NGO WORK
Development banks have no business financing agribusiness
Published
4 years agoon
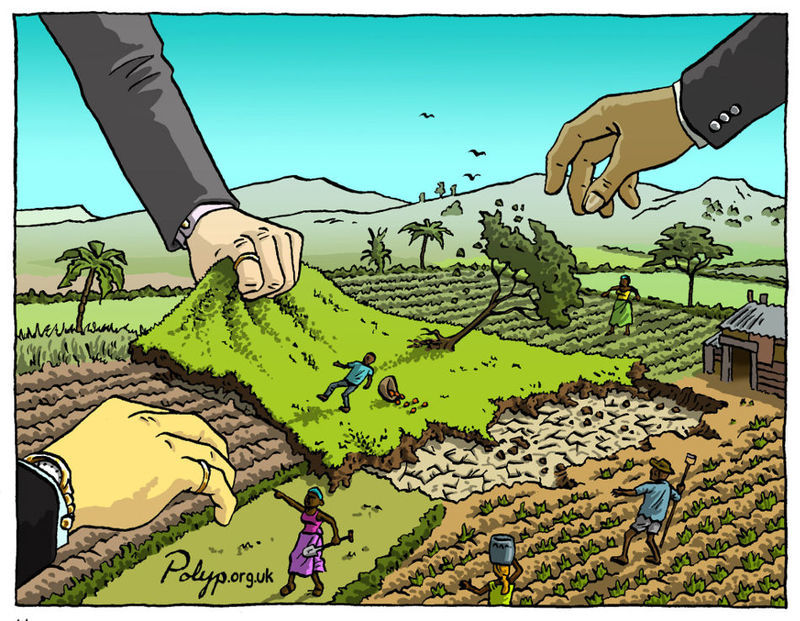

