MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
Three-quarters of Earth’s land became permanently drier in last three decades: UN
Published
1 year agoon

-
Aridity: The ‘existential crisis’ redefining life on Earth
-
Five billion people could be affected by 2100
Riyadh, Saudi Arabia – Even as dramatic water-related disasters such as floods and storms intensified in some parts of the world, more than three-quarters of Earth’s land became permanently drier in recent decades, UN scientists warned today in a stark new analysis.
Some 77.6% of Earth’s land experienced drier conditions during the three decades leading up to 2020 compared to the previous 30-year period, according to the landmark report from the UN Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD).
Over the same period, drylands expanded by about 4.3 million km2 – an area nearly a third larger than India, the world’s 7th largest country – and now cover 40.6% of all land on Earth (excluding Antarctica).
In recent decades some 7.6% of global lands – an area larger than Canada – were pushed across aridity thresholds (i.e. from non-drylands to drylands, or from less arid dryland classes to more arid classes).
Most of these areas have transitioned from humid landscapes to drylands, with dire implications for agriculture, ecosystems, and the people living there.
And the research warns that, if the world fails to curb greenhouse gas emissions, another 3% of the world’s humid areas will become drylands by the end of this century.
In high greenhouse gas emissions scenarios, expanding drylands are forecast across the Midwestern United States, central Mexico, northern Venezuela, north-eastern Brazil, south-eastern Argentina, the entire Mediterranean Region, the Black Sea coast, large parts of southern Africa, and southern Australia.
The report, The Global Threat of Drying Lands: Regional and global aridity trends and future projections, was launched at the 16th conference of UNCCD’s nearly 200 Parties in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia (COP16), the largest UN land conference to date, and the first UNCCD COP to be held in the Middle East, a region profoundly affected by impacts from aridity.
“This analysis finally dispels an uncertainty that has long surrounded global drying trends,” says Ibrahim Thiaw, UNCCD Executive Secretary. “For the first time, the aridity crisis has been documented with scientific clarity, revealing an existential threat affecting billions around the globe.”
“Unlike droughts—temporary periods of low rainfall—aridity represents a permanent, unrelenting transformation,” he adds. “Droughts end. When an area’s climate becomes drier, however, the ability to return to previous conditions is lost. The drier climates now affecting vast lands across the globe will not return to how they were and this change is redefining life on Earth.”
The report by UNCCD Science-Policy Interface (SPI) — the UN body for assessing the science of land degradation and drought — points to human-caused climate change as the primary driver of this shift. Greenhouse gas emissions from electricity generation, transport, industry and land use changes warm the planet and other human activities warm the planet and affect rainfall, evaporation and plant life, creating the conditions that increase aridity.
Global aridity index (AI) data track these conditions and reveal widespread change over the decades.
Aridification hotspots
Areas particularly hard-hit by the drying trend include almost all of Europe (95.9% of its land), parts of the western United States, Brazil, parts of Asia (notably eastern Asia), and central Africa.
-
Parts of the Western United States and Brazil: Significant drying trends, with water scarcity and wildfires becoming perennial hazards.
-
Mediterranean and Southern Europe: Once considered agricultural breadbaskets, these areas face a stark future as semi-arid conditions expand.
-
Central Africa and parts of Asia: Biologically megadiverse areas are experiencing ecosystem degradation and desertification, endangering countless species.
By contrast, less than a quarter of the planet’s land (22.4%) experienced wetter conditions, with areas in the central United States, Angola’s Atlantic coast, and parts of Southeast Asia showing some gains in moisture.
The overarching trend, however, is clear: drylands are expanding, pushing ecosystems and societies to suffer from aridity’s life-threatening impacts.
The report names South Sudan and Tanzania as nations with the largest percentage of land transitioning to drylands, and China as the country experiencing the largest total area shifting from non-drylands into drylands.
For the 2.3 billion people – well over 25% of the world’s population – living in the expanding drylands, this new normal requires lasting, adaptive solutions. Aridity-related land degradation, known as desertification, represents a dire threat to human well-being and ecological stability.
And as the planet continues to warm, report projections in the worst-case scenario suggest up to 5 billion people could live in drylands by the century’s end, grappling with depleted soils, dwindling water resources, and the diminishment or collapse of once-thriving ecosystems.
Forced migration is one of aridity’s most visible consequences. As land becomes uninhabitable, families and entire communities facing water scarcity and agricultural collapse often have no choice but to abandon their homes, leading to social and political challenges worldwide. From the Middle East to Africa and South Asia, millions are already on the move—a trend set to intensify in coming decades.
Aridity’s devastating impact
The effects of rising aridity are cascading and multifaceted, touching nearly every aspect of life and society, the report says.
It warns that one fifth of all land could experience abrupt ecosystem transformations from rising aridity by the end of the century, causing dramatic shifts (such as forests becoming grasslands and other changes) and leading to extinctions among many of the world’s plants, animals and other life.
