Campesina – Europe
Arab Watch Coalition – Middle East and North Africa
FIAN International – International
International Alliance of Inhabitants – International
Society for International Development – International
ActionAid International – International
International Accountability Project – International
Habitat International Coalition – General Secretariat – International
CIDSE – International
ESCR-Net – International
World Rainforest Movement – International
Transnational Institute – International
GRAIN – International
Original Source: grian.org
Related posts:

 DR Congo oil palm company bankrolled by development banks unleashes wave of violence against villagers after peaceful protests
DR Congo oil palm company bankrolled by development banks unleashes wave of violence against villagers after peaceful protests
 They should not be called public development banks
They should not be called public development banks
 Open letter to African Development Bank and Nordic Development Fund: Address reprisals against Paten Clan
Open letter to African Development Bank and Nordic Development Fund: Address reprisals against Paten Clan
 CSOs urge banks and other IFIs not to finance E.Africa oil pipeline project…
CSOs urge banks and other IFIs not to finance E.Africa oil pipeline project…
You may like
NGO WORK
Communities Under Siege: New Report Reveals World Bank Failures in Safeguard Compliance and Human Rights Oversight in Tanzania
Published
4 days agoon
July 2, 2025
Villagers living in the shadow of Ruaha National Park (RUNAPA) are under siege from a rogue –World Bank-funded paramilitary ranger force. Accountability Now – Tanzanian Communities Shattered by World Bank-funded Tourism Project, a new Oakland Institute report, shines a spotlight on the human toll of the Bank’s ongoing failure to correct the dire crisis it has created.
As previously exposed by the Institute, the Resilient Natural Resource Management for Tourism and Growth (REGROW) project enabled the violent expansion of RUNAPA in Tanzania, resulting in grave human rights abuses, devastation of livelihoods, and planned widespread evictions. These damning findings were confirmed by the Bank’s own Inspection Panel in its September 2024 investigation report. Accountability Now details the severely delayed and deficient action taken by the Bank in response to the blatant violation of its safeguards, which has allowed the cycle of violence and suffering to persist.
“This report is not only a scathing indictment of the Bank’s irresponsible financing and mishandling of the case, but also of the institution’s absence of accountability given its failure to correct its wrongs at every step. The Bank’s management admitted its responsibility for enabling this crisis – and yet, it has turned its back on villagers as human rights abuses and crippling livelihood restrictions continue unabated,” said Anuradha Mittal, Executive Director of the Oakland Institute.
The report documents how the Bank’s funding allowed the government to double the size of RUNAPA by over one million hectares through Government Notice 754 in October 2023 without the consent of those living on this land. This placed over 84,000 people from at least 28 villages at the risk of imminent eviction and resulted in over US$70 million of economic losses for farmers and pastoralists – suffering compounded by killings and violence at the hands of rangers funded by the Bank.
Between 2017-2024, the Tanzania National Parks Authority (TANAPA) rangers were equipped and emboldened by the World Bank, enabling the agency to carry out a brutal campaign against local residents. Communities have endured extrajudicial killings, enforced disappearances, torture, and sustained economic hardship – made possible by the Bank’s lack of oversight.
The World Bank-financed REGROW project was officially cancelled on November 6, 2024. On April 1, 2025, the Bank’s Board of Directors approved an Action Plan (MAP) to address the findings of the Inspection Panel’s investigation into the project. Instead of remedying the harms identified by the Panel and responding to the demands of the impacted communities, the MAP chose to narrowly focus on alternative livelihoods and accepted the government’s dubious promise that villages consumed by the park would not be resettled and residents could continue grazing, fishing, and farming.
Barely a month later, on April 26, 2025, 27-year-old fisherman Hamprey Mhaki disappeared after being shot by rangers in the Ihefu Basin. On May 7, rangers opened fire on herders in Iyala village, killing 20-year-old Kulwa Igembe, and seizing over 1,000 cattle in another devastating economic blow to herders.
The World Bank made a commitment to work with the Tanzanian government to “support communities in and around RUNAPA in an effort to balance conservation and development, including reducing incidences of conflict and violence in the Park and providing alternative livelihoods.” The latest killings, cattle seizures, and farming restrictions, expose the hollowness of the Bank’s commitment. Several villages have been instructed to relocate – directly contradicting the government’s prior assurances. Though it claims to be supervising the implementation of the MAP, the Bank’s management has entrusted the very government responsible for the violence to investigate it.
“If the core promise to allow daily life to resume for the villagers is not honored, their very survival is at risk. Impacted communities expected the Bank to supervise the MAP. They are appalled by the Bank’s response that the perpetrators of violence will provide them with justice. Given the Tanzanian government’s horrific record of human rights abuses, this is akin to letting the fox guard the henhouse,” Mittal concluded.
The time to deliver redress is long overdue. One impacted villager said, “We are crying for our lands…let us be free. We don’t want to leave and the World Bank should stop the government from taking our lands. Our suffering is directly because of the Bank. Let us be free.”
Source: oaklandinstitute.org
Related posts:

 The World Bank Must Be Held Accountable for Harm Inflicted on Tanzanian Communities by Tourism Project
The World Bank Must Be Held Accountable for Harm Inflicted on Tanzanian Communities by Tourism Project
 World Bank Project Cancelled in a Landmark Victory for Tanzanian Villagers
World Bank Project Cancelled in a Landmark Victory for Tanzanian Villagers
NGO WORK
World Bank-Funded TANAPA Rangers Murder Two Villagers in Ruaha National Park
Published
1 month agoon
May 22, 2025In the last two weeks, TANAPA rangers have killed two villagers within the disputed boundaries of the Ruaha National Park in Tanzania. These murders shatter promises made just a month ago by the Tanzanian government and the World Bank to end ranger violence and allow livelihood activities to continue within the park.
On April 26, 2025, six fishermen were confronted by rangers outside of Mwanjurwa, near Ikanutwa and Nyeregete villages in the Ihefu Basin. As they tried to escape, rangers shot 27-year-old Hamprey Mhaki in the back. It is believed that Mr. Mhaki succumbed to his gunshot wound, as the search party only found a large amount of blood where he was last seen. He remains missing – while his pregnant wife and grieving family search for answers and demand justice.
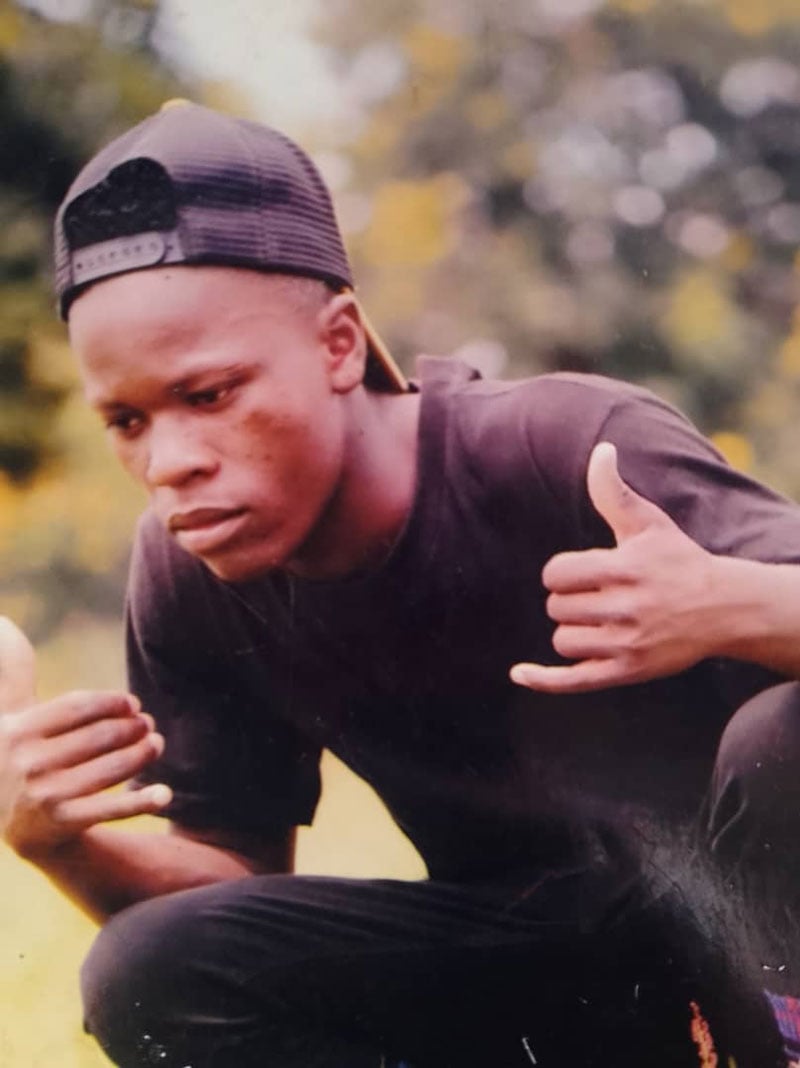

