By Witness Radio Team.
Emotions, tears, and testimonies exposing the dark side of industrial agriculture rocked activities to mark the International Day of Struggle against industrial plantations 2024 celebrations in Uganda.
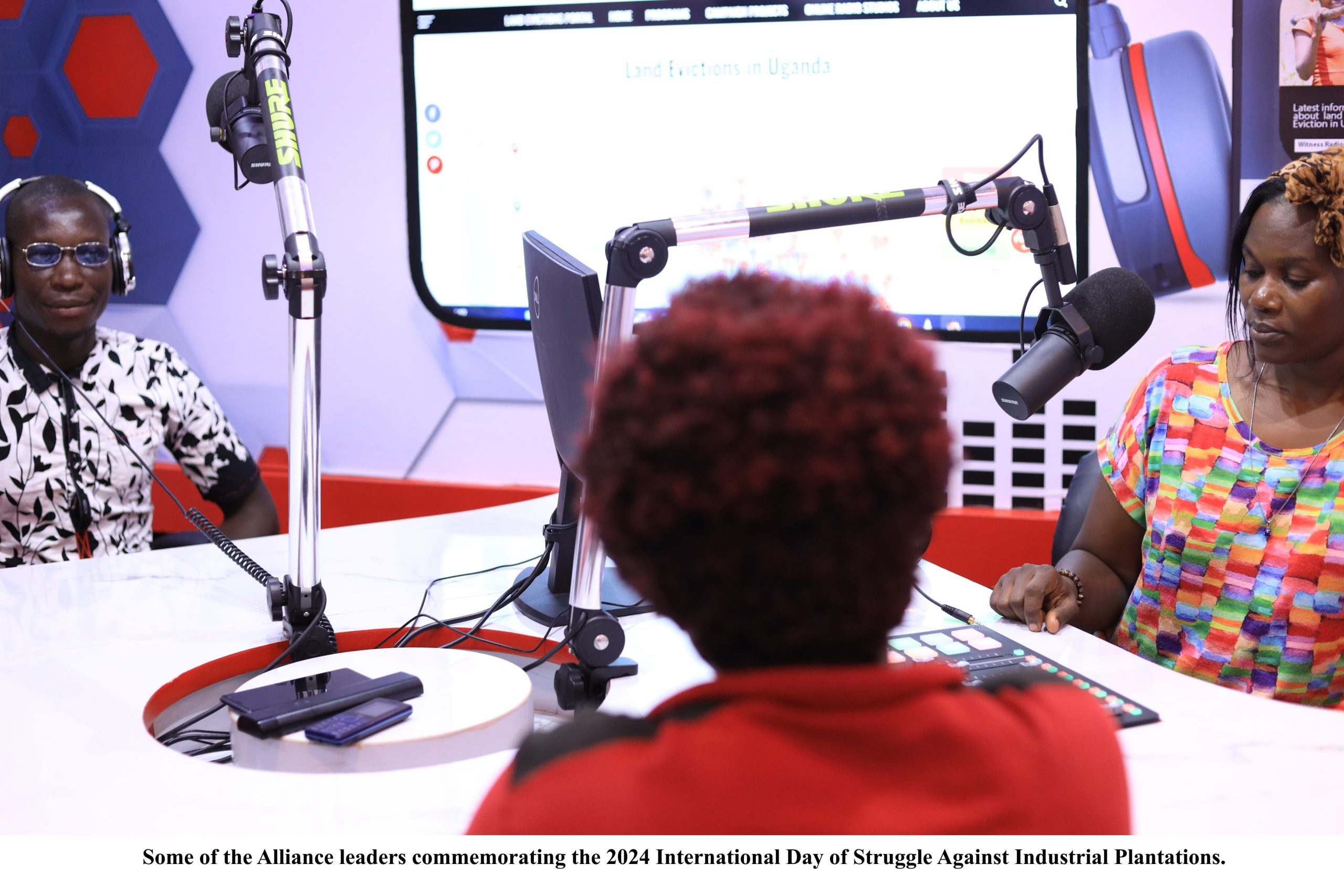
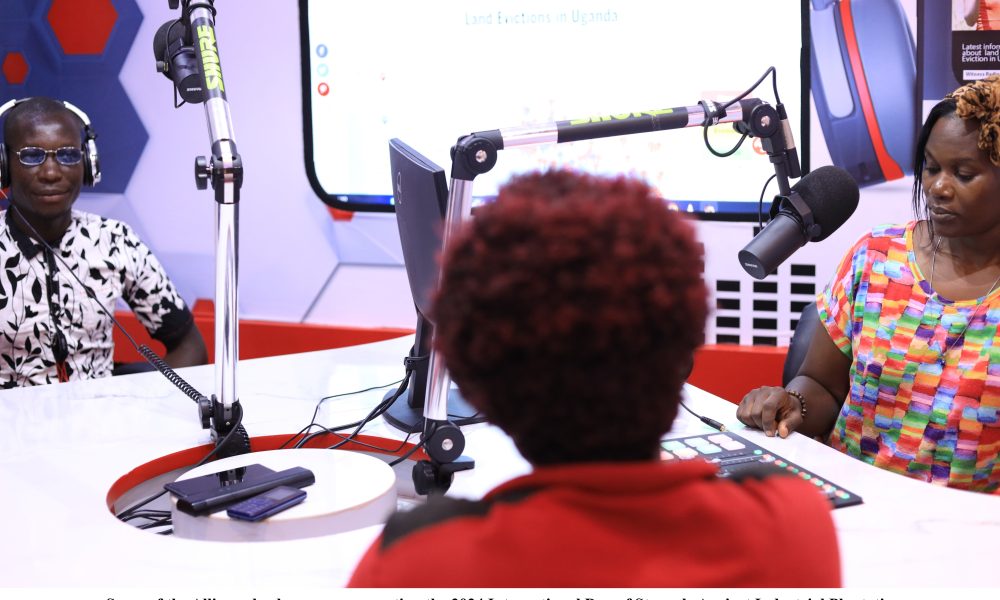
The day, celebrated in Uganda for the first time, began with a live radio talk show on Witness Radio, broadcast in the local dialect. Leaders of communities affected by industrial plantations in Uganda, under their umbrella organization—the Informal Alliance for Communities Affected by Irresponsible Land-Based Investments—shared harrowing accounts of forced evictions, lack of compensation, and broken promises by industrial plantation investors, all of which have escalated poverty and worsened the hunger crisis.
The Ugandan Alliance united with global informal alliances to collectively resist the rapid expansion of industrial plantations. Together, they resist increasing irresponsible land-based investments, threatening local communities’ human rights and destroying the environment. The day is commemorated every September 21st of the year.
Ugandan smallholder farmers are hugely under attack as their lands are being grabbed for large-scale industrial plantations despite being among the world’s largest food producers.
The 2021 report by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), titled “Which farms feed the world and has farmland become more concentrated?”, revealed that small-scale farmers produce up to 70%- 80% of the world’s food and contribute nearly a third of the global food supply.