-
Aridity is considered the world’s largest single driver behind the degradation of agricultural systems, affecting 40% of Earth’s arable lands
-
Rising aridity has been blamed for a 12% decline in gross domestic product (GDP) recorded for African countries between 1990–2015
-
More than two thirds of all land on the planet (excluding Greenland and Antarctica) is projected to store less water by the end of the century, if greenhouse gas emissions continue to rise even modestly
-
Aridity is considered one of the world’s five most important causes of land degradation (along with land erosion, salinization, organic carbon loss and vegetation degradation)
-
Rising aridity in the Middle East has been linked to the region’s more frequent and larger sand and dust storms
-
Increasing aridity is expected to play a role in larger and more intense wildfires in the climate-altered future—not least because of its impacts on tree deaths in semi-arid forests and the consequent growing availability of dry biomass for burning
-
Rising aridity’s impacts on poverty, water scarcity, land degradation and insufficient food production have been linked to increasing rates of sickness and death globally —especially among children and women
-
Rising aridity and drought play a key role in increasing human migration around the world—particularly in the hyper-arid and arid areas of southern Europe, the Middle East and North Africa and southern Asia.
Report marks a turning point
For years, documenting the rise of aridity proved a challenge, the report states. Its long-term nature and the intricate interplay of factors such as rainfall, evaporation, and plant transpiration made analysis difficult. Early studies produced conflicting results, often muddied by scientific caution.
The new report marks a turning point, leveraging advanced climate models and standardized methodologies to deliver a definitive assessment of global drying trends, confirming the inexorable rise of aridity, while providing critical insights into its underlying drivers and potential future trajectory.
Recommendations
The report offers a comprehensive roadmap for tackling aridity, emphasizing both mitigation and adaptation. Among its recommendations:
-
Strengthen aridity monitoring
Integrate aridity metrics into existing drought monitoring systems. This approach would enable early detection of changes and help guide interventions before conditions worsen. Platforms like the new Aridity Visual Information Tool provide policymakers and researchers with valuable data, allowing for early warnings and timely interventions. Standardized assessments can enhance global cooperation and inform local adaptation strategies. -
Improve land use practices
Incentivizing sustainable land use systems can mitigate the impacts of rising aridity, particularly in vulnerable regions. Innovative, holistic, sustainable approaches to land management are the focus of another new UNCCD SPI report, Sustainable Land Use Systems: The path to collectively achieving Land Degradation Neutrality, available at https://bit.ly/3ZwkLZ3. It considers how land-use at one location affect others elsewhere, makes resilience to climate change or other shocks a priority, and encourages participation and buy-in by Indigenous and local communities as well as all levels of government. Projects like the Great Green Wall—a land restoration initiative spanning Africa—demonstrate the potential for large-scale, holistic efforts to combat aridity and restore ecosystems, while creating jobs and stabilizing economies. -
Invest in water efficiency
Technologies such as rainwater harvesting, drip irrigation, and wastewater recycling offer practical solutions for managing scarce water resources in dry regions. -
Build resilience in vulnerable communities
Local knowledge, capacity building, social justice and holistic thinking are vital to resilience. Sustainable land use systems encourage decision makers to apply responsible governance, protect human rights (including secure land access) and ensure accountability and transparency. Capacity-building programmes, financial support, education programmes, climate information services and community-driven initiatives empower those most affected by aridity to adapt to changing conditions. Farmers switching to drought-resistant crops or pastoralists adopting more arid-tolerant livestock exemplify incremental adaptation. -
Develop international frameworks and cooperation
The UNCCD’s Land Degradation Neutrality framework provides a model for aligning national policies with international goals, ensuring a unified response to the crisis. National Adaptation Plans must incorporate aridity alongside drought planning to create cohesive strategies that address water and land management challenges. Cross-sectoral collaboration at the global level, facilitated by frameworks like the UNCCD, is essential for scaling solutions.
Comments
“For decades, the world’s scientists have signalled that our growing greenhouse gas emissions are behind global warming. Now, for the first time, a UN scientific body is warning that burning fossil fuels is causing permanent drying across much of the world, too—with potentially catastrophic impacts affecting access to water that could push people and nature even closer to disastrous tipping points. As large tracts of the world’s land become more arid, the consequences of inaction grow increasingly dire and adaptation is no longer optional—it is imperative.” – UNCCD Chief Scientist Barron Orr
“Without concerted efforts, billions face a future marked by hunger, displacement, and economic decline. Yet, by embracing innovative solutions and fostering global solidarity, humanity can rise to meet this challenge. The question is not whether we have the tools to respond—it is whether we have the will to act.” – Nichole Barger, Chair, UNCCD Science-Policy Interface
“The report’s clarity is a wake-up call for policymakers: tackling aridity demands more than just science—it requires a diversity of perspectives and knowledge systems. By weaving Indigenous and local knowledge with cutting-edge data, we can craft stronger, smarter strategies to slow aridity’s advance, mitigate its impacts and thrive in a drying world.” – Sergio Vicente-Serrano, co-lead author of the report and an aridity expert with Spain’s Pyrenean Institute of Ecology
“This report underscores the critical need to address aridity as a defining global challenge of our time. By uniting diverse expertise and leveraging breakthrough technologies, we are not just measuring change—we are crafting a roadmap for resilience. Tackling aridity demands a collaborative vision that integrates innovation, adaptive solutions, and a commitment to securing a sustainable future for all.” – Narcisa Pricope, co-lead author, professor of geosciences and associate vice president for research at Mississippi State University, USA.
