MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
61 CSOs want Ramsar Wetlands affected by EACOP and Tilenga projects in Uganda and Tanzania to be listed in the Montreux Record.
Published
2 years agoon
By Witness Radio team
As the Africa Climate Summit kicks off in Nairobi-Kenya today, at least 61 African Civil Society organizations (CSOs) have petitioned the Secretary-General of the Ramsar Wetlands Secretariat of International Importance demanding that the Ramsar Wetlands, which have experienced adverse impacts due to the East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP) and Tilenga projects in Uganda and Tanzania, be included in the Montreux Record.
EACOP is a project implemented by TotalEnergies and China National Offshore Oil Corporation (CNOOC). TotalEnergies is also the operator of the Tilenga project, with Uganda National Oil Company (UNOC) and China National Offshore Oil Corporation (CNOOC) as the partners.
The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands defines the Montreux Record as a register of wetland sites on the list of Wetlands of International Importance where changes in ecological character have occurred, are occurring, or are likely to occur as a result of technological developments, pollution, or other human interference.
The petition call for the Ramsar secretariat intervention comes at a time when Kenya and the African Union are organizing a three-day (4th to 6th September) Africa climate summit themed Driving Green Growth & Climate Finance Solutions for Africa and the World.
The Africa Climate Summit is aimed at addressing the increasing exposure to climate change and its associated costs, both globally and particularly in Africa. The Summit is a platform to inform, frame, and influence commitments, pledges, and outcomes, ultimately leading to the development of the Nairobi Declaration.
The CSOs are urging the Ramsar Secretariat should intervene and safeguard the Ramsar wetlands that have been affected, or could be affected, by oil activities in Uganda, Tanzania, and the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC).
CSOs’ action comes at a time when TotalEnergies, CNOOC, and the Ugandan government are developing the Tilenga and East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP) projects. The Tanzanian government is a co-developer of the EACOP alongside TotalEnergies, CNOOC, and the Ugandan government.
It’s evident that part of the Tilenga upstream project in Uganda lies within the boundaries of the Murchison Falls-Albert Delta Ramsar wetland, situated within the Murchison Falls National Park (MFNP).
Furthermore, the EACOP, a planned 1,443-kilometer pipe line is running from the Tilenga and Kingfisher oil fields in Uganda to the port of Tanga in Tanzania, poised to impact more than 158 wetland sections in Uganda.
According to the petition, several wetlands connected to Ramsar-designated sites in Uganda encompass: Kibale/Bukoora, Kisoma, Kasemugiri, Jemakunya and Katonga. The Ramsar sites that connect to the aforesaid wetlands include the Sango Bay-Musambwa Island-Kagera (SAMUKA) Ramsar Wetland System, which has an economic value of USD 117 million per year (Sango Bay only) and Nabajjuzi Ramsar Wetland.
In the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), the Congolese government launched an oil exploration licensing round for 27 oil and three (3) gas blocks in July 2022. Some blocks cover Virunga National Park, which contains a Ramsar site. The CSOs call for the Ramsar Secretariat to add Virunga National Park.
Dickens Kamugisha, a Director at the Africa Institute for Energy Governance (AFIEGO) in Uganda says, “We are worried about the high pollution risk that the Tilenga and EACOP projects pose to Ramsar wetlands in Uganda, Tanzania, and the DRC. The Victoria Nile Crossing is within the boundaries of the Murchison Falls-Albert Delta Ramsar site.”
He expressed his concerns about the substantial pollution risk presented by the Tilenga and EACOP projects to the Ramsar wetlands in Uganda, Tanzania, and the DRC. He emphasized that the Victoria Nile Crossing, situated within the confines of the Murchison Falls-Albert Delta Ramsar site, is particularly worrying.
Mr. Kamugisha further emphasized that while TotalEnergies has made promises regarding biodiversity conservation during its oil exploitation activities within Ramsar wetlands and other biodiverse regions, it is challenging to trust these assurances. He cited instances in Uganda and Tanzania where they struggled to manage the impacts arising from compulsory land acquisition processes for the Tilenga and EACOP projects, along with difficulties related to flooding, as well as dust, noise, and light pollution caused by the Tilenga project in Buliisa district, Uganda.