In another incident, on May 7, 2025, a group of herders and their cattle in the Udunguzi sub-village of Iyala village were attacked by a TANAPA helicopter that opened fire with live ammunition. Eyewitnesses report that Kulwa Igembe, a 20-year-old Sukuma herder, was shot in the chest by one of the rangers on the ground. He died at the scene. Mr. Igembe is survived by his widow and young daughter.
According to Tanzanian media, four TANAPA rangers are being held by the Mbeya Regional Police Force for their involvement in Mr. Igembe’s killing. His body remains at the Mochwari Mission hospital, as his family has refused to proceed with burial until authorities conduct a full and transparent investigation. Furthermore, local sources state that over 1,000 cattle belonging to several herders were seized and impounded at the Madundasi ranger post following the attack. About 500 cattle have been reclaimed after herders paid TSh100,000 per head [US$37] in fines – delivering a substantial financial blow.
The Bank’s REGROW project, now cancelled, built the enforcement capacity of the rangers who committed these murders. In the 2024 investigation by its Inspection Panel, the Bank conceded that by “enhancing TANAPA’s capacity to enforce the law,” the project “increased the possibility of violent confrontations” between rangers and villagers. The Panel found the Bank to have failed to adequately supervise TANAPA and ignored rangers use of “excessive force,” in violation of international standards. Already over the course of the REGROW project, at least 11 individuals were killed by police or rangers, five disappeared, and dozens suffered physical and psychological harm, including torture and sexual violence.
“The murders of Mr. Igembe and Mr. Mhaki make it painfully clear that the Tanzanian government has no intent to end atrocities against local communities for tourist revenue. These brutal actions not only constitute abject crimes but are also a blatant violation of the commitments the government made to the World Bank,” said Anuradha Mittal, Executive Director of the Oakland Institute. “The Bank created a monster in TANAPA and must be held accountable along with the rogue ranger force,” Mittal added.
In its April 2, 2025 press release, the World Bank stated that “The Government of Tanzania has committed to implementing the MAP [Management Action Plan], and the World Bank will support and supervise its implementation.” The Action Plan is based on the premise that the government will honor its now broken promise that there will be no resettlement and villagers can continue their livelihood activities, like grazing and fishing. Iyala village, where Mr. Igembe was killed, is one of the five villages consumed by the October 2023 expansion of Ruaha National Park.
The Bank also committed to addressing violence by TANAPA rangers through a grievance mechanism and trainings on “relevant good international practice in protected area management.” Unfortunately, the Oakland Institute’s warning to the Bank’s officials, that given the extent of TANAPA’s human rights abuses, these measures would fail in preventing future harms, has come true.
“The violence hasn’t stopped. Villagers are being killed, their cattle stolen, their lives destroyed. Local communities are desperate for the world to listen. The Oakland Institute joins them in demanding that the World Bank take responsibility and act now. Every day of silence costs lives. The victims and their families deserve justice, truth, and the chance to live without fear,” concluded Mittal.
Source:The Oakland Institute
Related posts:

 The World Bank Must Be Held Accountable for Harm Inflicted on Tanzanian Communities by Tourism Project
The World Bank Must Be Held Accountable for Harm Inflicted on Tanzanian Communities by Tourism Project
 Campaign Victory: World Bank Suspends Funding for REGROW, a Conservation Project Responsible for Evictions & Human Rights Abuses in Tanzania
Campaign Victory: World Bank Suspends Funding for REGROW, a Conservation Project Responsible for Evictions & Human Rights Abuses in Tanzania
 URGENT ALERT: Tanzanian Government on a Rampage Against Indigenous People
URGENT ALERT: Tanzanian Government on a Rampage Against Indigenous People
NGO WORK
Defending rights and realising just economies: Human rights defenders and business (2015-2024)
Published
1 month agoon
May 22, 2025
Over the past decade, human rights defenders (HRDs) have courageously organised to stop corporate abuse and prevent business activities from causing harm – exposing human rights and environmental violations, demanding accountability, and advocating for rights-respecting economic practices. From Indigenous Peoples protecting forests from mining activities to journalists exposing health and environmental harms related to logging to workers advocating for better conditions in the garment sector, HRDs are at the forefront of creating a more equitable, sustainable and abundant world where rights are protected, people and nature thrive, and just economies can flourish.
Every one of us has the right to take action to protect our rights and environments and contribute to creating a more just and equitable world, and yet those who do often face great risk. Businesses have the responsibility to respect human rights, including the right of all people to defend human rights. When companies fail to listen to HRDs, they lose important allies – people and groups fighting for transparency and accountability, and against corruption, which are all essential elements of an open and stable business operating environment. With authoritarianism on the rise, the imperative of realising a just global energy transition, and deepening inequality around the world, the role of business has rarely been so important – especially as HRDs pressing for rights-respecting corporate practice face increasing challenges.
From January 2015 to December 2024, the Business & Human Rights Resource Centre (the Resource Centre) recorded more than 6,400 attacks across 147 countries against people who voiced concerns about business-related risks or harms. This is close to two attacks on average every day over the past ten years. In 2024 alone, we tracked 660 attacks.

Civic space – the environment that enables all of us to organise, participate, and communicate freely in our societies – has also continued to deteriorate over the past decade. According to Civicus, only 3.6% of the world’s population currently lives in countries with open civic space, where citizens and civil society organisations are able to organise, participate and communicate without restrictions. In every region, governments have abused their power to limit the civic freedoms of people advocating for responsible business practice by detaining journalists, passing restrictive legislation (such as foreign funding bills and critical infrastructure laws), criminalising and prosecuting HRDs, and using violent force at protests, among other actions.
This is harmful for business. Civic space restrictions create an ‘information black box,’ leaving companies and investors with gaps in knowledge about potential or actual negative human rights impacts, which can lead to legal, financial, reputational and other risks. Democracy and full enjoyment of civic freedoms are central to addressing the key challenges humanity faces and to sustainable economic growth – some economists have found that democratisation causes an increase in GDP per capita of between 20% and 25%. In addition, under the UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights (UNGPs) and subsequent guidance, business actors also have a responsibility to respect human rights, which includes engaging in robust human rights due diligence that identifies and mitigates risks to civic freedoms and HRDs.
In our current context of continued erosion of democracy, deregulation, backlash against environmental, social and governance (ESG) concerns, increased conflict, and the weaponsation of both law and technology against human rights defence, HRDs remind us to transcend polarisation and persist in realising a more just and abundant future for us all. Key wins over the past decade include a legally binding instrument to protect environmental defenders, regulations to curb strategic lawsuits against public participation, and important victories advancing corporate accountability following advocacy and judicial efforts. Representatives from Indigenous communities have shared a powerful vision for a rights-respecting energy transition – an essential framework for the future. They are innovating, at times together with progressive businesses, to bring about transformative new business models designed to deliver shared prosperity in alignment with Indigenous Peoples’ self-determined priorities.

Between January 2015 and December 2024, the Resource Centre documented more than 6,400 cases of attacks globally against HRDs challenging corporate harm. These attacks were against Indigenous Peoples, youth leaders, elders, women defenders, journalists, environmental defenders, communities, non-profit organisations and others, negatively affecting tens of thousands of people.
This is just the tip of the iceberg. Our research is based on publicly available information, and given the severity of civic space restrictions in some countries and security concerns, many attacks go unreported. In addition, governments are largely failing in their duty to monitor attacks. In countries and regions where few attacks are documented, this does not mean that violence against defenders is nonexistent, but rather that the information is not accessible. Learn more about our research methodology.
Restrictions on civic space helped to facilitate these attacks. Other drivers included weak rule of law and unaccountable governance, economic models focused on profit maximisation through unsustainable resource extraction, racism and discrimination, and lack of consultation with potentially affected stakeholders.
“I routinely hear from Indigenous defenders working in isolated, remote or rural areas that businesses and governments do not consult with them properly – and that their right to give or withhold their free, prior and informed consent for activities negatively affecting their lives or their territories is either manipulated or ignored. Some attacks are committed by agents acting for businesses, others by government authorities and businesses acting together.”
– Mary Lawlor, UN Special Rapporteur on Human Rights Defenders