“The timeliness of this report cannot be overstated. Rising aridity will reshape the global landscape, challenging traditional ways of life and forcing societies to reimagine their relationship with land and water. As with climate change and biodiversity loss, addressing aridity requires coordinated international action and an unwavering commitment to sustainable development.” – Andrea Toreti, co-lead author and senior scientist, European Commission’s Joint Research Centre
By the Numbers:
Key global trends / projections
-
77.6%: Proportion of Earth’s land that experienced drier climates from 1990–2020 compared to the previous 30 years.
-
40.6%: Global land mass (excluding Antarctica) classified as drylands, up from 37.5% over the last 30 years.
-
4.3 million km²: Humid lands transformed into drylands in the last three decades, an area one-third larger than India
-
40%: Global arable land affected by aridity—the leading driver of agricultural degradation.
-
30.9%: Global population living in drylands in 2020, up from 22.5% in 1990
-
2.3 billion: People living in drylands in 2020, a doubling from 1990, projected to more than double again by 2100 under a worst-case climate change scenario.
-
1.35 billion: Dryland inhabitants in Asia—more than half the global total.
-
620 million: Dryland inhabitants in Africa—nearly half of the continent’s population.
-
9.1%: Portion of Earth’s land classified as hyperarid, including the Atacama (Chile), Sahara (Africa), Namib (Africa), and Gobi (China/Mongolia) deserts.
-
23%: Increase in global land at “moderate” to “very high” desertification risk by 2100 under the worst-case emissions scenario
-
+8% at “very high” risk
-
+5% at “high” risk
-
+10% at “moderate” risk
-
Environmental degradation
-
5: Key drivers of land degradation: Rising aridity, land erosion, salinization, organic carbon loss, and vegetation degradation
-
20%: Global land at risk of abrupt ecosystem transformations by 2100 due to rising aridity
-
55%: Species (mammals, reptiles, fish, amphibians, and birds) at risk of habitat loss from aridity. Hotspots: (Arid regions): West Africa, Western Australia, Iberian Peninsula; (Humid regions): Southern Mexico, northern Amazon rainforest
Economics
-
12%: African GDP decline attributed to aridity, 1990–2015
-
16% / 6.7%: Projected GDP losses in Africa / Asia by 2079 under a moderate emissions scenario
-
20M tons maize, 21M tons wheat, 19M tons rice: Expected losses in global crop yields by 2040 due to expanding aridity
-
50%: Projected drop in maize yields in Kenya by 2050 under a high emissions scenario
Water
-
90%: Rainfall in drylands that evaporates back into the atmosphere, leaving 10% for plant growth
-
67%: Global land expected to store less water by 2100, even under moderate emission scenarios
-
75%: Decline in water availability in the Middle East and North Africa since the 1950s
-
40%: Predicted Andean runoff decline by 2100 under a high emissions scenario, threatening water supplies in South America
Health
-
55%: Increase in severe child stunting in sub-Saharan Africa under a medium emissions scenario due to combined effects of aridity and climate warming
-
Up to 12.5%: Estimated rise in mortality risks during sand and dust storms in China, 2013–2018
-
57% / 38%: Increases in fine and coarse atmospheric dust levels, respectively, in the southwestern U.S. by 2100 under worst case climate scenarios
-
220%: Projected increase in premature deaths due to airborne dust in the southwestern United States by 2100 under the high-emissions scenario
-
160%: Expected rise in hospitalizations linked to airborne dust in the same region
Wildfires and forests
-
74%: Expected increase in wildfire-burned areas in California by 2100 under high emission scenarios
-
40: Additional annual high fire danger days in Greece by 2100 compared to late 20th century levels
Notes to editors:
Aridity versus drought
Highly arid regions are places in which a persistent, long-term climatic condition lacks available moisture to support most forms of life and atmospheric evaporative demand significantly exceeds rainfall.
Drought, on the other hand, is an anomalous, shorter-term period of water shortage affecting ecosystems and people and often attributed to low precipitation, high temperatures, low air humidity and/or anomalies in wind.
While drought is part of natural climate variability and can occur in almost any climatic regime, aridity is a stable condition for which changes occur over extremely long-time scales under significant forcing.
Media contacts: press@unccd.int
Fragkiska Megaloudi, +30 6945547877 (WhatsApp) fmegaloudi@unccd.int
Gloria Pallares, +34 606 93 1460 gpallares@unccd.int
Terry Collins, +1-416-878-8712 tc@tca.tc
Authors and other experts are available for advance interviews.
The full report, The Global Threat of Drying Lands: Regional and global aridity trends and future projections, is available for media preview at https://www.unccd.int/resources/reports/global-threat-drying-lands-regional-and-global-aridity-trends-and-future
Original Source: unccd.int
Related posts:

 UNCCD COP16: NGOs issue a stark warning and call for urgent actions to deal with the escalating threats of desertification, land degradation, and drought.