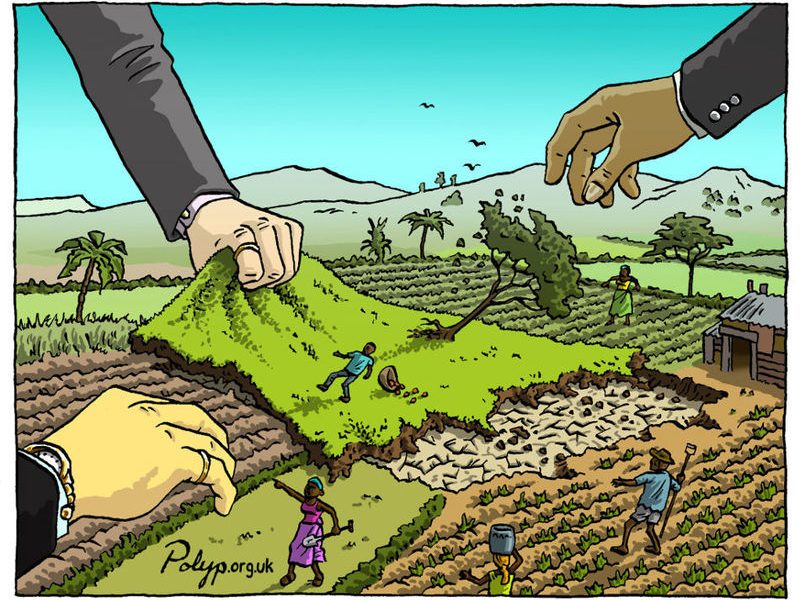
On the eve of an annual gathering of public development banks in Rome, 280 groups from 70 countries have signed a letter slamming them for bankrolling the expansion of industrial agriculture, environmental destruction and corporate control of the food system. The signatories affirm only fully public and accountable funding mechanisms based on people’s actual needs can achieve real solutions to the global food crisis.
Over 450 Public Development Banks (PDBs) from around the world are gathering in Rome from 19 to 20 October 2021 for a second international summit, dubbed Finance in Common. During the first summit in Paris in 2020, over 80 civil-society organizations published a joint statement demanding that the PDBs stop funding agribusiness companies and projects that take land and natural resources away from local communities. This year, however, PDBs have made agriculture and agribusiness the priority of their second summit. This is of serious concern for the undersigned groups as PDBs have a long track-record of making investments in agriculture that benefit private interests and agribusiness corporations at the expense of farmers, herders, fishers, food workers and Indigenous Peoples, undermining their food sovereignty, ecosystems and human rights.
Our concerns
PDBs are public institutions established by national governments or multilateral agencies to finance government programs and private companies whose activities are said to contribute to the improvement of people’s lives in the places where they operate, particularly in the Global South. Many multilateral development banks, a significant sub-group of PDBs, also provide technical and policy advice to governments to change their laws and policies to attract foreign investment.
As public institutions, PDBs are bound to respect, protect and fulfil human rights and are supposed to be accountable to the public for their actions. Today, development banks collectively spend over US$2 trillion a year financing public and private companies to build roads, power plants, factory farms, agribusiness plantations and more in the name of “development” – an estimated US$1.4 trillion goes into the sole agriculture and food sector. Their financing of private companies, whether through debt or the purchase of shares, is supposed to be done for a profit, but much of their spending is backed and financed by the public – by people’s labor and taxes.
The number of PDBs and the funding they receive is growing.The reach of these banks is also growing as they are increasingly channeling public funds through private equity, “green finance” and other financial schemes to deliver the intended solutions instead of more traditional support to government programs or non-profit projects. Money from a development bank provides a sort of guarantee for companies expanding into so-called high-risk countries or industries. These guarantees enable companies to raise more funds from private lenders or other development banks, often at favorable rates. Development banks thus play a critical role in enabling multinational corporations to expand further into markets and territories around the world – from gold mines in Armenia, to controversial hydroelectric dams in Colombia, to disastrous natural gas projects in Mozambique – in ways they could not do otherwise.
Additionally, many multilateral development banks work to explicitly shape national level law and policy through their technical advice to governments and ranking systems such as the Enabling the Business of Agriculture of the World Bank. The policies they support in key sectors — including health, water, education, energy, food security and agriculture — tend to advance the role of big corporations and elites. And when affected local communities, including Indigenous Peoples and small farmers protest, they are often not heard or face reprisals. For example, in India, the World Bank advised the government to deregulate the agricultural marketing system, and when the government implemented this advice without consulting with farmers and their organisations, it led to massive protests.
Public Development Banks claim that they only invest in “sustainable” and “responsible” companies and that their involvement improves corporate behavior. But these banks have a heavy legacy of investing in companies involved in land grabbing, corruption, violence, environmental destruction and other severe human rights violations, from which they have escaped any meaningful accountability. The increasing reliance of development banks on offshore private equity funds and complex investment webs, including so called financial intermediaries, to channel their investments makes accountability even more evasive and enables a small and powerful financial elite to capture the benefits.
It is alarming that Public Development Banks are now taking on more of a coordinated and central role when it comes to food and agriculture. They are a part of the global financial architecture that is driving dispossession and ecological destruction, much of which is caused by agribusiness. Over the years, their investment in agriculture has almost exclusively gone to companies engaged in monoculture plantations, contract growing schemes, animal factory farms, sales of hybrid and genetically modified seeds and pesticides, and digital agriculture platforms dominated by Big Tech. They have shown zero interest in or capacity to invest in the farm, fisher and forest communities that currently produce the majority of the world’s food. Instead, they are bankrolling land grabbers and corporate agribusinesses and destroying local food systems.
Painful examples
Important examples of the pattern we see Public Development Banks engaging in:
-
The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development and the European Investment Bank have provided generous financing to the agribusiness companies of some of Ukraine’s richest oligarchs, who control hundreds of thousands of hectares of land.
-
SOCFIN of Luxembourg and SIAT of Belgium, the two largest oil palm and rubber plantation owners in Africa, have received numerous financial loans from development banks, despite their subsidiaries being mired in land grabbing, corruption scandals and human rights violations.
-
Multiple development banks (including Swedfund, BIO, FMO and the DEG) financed the failed sugarcane plantation of Addax Bioenergy in Sierra Leone that has left a trail of devastation for local communities after the company’s exit.
-
The UK’s CDC Group and other European development banks (including BIO, DEG, FMO and Proparco) poured over $150 million into the now bankrupt Feronia Inc’s oil palm plantations in the DR Congo, despite long-standing conflicts with local communities over land and working conditions, allegations of corruption and serious human rights violations against villagers.
-
The United Nations’ Common Fund for Commodities invested in Agilis Partners, a US-owned company, which is involved in the violent eviction of thousands of villagers in Uganda for a large-scale grain farm.
-
Norfund and Finnfund own Green Resources, a Norwegian forestry company planting pine trees in Uganda on land taken from thousands of local farmers, with devastating effects on their livelihoods.
-
The Japan Bank for International Cooperation and the African Development Bank invested in a railway and port infrastructure project to enable Mitsui of Japan and Vale of Brazil to export coal from their mining operations in northern Mozambique. The project, connected to the controversial ProSavana agribusiness project, has led to land grabbing, forced relocations, fatal accidents and the detention and torture of project opponents.
-
The China Development Bank financed the ecologically and socially disastrous Gibe III dam in Ethiopia. Designed for electricity generation and to irrigate large-scale sugar, cotton and palm oil plantations such as the gargantuan Kuraz Sugar Development Project, it has cut off the river flow that the indigenous people of the Lower Omo Valley relied on for flood retreat agriculture.
-
In Nicaragua, FMO and Finnfund financed MLR Forestal, a company managing cocoa and teak plantations, which is controlled by gold mining interests responsible for displacement of Afro-descendant and Indigenous communities and environmental degradation.
-
The International Finance Corporation and the Inter-American Development Bank Invest have recently approved loans to Pronaca, Ecuador’s 4th largest corporation, to expand intensive pig and poultry production despite opposition from international and Ecuadorian groups, including local indigenous communities whose water and lands have been polluted by the company’s expansive operations.
-
The Inter-American Development Bank Invest is considering a new $43 million loan for Marfrig Global Foods, the world’s 2nd largest beef company, under the guise of promoting “sustainable beef.” Numerous reports have found Marfrig’s supply chain directly linked to illegal deforestation in the Amazon and Cerrado and human rights violations. The company has also faced corruption charges. A global campaign is now calling for PDBs to immediately divest from all industrial livestock operations.
We need better mechanisms to build food sovereignty
Governments and multilateral agencies are finally beginning to acknowledge that today’s global food system has failed to address hunger and is a key driver of multiple crises, from pandemics to biodiversity collapse to the climate emergency. But they are doing nothing to challenge the corporations who dominate the industrial food system and its model of production, trade and consumption. To the contrary, they are pushing for more corporate investment, more public private partnerships and more handouts to agribusiness.
This year’s summit of the development banks was deliberately chosen to follow on the heels of the UN Food Systems Summit. It was advertised as a global forum to find solutions to problems afflicting the global food system but was hijacked by corporate interests and became little more than a space for corporate greenwashing and showcasing industrial agriculture. The event was protested and boycotted by social movements and civil society, including through the Global People´s Summit and the Autonomous People´s response to the UN Food Systems Summit, as well as by academics from across the world.
The Finance in Common summit, with its focus on agriculture and agribusiness, will follow the same script. Financiers overseeing our public funds and mandates will gather with elites and corporate representatives to strategize on how to keep the money flowing into a model of food and agriculture that is leading to climate breakdown, increasing poverty and exacerbating all forms of malnutrition. Few if any representatives from the communities affected by the investments of the development banks, people who are on the frontlines trying to produce food for their communities, will be invited in or listened to. PDBs are not interested. They seek to fund agribusinesses, which produce commodities for trade and financial schemes for profits rather than food for nutrition.
Last year, a large coalition of civil-society organizations made a huge effort just to get the development banks to agree to commit to a human rights approach and community-led development. The result was only some limited language in the final declaration, which has not been translated into action.
We do not want any more of our public money, public mandates and public resources to be wasted on agribusiness companies that take land, natural resources and livelihoods away from local communities. Therefore:
We call for an immediate end to the financing of corporate agribusiness operations and speculative investments by public development banks.