During the one-hour radio program, the Alliance leaders representing Kiryandongo communities revealed that investors illegally evicted them to make way for coffee, maize, soya, and sugar cane plantations; Kalangala communities are victims of palm oil plantations; and Mubende communities are victims of carbon offset tree plantations, among other communities. They revealed that their communities were dumped in abject poverty while the industrial plantations made huge profits after forceful evictions.
“Millions of Ugandans have been brutally evicted for profit. They have not been compensated or resettled, and what is replacing their lands are plantations that serve no purpose to the common person since most the crops in the plantations serve an international market.” Akiteng Stella, the Informal Alliance Chairperson, was evicted from her land in Kiryandongo to make way for sugarcane plantations.
Akiteng added that people who once grew their food crops on fertile lands have been reduced to paupers in their own countries, as they no longer have land to farm.
“Ideally, there are many challenges facing these communities, and now their only means of survival is working on the investors’ plantations. So, you wonder how a former landlord earning millions of Uganda shillings each season from their land can be reduced to a casual laborer to earn a monthly salary of nearly 200,000/: Uganda shillings? Is that true development or simply profiting off our land and workforce?”
Currently, big corporations are promoting large-scale industrial agriculture, backed by significant funding from entities like the World Bank, claiming it’s the way to go for food security and climate protection.