UNCCD COP16: NGOs issue a stark warning and call for urgent actions to deal with the escalating threats of desertification, land degradation, and drought.
 Restoring Our Land: Tackling Degradation for Climate Resilience, Food Security, and Sustainable Development at COP16
Restoring Our Land: Tackling Degradation for Climate Resilience, Food Security, and Sustainable Development at COP16
 Climate change will see East Africa get wetter say scientists
Climate change will see East Africa get wetter say scientists
 Breaking: West and Central African women meet in Senegal over the climate crisis.
Breaking: West and Central African women meet in Senegal over the climate crisis.
You may like
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
CSOs push for reforms at the KFW Accountability Mechanism after experts discovered that it has weak remedies in addressing grievous harms caused by its investments.
Published
10 hours agoon
February 24, 2026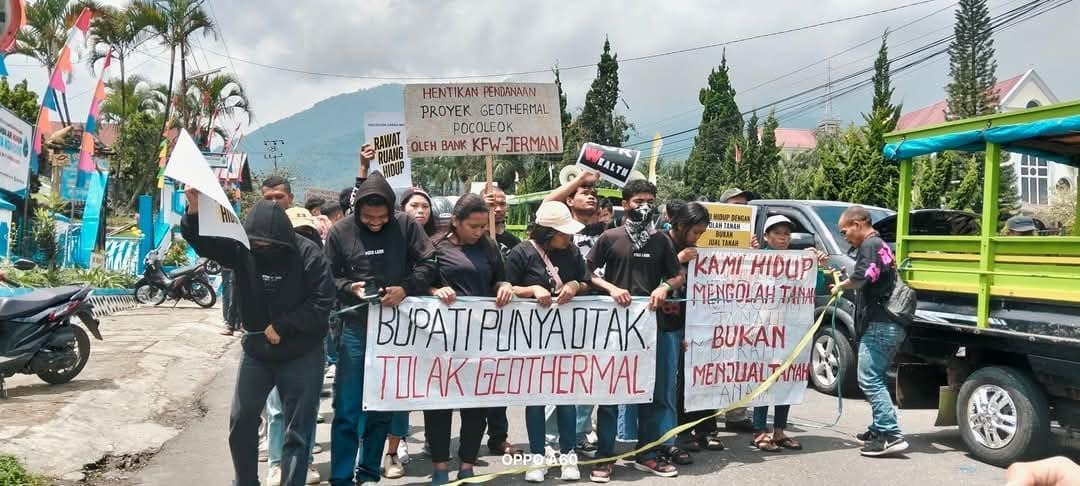
By Witness Radio Team
Germany’s state-owned development bank, KfW, is facing renewed scrutiny as Civil Society Organizations (CSOs) issue detailed recommendations to reform its Complaint Mechanism, citing systemic failures to prevent harm, address reprisals, and ensure accountability in projects it finances across developing countries.
The recommendations follow the release of “Irresponsible Banking”, a report by the Coalition for Human Rights in Development launched in September 2025, which documented alleged links between KfW-backed projects and land dispossession, environmental degradation, and threats against human rights defenders (HRDs).
The report documented cases in Indonesia, Mexico, and Tanzania in which affected communities claimed to have faced intimidation, livelihood losses, and violations of their right to Free, Prior, and Informed Consent (FPIC) by KFW-backed projects.
In response, a coalition of organizations, including Asia Indigenous Peoples Network on Extractive Industries and Energy (AIPNEE), Community Empowerment and Social Justice Network (CEMSOJ), Defenders in Development Campaign (DiD), and Protection International, has submitted over 20 detailed recommendations aimed at fundamentally strengthening the independence, transparency, and effectiveness of KfW’s Complaint Mechanism.
Some of the key recommendations include a call for structural independence, a separate budget for the mechanism established and managed independently of the management of the KFW Bank, taking into consideration reprisals suffered by project-affected people, and mentioning that the Complaints Office will commit to implementing a more comprehensive approach, looking beyond individual complainants, among others.
These proposals stem from documented concerns that communities affected by KfW-funded projects struggle to access meaningful remedies.
According to the KFW irresponsible banking report, projects branded as sustainable and pro-development have, in several cases, been linked with forced displacement, inadequate consultation, and reprisals against those who speak out.
“KfW calls it ‘responsible banking’, but it’s using German taxpayers’ money to bankroll projects that displace Indigenous Peoples, destroy ecosystems, and endanger human rights defenders. If KfW wants to demonstrate real responsibility, it needs to listen to local communities and ensure their voices are not silenced.” Dalile Antunez, collaborative researcher at the Coalition for Human Rights in Development.
Being fully owned by the German government, CSOs emphasize that its operations must align with the United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights and Germany’s Supply Chain Due Diligence Act.
According to the United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights, business enterprises are expected to respect human rights, meaning they should avoid infringing on others’ human rights and address adverse human rights impacts with which they are involved. This is in addition to Germany’s Supply Chain Due Diligence Act, which requires enforcement of corporate accountability for human rights and environmental standards across global operations.