Latin America and the Caribbean and Asia and the Pacific have consistently been the most dangerous regions for HRDs raising concerns about corporate harm, accounting for close to three in four (71%) attacks in the past decade. Africa follows with 583 instances of attacks – close to a third of these occurred in Uganda.
In Latin America, the majority of attacks are concentrated in six countries that account for 35% of all attacks globally – Brazil (473), Mexico (455), Honduras (418), Colombia (331), Peru (299) and Guatemala (256). Despite comprising only 0.1% of the world’s population, 6.5% of attacks took place in Honduras. In Asia, the highest number of attacks occurred in the Philippines (411), India (385), Cambodia (279) and Indonesia (216).
Another trend is an increase in attacks in the United Kingdom, where 91% of attacks have been judicial harassment (arrests, criminal charges and SLAPPs). Attacks in the UK notably increased from seven in 2022 to 21 in 2023 – the same year the UK Government’s Public Order Act, which significantly increased the police’s power to respond to protests, came into force, undermining freedom of expression, peaceful assembly and association. Attacks further increased in 2024 to 34. Almost all of these attacks were against people raising concerns about the fossil fuel sector.

Attacks target individuals, organisations and communities, causing physical harm, draining resources and obstructing human rights work. They can also have a chilling effect on civic space and weaken the social fabric vital for resista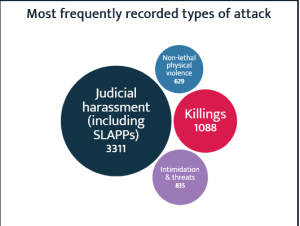 nce, community cohesion, and an inclusive and peaceful society. In addition to harming physical security, attacks can also negatively affect HRDs’ mental, emotional and economic well-being.
nce, community cohesion, and an inclusive and peaceful society. In addition to harming physical security, attacks can also negatively affect HRDs’ mental, emotional and economic well-being.
Since 2015, the Resource Centre has tracked 5,323 non-lethal attacks on HRDs challenging corporate harm.Through our research and collective work with the ALLIED Coalition, we have also identified numerous cases of escalations and cyclical attacks against HRDs where threats and judicial harassment precede physical violence.
Escalation of attacks: Tumandok Peoples’ opposition to dam project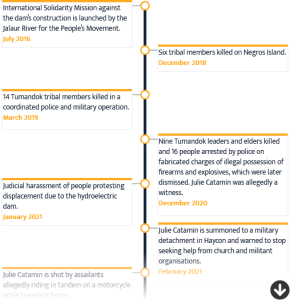
Co-authored with ALLIED and ANGOC
The Tumandok People are an Indigenous group whose ancestral lands in the Philippines have been targeted for numerous private and public development projects, driving ongoing conflict for the community. Community members have actively opposed the Jalaur River Multipurpose Project (JRMP) II infrastructure project, which includes the construction of a dam that would displace Indigenous villages and proceed without their FPIC. Daewoo Engineering & Construction Co. Ltd was awarded the construction contract and the project is supported by Export-Import Bank of Korea.
Numerous attacks have been carried out against community members who voiced opposition to this project. This cyclical violence against the Tumandok is reflected in data from the Asian NGO Coalition for Agrarian Reform and Rural Development (ANGOC), ALLIED and other sources.
We invited Export-Import Bank of Korea and Daewoo E&C to respond. Export-Import Bank’s full response to the killing of HRDs in December 2020 is available here. Daewoo E&C did not respond.
Killings and disappearances
Over the past decade, we documented close to 1,100 killings of HRDs who bravely spoke out against corporate harm. In 2024 alone, we recorded the murders of 52 people.
We commemorate the lives, courage and vital work of these HRDs and their communities. While governments have a duty to investigate these murders, the majority of attacks – both lethal and non-lethal – go uninvestigated and unpunished, fostering a culture of impunity that only emboldens further violence.
Indigenous defenders are particularly at risk. Close to a third (31%) of those killed were Indigenous defenders. Most of the killings of Indigenous defenders occurred in Latin America, as well as the Philippines.
We also tracked 116 abductions and disappearances, which leave families and communities bereft, in the dark as to the safety and whereabouts of their loved one. Most took place in Mexico and the Philippines.
Disappearence of two defenders in Mexico
Co-authored with Global Rights Advocacy
The mining sector is the most dangerous sector for HRDs in Mexico. Over the past decade, a quarter of attacks were against HRDs raising concerns about mining; 40% of those attacks were killings. In the coastal mountains of Michoacán, there is powerful resistance by Indigenous Peoples to mining, amidst a generalised atmosphere of violence. Indigenous Peoples are defending their territories against private interests and organised crime, facing criminalisation, persecution, aggression and killings.
Read full report: Business & Human Rights Resource Centre
Related posts:

 Attacks fueled by governments’ double standards fail to deter human rights defenders
Attacks fueled by governments’ double standards fail to deter human rights defenders
 Human rights defenders & business in 2022: People challenging corporate power to protect our planet.
Human rights defenders & business in 2022: People challenging corporate power to protect our planet.
 Human rights defenders show remarkable courage in the face of attacks and killings – new report
Human rights defenders show remarkable courage in the face of attacks and killings – new report
 #COP27: HUMAN RIGHTS ADVOCATES URGE PARTIES TO INCREASE RECOGNITION AND PROTECTION OF ENVIRONMENTAL AND LAND DEFENDERS.
#COP27: HUMAN RIGHTS ADVOCATES URGE PARTIES TO INCREASE RECOGNITION AND PROTECTION OF ENVIRONMENTAL AND LAND DEFENDERS.

Communities Under Siege: New Report Reveals World Bank Failures in Safeguard Compliance and Human Rights Oversight in Tanzania

A decade of displacement: How Uganda’s Oil refinery victims are dying before realizing justice as EACOP secures financial backing to further significant environmental harm.

Carbon Markets Are Not the Solution: The Failed Relaunch of Emission Trading and the Clean Development Mechanism

Govt launches Central Account for Busuulu to protect tenants from evictions

Uganda’s top Lands Ministry official has been arrested and charged with Corruption and Abuse of Office, a significant event that will have far-reaching implications for land governance in the country.

A decade of displacement: How Uganda’s Oil refinery victims are dying before realizing justice as EACOP secures financial backing to further significant environmental harm.

Govt launches Central Account for Busuulu to protect tenants from evictions

Despite harsh repression, opposition to the EACOP pipeline in Uganda remains strong

Innovative Finance from Canada projects positive impact on local communities.
Over 5000 Indigenous Communities evicted in Kiryandongo District
Petition To Land Inquiry Commission Over Human Rights In Kiryandongo District
Invisible victims of Uganda Land Grabs
Resource Center
- LAND GRABS AT GUNPOINT REPORT IN KIRYANDONGO DISTRICT
- RESEARCH BRIEF -TOURISM POTENTIAL OF GREATER MASAKA -MARCH 2025
- The Mouila Declaration of the Informal Alliance against the Expansion of Industrial Monocultures
- FORCED LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA TRENDS RIGHTS OF DEFENDERS IMPACT AND CALL FOR ACTION
- 12 KEY DEMANDS FROM CSOS TO WORLD LEADERS AT THE OPENING OF COP16 IN SAUDI ARABIA
- PRESENDIANTIAL DIRECTIVE BANNING ALL LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA
- FROM LAND GRABBERS TO CARBON COWBOYS A NEW SCRAMBLE FOR COMMUNITY LANDS TAKES OFF
- African Faith Leaders Demand Reparations From The Gates Foundation.
Legal Framework
READ BY CATEGORY
Newsletter
Trending
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks agoA decade of displacement: How Uganda’s Oil refinery victims are dying before realizing justice as EACOP secures financial backing to further significant environmental harm.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks agoGovt launches Central Account for Busuulu to protect tenants from evictions
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks agoCarbon Markets Are Not the Solution: The Failed Relaunch of Emission Trading and the Clean Development Mechanism
-

 NGO WORK4 days ago
NGO WORK4 days agoCommunities Under Siege: New Report Reveals World Bank Failures in Safeguard Compliance and Human Rights Oversight in Tanzania