We call for the creation of fully public and accountable funding mechanisms that support peoples’ efforts to build food sovereignty, realize the human right to food, protect and restore ecosystems, and address the climate emergency.
We call for the implementation of strong and effective mechanisms that provide communities with access to justice in case of adverse human rights impacts or social and environmental damages caused by PDB investments.
Fundación Plurales – Argentina
Fundación Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (FARN) – Argentina
Foro Ambiental Santiagueño – Argentina
Armenian Women For Health &Healthy Environment NGO /AWHHE/ – Armenia
Australian Food Sovereignty Alliance – Australia
SunGem – Australia
Welthaus Diözese Graz-Seckau – Austria
Turkmen Initiative for Human Rights – Austria
FIAN Austria – Austria
Oil Workers’ Rights Protection Organization Public Union – Azerbaijan
Initiative for Right View – Bangladesh
Right to Food South Asia – Bangladesh
IRV – Bangladesh
Bangladesh Agricultural Farm Labour Federation [BAFLF] – Bangladesh
NGO “Ecohome” – Belarus
Eclosio – Belgium
AEFJN – Belgium
FIAN Belgium – Belgium
Entraide et Fraternité – Belgium
Africa Europe Faith & Justice Network (AEFJN) – Belgium
Coalition for Fair Fisheries Arrangements – Belgium
Eurodad – Belgium
Friends of the Earth Europe – Belgium
Alianza Animalista La Paz – Bolivia
Instituto de Estudos Socioeconômicos (Inesc) – Brazil
Centro Ecologico – Brazil
FAOR Fórum da Amazônia Oriental – Brazil
Articulação Agro é Fogo – Brazil
Campanha Nacional de Combate e Prevenção ao Trabalho Escravo – Comissão Pastoral da Terra/CPT – Brazil
Clínica de Direitos Humanos da Amazônia -PPGD/UFPA – Brazil
Universidade Federal Fluminense IPsi – Brazil
Associação Brasileira de Reforma Agrária – Brazil
Rede Jubileu Sul Brasil – Brazil
Alternativas para pequena agricultura no Tocantins APATO – Brazil
CAPINA Cooperação e Apoio a Projetos de Inspiração Alternativa – Brazil
Marcha Mundial por Justiça Climática / Marcha Mundial do Clima – Brazil
MNCCD – Movimento Nacional Contra Corrupção e pela Democracia – Brazil
Marcha Mundial por Justiça Climática/Marcha Mundial do Clima – Brazil
Support Group for Indigenous Youth – Brazil
Comissão Pastoral da Terra -CPT – Brazil
Equitable Cambodia – Cambodia
Coalition of Cambodian Farmers Community – Cambodia
Struggle to Economize Future Environment (SEFE) – Cameroon
Synaparcam – Cameroon
APDDH -ASSISTANCE – Cameroon
Inter Pares – Canada
Vigilance OGM – Canada
National Farmers Union – Canada
SeedChange – Canada
Place de la Dignité – Canada
Corporación para la Protección y Desarrollo de Territorios Rurales- PRODETER – Colombia
Grupo Semillas – Colombia
Groupe de Recherche et de Plaidoyer sur les Industries Extractives (GRPIE) – Côte d’Ivoire
Réseau des Femmes Braves (REFEB) – Côte d’Ivoire
CLDA – Côte d’Ivoire
Counter Balance – Czech Republic
AfrosRD – Dominican Republic
Conseil Régional des Organisations Non gouvernementales de Développement – DR Congo
Construisons Ensemble le MONDE – DR Congo
Synergie Agir Contre la Faim et le Réchauffement Climatique , SACFRC. – DR Congo
COPACO-PRP – DR Congo
AICED – DR Congo
Réseaux d’informations et d’appui aux ONG en République Démocratique du Congo ( RIAO – RDC) – DR Congo
Latinoamérica Sustentable – Ecuador
Housing and Land Rights Network – Habitat International Coalition – Egypt
Pacific Islands Association of Non-Governmental Organisations (PIANGO) – Fiji
Internationale Situationniste – France
Pouvoir d’Agir – France
Europe solidaire sans frontières (ESSF) – France
Amis de la Terre France – France
Médias Sociaux pour un Autre Monde – France
ReAct Transnational – France
CCFD-Terre Solidaire – France
CADTM France – France
Coordination SUD – France
Движение Зеленных Грузии – Georgia
NGO “GAMARJOBA” – Georgia
StrongGogo – Georgia
FIAN Deutschland – Germany
Rettet den Regenwald – Germany
Angela Jost Translations – Germany
urgewald e.V. – Germany
Abibinsroma Foundation – Ghana
Alliance for Empowering Rural Communities – Ghana
Organización de Mujeres Tierra Viva – Guatemala
Campaña Guatemala sin hambre – Guatemala
PAPDA – Haïti
Centre de Recherche et d’Action pour le Developpement (CRAD) – Haiti
Ambiente, Desarrollo y Capacitación (ADC ) – Honduras
Rashtriya Raithu Seva Samithi – India
All India Union of Forest Working People AIUFWP – India
Centre for Financial Accountability – India
People First – India
Environics Trust – India
ToxicsWatch Alliance – India
Food Sovereignty Alliance – India
Indonesia for Global Justice (IGJ) – Indonesia
kruha – Indonesia
Wahana Lingkungan Hidup Indonesia (WALHI) – Indonesia
JPIC Kalimantan – Indonesia
تانيا جمعه /منظمه شؤون المراه والطفل – Iraq
ICW-CIF – Italy
PEAH – Policies for Equitable Access to Health – Italy
Focsiv Italian federation christian NGOs – Italy
Schola Campesina APS – Italy
Casa Congo- Italy
ReCommon – Italy
Japan International Volunteer Center (JVC) – Japan
Team OKADA – Japan
taneomamorukai – Japan
VoiceForAnimalsJapan – Japan
Keisen University – Japan
000 PAF NPO – Japan
Missionary Society of Saint Columban, Japan – Japan
Migrants around 60 – Japan
Mura-Machi Net (Network between Villages and Towns) – Japan
Japan Family Farmers Movement (Nouminren) – Japan
Pacific Asia Resorce Center(PARC) – Japan
A Quater Acre Farm-Jinendo – Japan
Friends of the Earth Japan – Japan
Alternative People’s Linkage in Asia (APLA) – Japan
Mekong Watch – Japan
Family Farming Platform Japan – Japan
Africa Japan Forum – Japan
ATTAC Kansai – Japan
ATTAC Japan – Japan
Association of Western Japan Agroecology (AWJA) – Japan
Mennovillage Naganuma – Japan
Phenix Center – Jordan
Mazingira Institute – Kenya
Dan Owala – Kenya
Jamaa Resource Initiatives – Kenya
Kenya Debt Abolition Network – Kenya
Haki Nawiri Afrika – Kenya
Euphrates Institute-Liberia – Liberia
Green Advocates International (Liberia) – Liberia
Sustainable Development Institute (SDI) – Liberia
Alliance for Rural Democracy (ARD) – Liberia
Frères des Hommes – Luxembourg
SOS FAIM – Luxembourg
Collectif pour la défense des terres malgaches – TANY – Madagascar
Third World Network – Malaysia
Appui Solidaire pour le Développement de l’Aide au Développement – Mali
Réseau CADTM Afrique – Mali
Lalo – Mexico
Tosepanpajt A.C – Mexico
Maya sin Fronteras – Mexico
Centro de Educación en Apoyo a la Producción y al Medio Ambiente, A.C. – Mexico
Mujeres Libres COLEM AC – México
Grupo de Mujeres de San Cristóbal Las Casas AC – México
Colectivo Educación para la Paaz y los Derechos Humanos A.C. (CEPAZDH) – México
Red Nacional de Promotoras Rurales – México
Dinamismo Juvenil A.C – México
Cultura Ambiental en Expansión AC – México
Observatorio Universitario de Seguridad Alimentaria y Nutricional del Estado de Guanajuato – México
Centro Interdisciplinario de Investigación y Desarrollo Alternativo U Yich Lu’um AC – México
The Hunger Project México – México
Americas Program/Americas.Org – México
Association Talassemtane pour l’Environnement et Développement (ATED) – Morocco
Espace de Solidarité et de Coopération de l’Oriental – Morocco
LVC Maroc – Morocco
EJNA – Morocco
NAFSN – Morocco
Fédération nationale du secteur agricole – Morocco
Association jeunes pour jeunes – Morocco
Plataforma Mocambicana da Mulher e Rapariga Cooperativistas/AMPCM – MOZAMBIQUE – Mozambique
Justica Ambiental – JA! – Mozambique
Community Empowerment and Social Justice Network (CEMSOJ) – Nepal
WILPF NL – Netherlands
Milieudefensie – Netherlands
Platform Aarde Boer Consument – Netherlands
Both ENDS – Netherlands
Foundation for the Conservation of the Earth,FOCONE – Nigeria
Lekeh Development Foundation (LEDEF) – Nigeria
Nigeria Coal Network – Nigeria
Spire – Norway
Pakistan Fisherfolk Forum – Pakistan
Gaza Urban Agriculture Platform (GUPAP) – Palestine
Union of Agricultural Work Committees – Palestine
WomanHealth Philippines – Philippines
Agroecology X – Philippines
SEARICE – Philippines
Alter Trade Foundation for Food Sovereignty, Inc – Philippines
Association pour la défense des droits à l’eau et à l’assainissement – Sénégal
Biotech Services Sénégal – Sénégal
Association Sénégalaise des Amis de la Nature – Sénégal
Alliance Sénégalaise Contre la Faim et la Malnutrition – Sénégal
Association Sénégalaise des Amis de la Nature – Sénégal
Alliance Sénégalaise Contre la Faim et la Malnutrition – Sénégal
Green Scenery – Sierra Leone
Land for Life – Sierra Leone
JendaGbeni Centre for Social Change Communications – Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone Land Alliance – Sierra Leone
African Centre for Biodiversity – South Africa
African Children Empowerment – South Africa
Cooperative and Policy Alternative Centre – South Africa
Fish Hoek Valley Ratepayers and Residents Association – South Africa
Consciously Organic – South Africa
Wana Johnson Learning Centre – South Africa
Aha Properties – South Africa
Sacred Earth & Storm School – South Africa
Earth Magic – South Africa
Oasis – South Africa
Envirosense – South Africa
Greenstuff – South Africa
WoMin African Alliance – South Africa
Seonae Eco Centre – South Africa
Eco Hope – South Africa
Kos en Fynbos – South Africa
Ghostwriter Grant – South Africa
Mariann Coordinating Committee – South Africa
Khanyisa Education and Development Trust – South Africa
LAMOSA – South Africa
Ferndale Food Forest and Worm Farm – South Africa
Mxumbu Youth Agricultural Coop – South Africa
PHA Food & Farming Campaign – South Africa
SOLdePAZ.Pachakuti – Spain
Amigos de la Tierra – Spain
Sindicato Andaluz de Trabajadores/AS – Spain
Salva la Selva – Spain
Loco Matrifoco – Spain
National Fisheries Solidarity(NAFSO) – Sri Lanka
Movement for Land and Agricultural Reform (MONLAR) – Sri Lanka
Agr. Graduates Cooperatives Union – Sudan
FIAN Sweden – Sweden
FIAN Suisse – Switzerland
Bread for all – Switzerland
Foundation for Environmental Management and Campaign Against Poverty – Tanzania
World Animal Protection – Thailand
Asia Indigenous Peoples Pact – Thailand
PERMATIL – Timor-Leste
Afrique Eco 2100 – Togo
AJECC – Togo
ATGF – Tunisia
Forum Tunisien des Droits Economiques et Sociaux – Tunisia
Agora Association – Turkey
Uganda Land Rights Defenders – Uganda
Hopes for youth development Association – Uganda
Uganda Consortium on Corporate Accountability – Uganda
Centre for Citizens Conserving Environment &Management (CECIC) – Uganda
Buliisa Initiative for Rural Development Organisation (BIRUDO)) – Uganda
Twerwaneho Listeners Club – Uganda
Alliance for Food Soverignity in Africa – Uganda
Global Justice Now – UK
Friends of the Earth International – UK
Compassion in World Farming – UK
Environmental Justice Foundation – UK
Fresh Eyes – UK
War on Want – UK
Friends of the Earth US – US
A Growing Culture – US
Center for Political Innovation – US
GMO/Toxin Free USA – US
Friends of the Earth US – US
Thousand Currents – US
Local Futures – US
National Family Farm Coalition – US
Community Alliance for Global Justice/AGRA Watch – US
Bank Information Center – US
Seeding Sovereignty – US
Yemeni Observatory for Human Rights – Yemen
Zambia Alliance for Agroecology and Biodiversity – Zambia
Zambian Governance Foundation for Civil Society – Zambia
Urban Farming Zimbabwe – Zimbabwe
Centre for Alternative Development – Zimbabwe
FACHIG Trust – Zimbabwe
Red Latinoamericana por Justicia Económica y Social – Latindadd – América Latina
European Coordination Via Campesina – Europe
Arab Watch Coalition – Middle East and North Africa
FIAN International – International
International Alliance of Inhabitants – International
Society for International Development – International
ActionAid International – International
International Accountability Project – International
Habitat International Coalition – General Secretariat – International
CIDSE – International
ESCR-Net – International
World Rainforest Movement – International
Transnational Institute – International
GRAIN – International
Original Source: grian.org
Related posts:

 DR Congo oil palm company bankrolled by development banks unleashes wave of violence against villagers after peaceful protests
DR Congo oil palm company bankrolled by development banks unleashes wave of violence against villagers after peaceful protests
 They should not be called public development banks
They should not be called public development banks
 Open letter to African Development Bank and Nordic Development Fund: Address reprisals against Paten Clan
Open letter to African Development Bank and Nordic Development Fund: Address reprisals against Paten Clan
 CSOs urge banks and other IFIs not to finance E.Africa oil pipeline project…
CSOs urge banks and other IFIs not to finance E.Africa oil pipeline project…
You may like
NGO WORK
Violations against Kenya’s indigenous Ogiek condemned yet again by African Court
Published
3 weeks agoon
January 13, 2026
Minority Rights Group welcomes today’s decision by the African Court on Human and Peoples’ Rights in the case of Ogiek people v. Government of Kenya. The decision reiterates previous findings of more than a decade of unremedied violations against the indigenous Ogiek people, centred on forced evictions from their ancestral lands in the Mau forest.
The Court showed clear impatience concerning Kenya’s failure to implement two landmark rulings in favour of the indigenous Ogiek people: in a 2017 judgment, that their human rights had been violated by Kenya’s denial of access to their land, and in a 2022 judgment, which ordered Kenya to pay nearly 160 million Kenyan shillings (about 1.3 million USD) in compensation and to restitute their ancestral lands, enabling them to enjoy the human rights that have been denied them.
Despite tireless activism from the community and the historic nature of both judgments, Kenya has not implemented any part of either decision. The community remains socioeconomically marginalized as a result of their eviction and dispossession. Evictions have continued, notably in 2023 with 700 community members made homeless and their property destroyed, and in 2020 evicting about 600, destroying their homes in the midst of the Covid-19 pandemic.
Daniel Kobei, Executive Director of the Ogiek Peoples’ Development Program stated, ‘We have been at the African Court six times to fight for our rights to live on our lands as an indigenous people – rights which our government has denied us and continues to violate, compounding our plights and marginalization, despite clear orders from the African Court for our government to remedy the violations. This is the seventh time, and we were hopeful that the Court would be more strict to the government of Kenya in ensuring that a workable roadmap be followed in implementation of the two judgments.’