But such standards have never been adhered to by development projects such as KFW-funded projects.
KfW bank is further urged to adopt a comprehensive anti-reprisals framework, including concrete measures such as suspending project disbursements where threats persist, documenting all reported reprisals in a public registry, providing emergency assistance where needed, and communicating incidents to oversight bodies such as the German Institute for Human Rights.
Civil society groups argue that these recommendations demonstrate the need not only for stronger safeguards but also for genuine participation by affected communities in remedial processes.
The recommendations, therefore, propose that complainants have the authority to choose whether their case proceeds through dispute resolution, prior resolution, or compliance review.
They also call for guaranteed access to all information used in decision-making, publication of both admissible and inadmissible complaints, and extended deadlines for filing complaints to account for delayed discovery of harm.
Additionally, CSOs advocate for a simplified complaint process that allows grievances to be submitted orally or through accessible channels, recognizing the barriers faced by remote or marginalized communities.
“Many Indigenous communities in remote areas may face barriers such as limited access to technical support or a lack of experience in preparing formal written complaints, particularly in the absence of supporting NGOs. So, they should be able to file complaints verbally or in other forms and through various channels. The current system is overly complex, creating barriers for communities to submit grievances independently without supporting NGOs,” reads part of the recommendations.
CSOs argue that unless KfW Bank strengthens the independence of its Complaint Mechanism and adopts enforceable protections against reprisals, its sustainability commitments risk remaining utopian rather than realistic and transformative.
Related posts:

 CSOs call for meaningful changes in the World Bank’s Dispute Resolution Service to foster access to justice for project-affected communities.
CSOs call for meaningful changes in the World Bank’s Dispute Resolution Service to foster access to justice for project-affected communities.
 Joint Statement on World Bank Accountability Mechanism’s Decision to Limit Application of Operating Procedures
Joint Statement on World Bank Accountability Mechanism’s Decision to Limit Application of Operating Procedures
 Witness Radio, private companies, CSOs and local government officials are meeting to discuss alternative remedies to salvage the appalling land and environmental rights situation in Kiryandongo district.
Witness Radio, private companies, CSOs and local government officials are meeting to discuss alternative remedies to salvage the appalling land and environmental rights situation in Kiryandongo district.
 U.S. Congress Requires USAID to Create an Accountability Mechanism.
U.S. Congress Requires USAID to Create an Accountability Mechanism.
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
UPDF General on the spot over fresh evictions in Hoima
Published
1 week agoon
February 17, 2026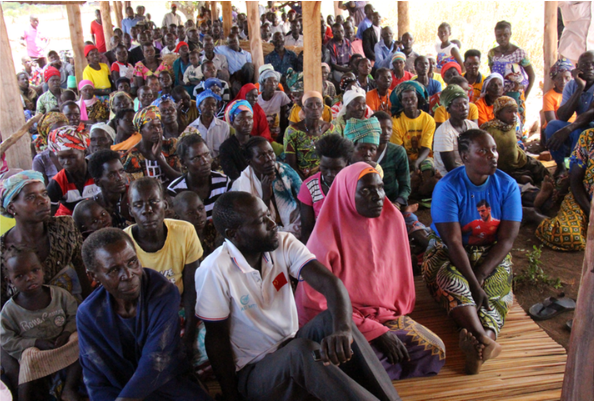
Over 1,000 residents in Kapapi Sub-County, Hoima District, are facing a second forced eviction from their ancestral land in three years, sparking widespread tension and anger among the community.
The latest evictions have been linked to a senior Uganda Peoples’ Defence Forces (UPDF) officer, Brigadier General Peter Nabasa, whom residents accuse of masterminding the displacement, allegedly in defiance of earlier government directives issued by the state minister for Lands, Dr. Sam Mayanja.
In October 2025, Minister Mayanja ordered that over 1,000 families who had been evicted from contested land in Kapapi Sub-County be resettled back onto their bibanja.
He also directed security commanders in the area to withdraw armed personnel and allow the affected communities to return. However, residents claim the situation has worsened, with renewed evictions pushing thousands into uncertainty once again.
The affected families, estimated to be over 1,000 and comprising over 4,000 people, include both cultivators and pastoralists. They were evicted from their homes in several villages, including Waaki North, Kapapi Central, Waaki South, Runga, Kiryatete, and Kiganja, all located in Kapapi and Kiganja sub-counties, Hoima District.
Residents insist the land has been their home for decades, passed down through generations, and accuse powerful individuals of using land titles and security enforcement to displace them.
“We were returned to our land in October last year on the orders of President Museveni and Minister Mayanja, but shortly after the elections, we were evicted again,” said Deusi Mugume, a resident of Runga.
“The Brigadier General came with armed security personnel and ordered us to vacate the land immediately. They even fired bullets in the air to disperse us, disrespecting the orders of both the Minister and the President.”