While doing so, they have received criticism that their businesses are doing the opposite. Recently, African faith leaders, alongside hundreds of civil society and farmer groups, revealed that industrialized plantations had done more harm than good, increasing poverty, exacerbating food insecurity, eroding local seed varieties, and degrading the environment across Africa. The faith leaders said that the promoted initiatives have increased dependence on expensive farm inputs, eroded local seed varieties, degraded soil fertility, and weakened farmers’ resilience to climate shocks like drought.
However, the expansion of industrial plantations serves only the interests of investors and governments, as many of these ventures are backed by influential government figures. For example, the so-called development that the New Forests Company claimed to have brought to the community in Mubende District can only be applauded by those who choose to disregard the realities on the ground.
Being evicted from fertile lands without compensation and abandoned in the wilderness feels incomprehensible to someone accustomed to actively farming their land and relying on agriculture for daily survival. According to its Senior Corporate Social Responsibility Programme Manager, Mr. Alex Kyabawampi, the company fully compensated the affected residents.
However, the leaders of the affected residents questioned what the company called compensation. Saying that even those who were allegedly compensated received land that was practically worthless, hilly and rocky terrain that yielded nothing, and to make matters worse, the residents were reportedly instructed to use the same land to plant more trees for the company.
“People are starving day and night. They resettled to a terrible place, and nothing could grow on it. Moreover, the land allocation was not done fairly—you find older adults being given land on top of a hill. How are they expected to reach it? People should come to the ground to witness our suffering,” Julius Ndagize revealed angrily during the radio program, adding that people are dying helplessly with nowhere to bury their dead, children are becoming malnourished, and families are being torn apart.
In the 2023 Global Hunger Index, Uganda ranked 95th out of 125 countries with a score of 25.2, highlighting the severity of the problem. Alliance leaders argue that this is the result of industrial farms. “Take, for instance, Kiryandongo, where over 35,000 people were illegally evicted to make way for industrial plantations. They could have contributed to food production if these individuals had been meaningfully engaged and empowered on their land,” Beryaija Benon, chairman of the Kiryandongo affected communities, wondered.
According to the World Bank’s compensation and resettlement guidelines, a person evicted from their land is entitled to a range of measures comprising compensation, income restoration support, transfer assistance, income restoration, and relocation support, which are due to affected people, depending on the nature of their losses, to restore their economic and social base.
Not only are people suffering, but the environment is also being harmed. For instance, Julius Ndagize, the leader of communities affected by New Forest Company evictions in Mubende, explained how the replacement of Indigenous trees with eucalyptus and pines has destroyed the environment. The loss of natural trees, critical for rainfall, has extended the dry season, delaying farming seasons and worsening food shortages.
“When these companies arrive, they destroy the environment. They cut down our indigenous trees, which contribute to rainfall formation, and replace them with trees that don’t support it. In Mubende, by July, we should be planting maize, Irish potatoes, and other crops, but nowadays, we can go as late as September without rain. In Kalangala, they planted palm oil trees near Lake Victoria, and these trees are sprayed with chemicals, including fertilizers. When it rains, runoff from the plantations flows into the lake, causing severe consequences for the lake and the people who depend on it,” said Julius.
Despite the hardships, the Informal Alliance continues to fight for the rights of affected communities. Their movement spans Uganda, mobilizing, sensitizing, and equipping communities with the knowledge to resist industrial plantation land grabs.
“We are reaching every corner of Uganda to mobilize and sensitize communities, broadening the fight against these land grabs. You have heard the stories of people suffering, and many more continue to face the same fate as a result of their expansion. We are urging communities to resist these land grabs,” revealed Nakato Priscilla, the Alliance’s vice chairperson.
She added, “As an alliance, they regularly hold meetings to evaluate their progress, educate people about their land rights, and assist in following up on cases, such as arrests by the police and in courts of law, to ensure that the law addresses the issues raised.”
Further, the Alliance emphasized that their movement is not against development or investors but insists that land acquisitions follow proper procedures. “We want investors to seek consent from communities, pay fairly for the land they take, and offer meaningful resettlement,” said Benon Beryaija, a member of the Alliance.
The Alliance urges the Ugandan government to compensate affected communities and that future investors use unoccupied land to avoid further displacements.