Kenya has repeatedly justified the eviction of Ogiek as necessary for conservation, although the forest has seen significant harm since evictions began. Many in the community see a connection between their eviction and Kenya’s participation in lucrative carbon credit schemes.
‘The Court’s decision underscores the importance of timely and full implementation of measures imposed on a state which has been found to be in breach of their internationally agreed obligations. Kenya must now repay its debt to the indigenous Ogiek by restituting their land and making reparations, among other remedies ordered by the Court’, said Samuel Ade Ndasi, African Union Advocacy and Litigation Officer at Minority Rights Group.
The decision states, ‘the court orders the respondent state to immediately take all necessary steps, be they legislative or administrative or otherwise, to remedy all the violations established in the judgment on merits.’ The court also reaffirmed that no state can invoke domestic laws to justifiy a breach of international obligations.
Both of the original judgments were historic precedents, breaking new ground on the issue of restitution and compensation for collective violations experienced by indigenous peoples and confirming the vital role of indigenous peoples in safeguarding ecosystems, that states must respect and protect their land rights, that lands appropriated from them in the name of conservation without free, prior and informed consent must be returned, and their right to be the ultimate decision makers about what happens on their lands. Today’s decision adds to this tally of precedents as it is the first decision of the African Court on Human and Peoples’ Rights concerning the record of a state in implementing a binding decision.
The case
In October 2009, the Kenyan government, through the Kenya Forestry Service, issued a 30-day eviction notice to the Ogiek and other settlers of the Mau Forest, demanding that they leave the forest. Concerned that this was a perpetuation of the historical land injustices already suffered, and having failed to resolve these injustices through repeated national litigation and advocacy efforts, the Ogiek decided to lodge a case against their government before the African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights with the assistance of Minority Rights Group, the Ogiek Peoples’ Development Program and the Centre for Minority Rights Development. The African Commission issued interim measures, which were flouted by the Government of Kenya and thereafter referred the case to the African Court based on the complementarity relationship between the African Commission and the African Court on Human and Peoples’ Rights and on the grounds that there was evidence of serious or massive human rights violations.
On 26 May 2017, after years of litigation, a failed attempt at amicable settlement and an oral hearing on the merits, the African Court on Human and Peoples’ Rights rendered a merits judgment in favour of the Ogiek people. It held that the government had violated the Ogiek’s rights to communal ownership of their ancestral lands, to culture, development and use of natural resources, as well as to be free from discrimination and practise their religion or belief. On 23 June 2022, the Court rejected Kenya’s objections and set out the reparations owed for the violations established in the 2017 judgment.
Source: minorityrights.org
Related posts:

 Trauma and Land Loss: New Study Focuses on Mental Health of Evicted Indigenous People
Trauma and Land Loss: New Study Focuses on Mental Health of Evicted Indigenous People
 Justice Denied: East African Court of Justice Grants Tanzanian Government Impunity to Trample Human Rights of the Maasai
Justice Denied: East African Court of Justice Grants Tanzanian Government Impunity to Trample Human Rights of the Maasai
 EACOP: East African Court of Justice will hear arguments on court’s jurisdiction
EACOP: East African Court of Justice will hear arguments on court’s jurisdiction
 Tanzanian High Court Tramples Rights of Indigenous Maasai Pastoralists to Boost Tourism Revenues
Tanzanian High Court Tramples Rights of Indigenous Maasai Pastoralists to Boost Tourism Revenues
NGO WORK
Climate wash: The World Bank’s Fresh Offensive on Land Rights
Published
3 months agoon
November 13, 2025
Climate wash: The World Bank’s Fresh Offensive on Land Rights reveals how the Bank is appropriating climate commitments made at the Conference of the Parties (COP) to justify its multibillion-dollar initiative to “formalize” land tenure across the Global South. While the Bank claims that it is necessary “to access land for climate action,” Climatewash uncovers that its true aim is to open lands to agribusiness, mining of “transition minerals,” and false solutions like carbon credits – fueling dispossession and environmental destruction. Alongside plans to spend US$10 billion on land programs, the World Bank has also pledged to double its agribusiness investments to US$9 billion annually by 2030.
This report details how the Bank’s land programs and policy prescriptions to governments dismantle collective land tenure systems and promote individual titling and land markets as the norm, paving the way for private investment and corporate takeover. These reforms, often financed through loans taken by governments, force countries into debt while pushing a “structural transformation” that displaces smallholder farmers, undermines food sovereignty, and prioritizes industrial agriculture and extractive industries.
Drawing on a thorough analysis of World Bank programs from around the world, including case studies from Indonesia, Malawi, Madagascar, the Philippines, and Argentina, Climatewash documents how the Bank’s interventions are already displacing communities and entrenching land inequality. The report debunks the Bank’s climate action rhetoric. It details how the Bank’s efforts to consolidate land for industrial agriculture, mining, and carbon offsetting directly contradict the recommendations of the IPCC, which emphasizes the protection of lands from conversion and overexploitation and promotes practices such as agroecology as crucial climate solutions.
Read full report: Climatewash: The World Bank’s Fresh Offensive on Land Rights
Source: The Oakland Institute
Related posts:

 30 civil society organizations have written to the World Bank Group demanding to publicly disclose the Africa Energy Approach paper.
30 civil society organizations have written to the World Bank Group demanding to publicly disclose the Africa Energy Approach paper.
 World Bank’s new scheme to privatize land in the developing world exposed
World Bank’s new scheme to privatize land in the developing world exposed
 World Bank is backing dozens of new coal projects, despite climate pledges
World Bank is backing dozens of new coal projects, despite climate pledges
 Communities Under Siege: New Report Reveals World Bank Failures in Safeguard Compliance and Human Rights Oversight in Tanzania
Communities Under Siege: New Report Reveals World Bank Failures in Safeguard Compliance and Human Rights Oversight in Tanzania
NGO WORK
Africa’s Land Is Not Empty: New Report Debunks the Myth of “Unused Land” and Calls for a Just Future for the Continent’s Farmland
Published
3 months agoon
November 13, 2025
A new report challenges one of the most persistent and harmful myths shaping Africa’s development agenda — the idea that the continent holds vast expanses of “unused” or “underutilised” land waiting to be transformed into industrial farms or carbon markets.
Titled Land Availability and Land-Use Changes in Africa (2025), the study exposes how this colonial-era narrative continues to justify large-scale land acquisitions, displacements, and ecological destruction in the name of progress.
Drawing on extensive literature reviews, satellite data, and interviews with farmers in Zambia, Mozambique, South Africa, and Zimbabwe, the report systematically dismantles five false assumptions that underpin the “land abundance” narrative:
-
That Africa has vast quantities of unused arable land available for cultivation
-
That modern technology can solve Africa’s food crisis
-
That smallholder farmers are unproductive and incapable of feeding the continent
-
That markets and higher yields automatically improve food access and nutrition
-
That industrial agriculture will generate millions of decent jobs
Each of these claims, the report finds, is deeply flawed. Much of the land labelled as “vacant” is, in reality, used for grazing, shifting cultivation, foraging, or sacred and ecological purposes. These multifunctional landscapes sustain millions of people and are far from empty.
The study also shows that Africa’s food systems are already dominated by small-scale farmers, who produce up to 80% of the continent’s food on 80% of its farmland. Rather than being inefficient, their agroecological practices are more resilient, locally adapted, and socially rooted than the industrial models promoted by external donors and corporations.
Meanwhile, the promise that industrial agriculture will lift millions out of poverty has not materialised. Mechanisation and land consolidation have displaced labour, while dependency on imported seeds and fertilisers has trapped farmers in cycles of debt and dependency.
A Continent Under Pressure
Beyond these myths, the report reveals a growing land squeeze as multiple global agendas compete for Africa’s territory: the expansion of mining for critical minerals, large-scale carbon-offset schemes, deforestation for timber and commodities, rapid urbanisation, and population growth.
Between 2010 and 2020, Africa lost more than 3.9 million hectares of forest annually — the highest deforestation rate in the world. Grasslands, vital carbon sinks and grazing ecosystems, are disappearing at similar speed.
Powerful actors — from African governments and Gulf states to Chinese investors, multinational agribusinesses, and climate-finance institutions — are driving this race for land through opaque deals that sideline local communities and ignore customary tenure rights.
A Call for a New Vision
The report calls for a radical shift away from high-tech, market-driven, land-intensive models toward people-centred, ecologically grounded alternatives. Its key policy recommendations include:
-
Promoting agroecology as a pathway for food sovereignty, ecological regeneration, and rural livelihoods.
-
Reducing pressure on land by improving agroecological productivity, cutting food waste, and prioritising equitable distribution.
-
Rejecting carbon market schemes that commodify land and displace communities.
-
Legally recognising customary land rights, particularly for women and Indigenous peoples.
-
Upholding the principle of Free, Prior, and Informed Consent (FPIC) for all land-based investments.
This report makes it clear: Africa’s land is not “empty” — it is lived on, worked on, and cared for. The future of African land must not be dictated by global capital or outdated development theories, but shaped by the people who depend on it.
Download the Report
Read the full report Land Availability and Land-Use Changes in Africa (2025) to explore the evidence and policy recommendations in detail.
Related posts:

 Financial Institutions from Africa have made a monumental commitment of $100 billion to Africa’s green industrialization, a decision of immense significance that has the potential to shape Africa’s future.
Financial Institutions from Africa have made a monumental commitment of $100 billion to Africa’s green industrialization, a decision of immense significance that has the potential to shape Africa’s future.
 Africa adopts the Africa Climate Innovation Compact (ACIC) Declaration to drive the continent towards innovative climate solutions.
Africa adopts the Africa Climate Innovation Compact (ACIC) Declaration to drive the continent towards innovative climate solutions.
 One in three people sleeps on an empty stomach – World Bank Report.
One in three people sleeps on an empty stomach – World Bank Report.
 Transforming Africa’s livestock sector is key to food security-Report
Transforming Africa’s livestock sector is key to food security-Report

Why govt is launching a comprehensive digital land registry

Witness Radio and Seed Savers Network are partnering to produce radio content to save indigenous seeds in Africa.

Evicted from their land to host Refugees: A case of Uganda’s Kyangwali refugee settlement expansion, which left host communities landless.

Women environmental rights defenders in Africa are at the most significant risk of threats and attacks – ALLIED New report

Will Uganda’s next government break the land-grabbing cycle?

Women environmental rights defenders in Africa are at the most significant risk of threats and attacks – ALLIED New report

Swedish pension fund drops TotalEnergies amid rising EACOP risks

Land tenure security as an electoral issue: Museveni warns Kayunga land grabbers, reaffirms protection of sitting tenants.

Innovative Finance from Canada projects positive impact on local communities.
Over 5000 Indigenous Communities evicted in Kiryandongo District
Petition To Land Inquiry Commission Over Human Rights In Kiryandongo District
Invisible victims of Uganda Land Grabs
Resource Center
- Land And Environment Rights In Uganda Experiences From Karamoja And Mid Western Sub Regions
- REPARATORY AND CLIMATE JUSTICE MUST BE AT THE CORE OF COP30, SAY GLOBAL LEADERS AND MOVEMENTS
- LAND GRABS AT GUNPOINT REPORT IN KIRYANDONGO DISTRICT
- THOSE OIL LIARS! THEY DESTROYED MY BUSINESS!
- RESEARCH BRIEF -TOURISM POTENTIAL OF GREATER MASAKA -MARCH 2025
- The Mouila Declaration of the Informal Alliance against the Expansion of Industrial Monocultures
- FORCED LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA TRENDS RIGHTS OF DEFENDERS IMPACT AND CALL FOR ACTION
- 12 KEY DEMANDS FROM CSOS TO WORLD LEADERS AT THE OPENING OF COP16 IN SAUDI ARABIA
Legal Framework
READ BY CATEGORY
Newsletter
Trending
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week agoWomen environmental rights defenders in Africa are at the most significant risk of threats and attacks – ALLIED New report
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks agoUganda moves toward a Bamboo Policy to boost environmental conservation and green growth.
-

 FARM NEWS1 week ago
FARM NEWS1 week ago200 farmers demonstrate at parliament, worried about new seed monopoly
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK4 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK4 days agoEvicted from their land to host Refugees: A case of Uganda’s Kyangwali refugee settlement expansion, which left host communities landless.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK4 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK4 days agoWitness Radio and Seed Savers Network are partnering to produce radio content to save indigenous seeds in Africa.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 day ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 day agoWhy govt is launching a comprehensive digital land registry