The residents were evicted from two titled pieces of land said to belong to businessmen and private individuals based in Hoima and Kampala. One of the contested titles measures approximately 2,545 acres (1,030 hectares) and is reportedly owned by seven individuals, including Ndahura William Gafayo, Aston Muhwezi, Alex Kyamanywa, Nathan Kiiza Byarugonjo, Bahuzya, Monica Rwashadika, and Wilber Kiiza. This land reportedly covers parts of Kapapi and Kiganja sub-counties.
Another title, measuring about three square miles, is said to belong to the family of the late Tito Byangire of Kigorobya, Hoima District. This land reportedly covers four villages, including Waaki South, Waaki North, Runga, Kapapi Central, and Kiryatete.
Brig Gen Nabasa claims he legally leased 700 acres of land from the Byangire family for 10 years starting in 2023.
“The residents were allowed to live there temporarily because elections were approaching, but they were supposed to leave immediately after the polls,” he said.
The residents, who are now living in temporary structures in Rwenyana, say their food and cash crops were destroyed after cattle were introduced onto the land following their eviction.
“We are going through many difficulties. We have no food, we are sleeping in makeshift shelters, children are not going to school, and we don’t know if we shall ever return to our land,” said Madinah Nyanjura and Nyarabiraho Cheya, both residents of Kapapi.
The Hoima Deputy Resident District Commissioner, Christopher Aine, blamed land brokers for misleading residents and bringing more people onto the contested land.
Minister Mayanja had previously directed the arrest of Brig Gen Peter Nabasa, Capt Rogers Karamagi, former Hoima Deputy Resident District Commissioner Michael Muramira Kyakashari, and William Ndahura Gafayo for allegedly illegally evicting residents from their bibanja land.
Mr Joshua Byangire, one of the administrators of the late Byangire estate, said the family has faced continued disruption and appealed to the government to buy off the land title.
“We have been disturbed on our family land. I request the government to buy off our land title. I don’t understand why soldiers have been deployed there, yet we are civilians and cannot access our property,” he said.
Original Source: monitor.co.ug
Related posts:

 Breaking: The army general, police chief, presidential representative, and others are appearing before the Hoima Chief Magistrate court today.
Breaking: The army general, police chief, presidential representative, and others are appearing before the Hoima Chief Magistrate court today.
 Court issues fresh criminal summonses against army general, police chief and presidential representative and others in a private criminal case.
Court issues fresh criminal summonses against army general, police chief and presidential representative and others in a private criminal case.
 Over 500 Kapapi families in Hoima district remain stranded after the district security committee fails to resettle them back on their land as directed by the minister.
Over 500 Kapapi families in Hoima district remain stranded after the district security committee fails to resettle them back on their land as directed by the minister.
 UPDF General, District Police Commander, and Presidential Representative defy Court summonses for the second time as DPP takes over the EACOP-PAP’s case.
UPDF General, District Police Commander, and Presidential Representative defy Court summonses for the second time as DPP takes over the EACOP-PAP’s case.
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
Small-scale fishers and coastal communities are pushing to testify before a human rights commission investigating the causes of food inequality in South Africa.
Published
1 week agoon
February 17, 2026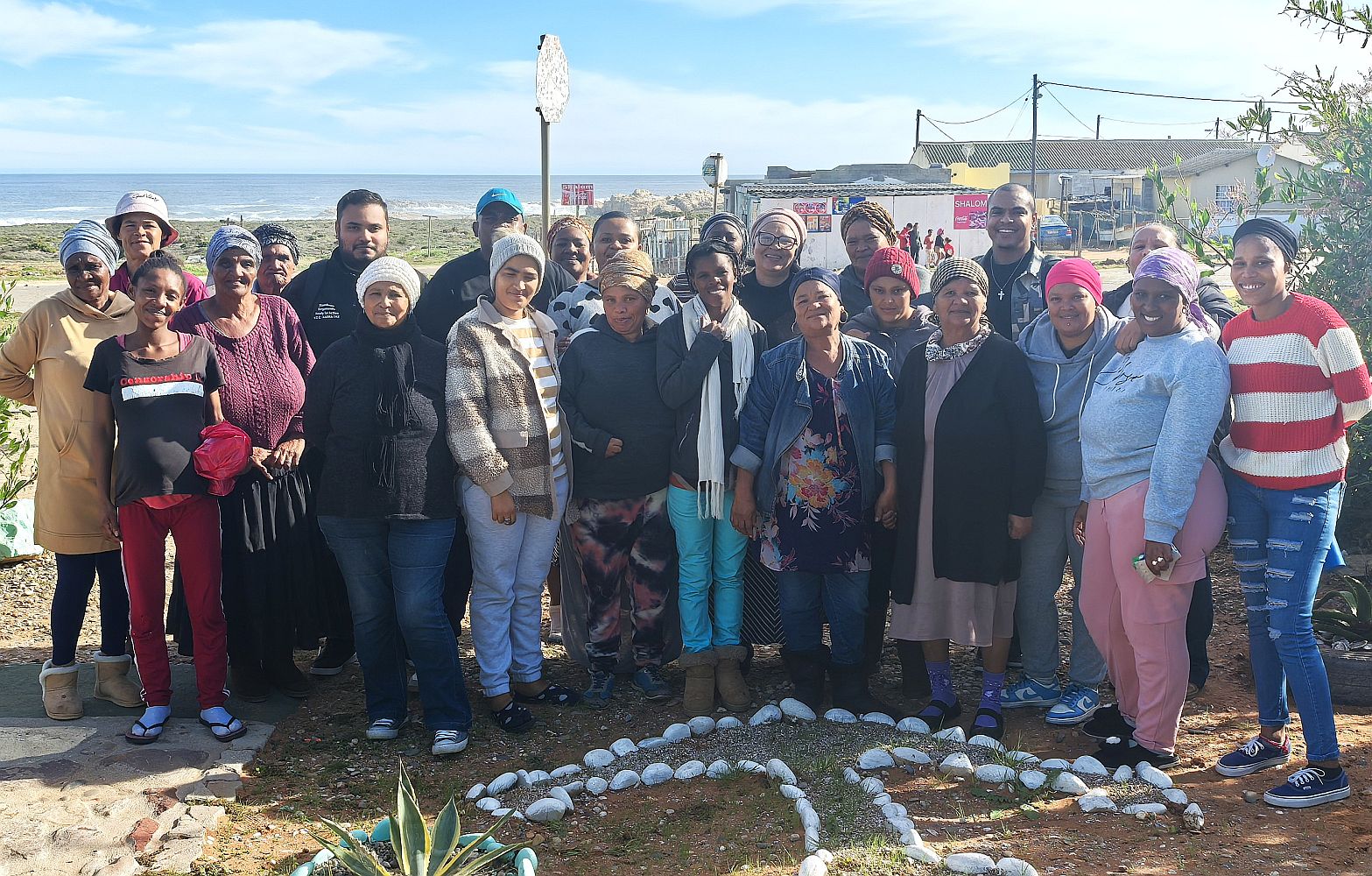
Fisher women play a vital role in sustaining household food security, yet remain under‑recognised, excluded from permits, and denied equal income opportunities in the fishing sector.Photo Credit: The Green Connection.
By Witness Radio team.
South Africa produces enough food to feed its population, yet millions go to bed hungry every night.
According to Statistics South Africa’s General Household Survey 2024, released in 2025, about 14 million people experienced hunger, representing 22.2% of households reporting inadequate or severely inadequate access to food. The Northern Cape (34.3%), Eastern Cape (31.3%), and Mpumalanga (30.4%) recorded the highest levels of food insecurity.
One in four children in South Africa is stunted due to chronic malnutrition. In the Eastern Cape alone, 70 children under the age of five reportedly died from malnutrition-related complications between January and July 2025.
In response to the growing problem, the South African Human Rights Commission, a national institution established to support constitutional democracy, declared last year that it would hold a National Public Inquiry into the Constitutional Right to Food. This inquiry will examine how communities, corporations, laws, and policies shape food systems and seek to address the structural causes of hunger.
As a result, the investigation will try to describe a future in which food is once again understood as sustenance, dignity, and justice.
Thousands of small-scale fishers along South Africa’s 3,000 km coastline depend on marine resources for their livelihoods, highlighting their vital role in the nation’s food security and cultural fabric.
Many fishing families struggle to make ends meet, even though they harvest food from the ocean. The livelihoods and food security of about 28,000 small-scale fishermen are directly reliant on marine resources. Yet, existing policies-such as restrictive permits and limited market access-exclude them from full participation, perpetuating food insecurity.
For these communities, food systems are not abstract policy concepts. They shape daily survival, dignity, livelihoods, and cultural identity.
“As part of our submission, we emphasize that concrete policy changes-such as recognizing customary fishing rights and improving market access-will directly enhance the livelihoods and food security of small-scale fishers and coastal communities, making the case for urgent reform.” Says Buthelezi
The Green Connection, a registered non-profit organisation, works with coastal communities to promote environmental justice, human rights, and accountable governance.
In the submission, the Green Connection states that the inquiry is timely as it will examine the structural and economic dynamics that perpetuate hunger. “It will assess the concentration of power in the food value chain, affordability and access, land and tenure security, policy coordination, and the realization of the constitutional right to food. This includes its links to dignity, health, water, culture, and a healthy environment.” The submission reads.
The Green Connection further argues that the Commission’s examination of governance, participation, and accountability must include scrutiny of marine and ocean policy.
“Poor implementation of the Small-Scale Fisheries Policy, limited market access, inadequate infrastructure, and weak consultation processes continue to undermine the sector. Women – who make up less than 30% of participants – remain under-recognised. At the same time, young people leave coastal communities due to declining economic prospects,” says Khetha Buthelezi, Economics Officer at The Green Connection, adding that, “Food and the systems we put in place to produce it cannot be separated from human dignity, livelihoods, and cultural rights. These issues are not abstract policy debates. For small-scale fishing communities, food from the ocean is not merely a commodity – it is a foundation of identity, survival, and social cohesion.”
The organisation also raises concerns about the potential impacts of offshore oil and gas expansion under Operation Phakisa. It further adds that Seismic surveys, drilling, and increased shipping activity can threaten fish stocks and restrict access to traditional fishing grounds, thereby directly affecting food security and livelihoods.
“For small-scale fishers, these are not abstract environmental issues. It is about income stability, cultural survival, and the constitutional rights to food, livelihoods, and participation in decision-making, and protecting these rights and resources for future generations,” says Buthelezi
Several fishing communities consulted shared testimonies describing worsening conditions.
“While small‑scale fishers support around 28000 people in South Africa, many of us can no longer catch or sell enough fish to feed our own families. Walter Steenkamp says on behalf of Aukotowa Small‑Scale Fishers Co‑operative in Port Nolloth, Northern Cape.
Steenkamp adds that Decisions are often made without consulting them, which reflects an intended exclusion from decision-making. “We hope this inquiry will result in the recognition of our customary rights, the return of our fishing grounds, and for the government to listen to those of us who live from the sea, so that we can feed our families with dignity.”
According to Kristie Links from the Sal-Diaz Small-Scale Fisher Co-operative in Saldanha Bay, Western Cape, farmers are forced to use larger boats that they cannot afford. “We have no money for the bigger boats they want us to use, and the areas we are given have little or no fish.
Industrial boats continue to overfish, especially at night, while our communities struggle to put food on the table. This situation is destroying our livelihoods, our food security, and our right to be recognised as small-scale fishers,” Kristie adds.
The organisation argues that poor implementation of the Small-Scale Fisheries Policy, weak consultation processes, and inadequate infrastructure continue to undermine the sector.
“Our message to the SAHRC is clear. If South Africa is serious about tackling hunger and inequality, it must ensure food systems governance is transparent, inclusive, and accountable. Coastal communities are not asking for charity – they are demanding justice.” Buthelezi concludes
The deadline for written submissions has been extended to 27 February 2026, with public hearings scheduled for March during Human Rights Month.
Related posts:

 About 41 million people food insecure in E. Africa amid COVID-19 pandemic: UN
About 41 million people food insecure in E. Africa amid COVID-19 pandemic: UN
 63 million people food insecure in Horn of Africa: report
63 million people food insecure in Horn of Africa: report
 “Vacant Land” Narrative Fuels Dispossession and Ecological Crisis in Africa – New report.
“Vacant Land” Narrative Fuels Dispossession and Ecological Crisis in Africa – New report.
 Community land rights at stake amid looming large-scale investment interests
Community land rights at stake amid looming large-scale investment interests

CSOs push for reforms at the KFW Accountability Mechanism after experts discovered that it has weak remedies in addressing grievous harms caused by its investments.

UPDF General on the spot over fresh evictions in Hoima

Small-scale fishers and coastal communities are pushing to testify before a human rights commission investigating the causes of food inequality in South Africa.

The Kenyan government insists on maintaining provisions of the Seed Act that the court nullified: farmers and legal experts question the motive.

Evicted from their land to host Refugees: A case of Uganda’s Kyangwali refugee settlement expansion, which left host communities landless.

US-DRC Strategic Partnership Agreement Faces Constitutional Challenge in Court

Why govt is launching a comprehensive digital land registry

Indigenous communities in Eastern Nepal accuse the World Bank’s Linked Cable Car Project of rights violations.

Innovative Finance from Canada projects positive impact on local communities.
Over 5000 Indigenous Communities evicted in Kiryandongo District
Petition To Land Inquiry Commission Over Human Rights In Kiryandongo District
Invisible victims of Uganda Land Grabs
Resource Center
- Land And Environment Rights In Uganda Experiences From Karamoja And Mid Western Sub Regions
- REPARATORY AND CLIMATE JUSTICE MUST BE AT THE CORE OF COP30, SAY GLOBAL LEADERS AND MOVEMENTS
- LAND GRABS AT GUNPOINT REPORT IN KIRYANDONGO DISTRICT
- THOSE OIL LIARS! THEY DESTROYED MY BUSINESS!
- RESEARCH BRIEF -TOURISM POTENTIAL OF GREATER MASAKA -MARCH 2025
- The Mouila Declaration of the Informal Alliance against the Expansion of Industrial Monocultures
- FORCED LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA TRENDS RIGHTS OF DEFENDERS IMPACT AND CALL FOR ACTION
- 12 KEY DEMANDS FROM CSOS TO WORLD LEADERS AT THE OPENING OF COP16 IN SAUDI ARABIA
Legal Framework
READ BY CATEGORY
Newsletter
Trending
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week agoSmall-scale fishers and coastal communities are pushing to testify before a human rights commission investigating the causes of food inequality in South Africa.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks agoFEATURE: What Lagos Can Learn From Kenya, Morocco, Uganda’s Forced Evictions
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week agoThe Kenyan government insists on maintaining provisions of the Seed Act that the court nullified: farmers and legal experts question the motive.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week agoUPDF General on the spot over fresh evictions in Hoima
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago13 years after the refugee host community was forcefully evicted to expand a refugee settlement, thousands remain unsettled.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK10 hours ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK10 hours agoCSOs push for reforms at the KFW Accountability Mechanism after experts discovered that it has weak remedies in addressing grievous harms caused by its investments.