Bantu Lukambo, representing, the Innovation pour le Développement et la Protection de l’Environnement (IDPE) in the DRC, says Virunga National Park, which doubles as a Ramsar site and a UNESCO World Heritage Site is at a risk because the DRC government has been emboldened by Uganda’s example. Because the world looks on as oil exploitation goes on in MFNP, Lukambo adds, the Congolese government also developed the courage to put oil blocks covering Virunga up for exploration licensing in July 2022. Moreover, the construction of the EACOP will make oil exploitation in the DRC Albertine Graben more viable.”
Mr. Lukambo called upon international bodies, such as the Ramsar Secretariat, to act and engage with the Ugandan, Tanzanian, and Congolese governments to halt any oil exploitation plans that could affect Ramsar sites.
Ms. Patience Katusiime from the Environment Governance Institute in Uganda reveals that the mapping analysis shows that TotalEnergies is already constructing seven of the ten well pads that are to be located within MFNP and two of the pads are too close to the Murchison Falls-Albert Delta Ramsar site.
“This is disheartening to see. The large swathes of the park have been pockmarked by oil exploration wells, roads, and other infrastructure. TotalEnergies often says that they are using a small part of the park but these new satellite images show that a combination of oil roads, bridges, oil feeder pipelines, and well pads could destroy the park.” Ms. Katusiime says.
She adds, “No well-meaning institution, including the Ugandan government, Ramsar Secretariat, financial institutions, export credit agencies, and others should support TotalEnergies in its oil exploitation misadventures in our national park. The above institutions should call on TotalEnergies to invest in renewable energy instead of oil projects.”
Mr. Richard Sekondo of the Organisation for Community Engagement (OCE) in Tanzania says, “Along the Tanzanian shore, two important Ecologically or Biologically Significant Marine Areas (EBSAs) – the Pemba-Shimoni-Kisite site and the Tanga Coelacanth site – are at high risk from oil leaving the port at Tanga. These EBSAs host several Marine Protected Areas, as well as Mangrove Forest Reserves. The Pemba-Shimoni-Kisite site is known for its coral reefs, as well as the endemic coconut crab (Birgus latro), the largest land-living arthropod. These need to be protected.”
Related posts:

 A reference filed by CSOs against the planned construction of the East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP) is set for hearing.
A reference filed by CSOs against the planned construction of the East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP) is set for hearing.
 EACOP Was Anchored On Disinformation, Persons Affected By Pipeline Declare
EACOP Was Anchored On Disinformation, Persons Affected By Pipeline Declare
 Breaking: Criminal trial for seven community defenders opposed to EACOP/Tilenga project forced land eviction has been fixed.
Breaking: Criminal trial for seven community defenders opposed to EACOP/Tilenga project forced land eviction has been fixed.
 “Our Trust is Broken”: Oil Pipeline Project Impoverishes Thousands
“Our Trust is Broken”: Oil Pipeline Project Impoverishes Thousands
You may like
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
CSOs push for reforms at the KFW Accountability Mechanism after experts discovered that it has weak remedies in addressing grievous harms caused by its investments.
Published
10 hours agoon
February 24, 2026
By Witness Radio Team
Germany’s state-owned development bank, KfW, is facing renewed scrutiny as Civil Society Organizations (CSOs) issue detailed recommendations to reform its Complaint Mechanism, citing systemic failures to prevent harm, address reprisals, and ensure accountability in projects it finances across developing countries.
The recommendations follow the release of “Irresponsible Banking”, a report by the Coalition for Human Rights in Development launched in September 2025, which documented alleged links between KfW-backed projects and land dispossession, environmental degradation, and threats against human rights defenders (HRDs).
The report documented cases in Indonesia, Mexico, and Tanzania in which affected communities claimed to have faced intimidation, livelihood losses, and violations of their right to Free, Prior, and Informed Consent (FPIC) by KFW-backed projects.
In response, a coalition of organizations, including Asia Indigenous Peoples Network on Extractive Industries and Energy (AIPNEE), Community Empowerment and Social Justice Network (CEMSOJ), Defenders in Development Campaign (DiD), and Protection International, has submitted over 20 detailed recommendations aimed at fundamentally strengthening the independence, transparency, and effectiveness of KfW’s Complaint Mechanism.
Some of the key recommendations include a call for structural independence, a separate budget for the mechanism established and managed independently of the management of the KFW Bank, taking into consideration reprisals suffered by project-affected people, and mentioning that the Complaints Office will commit to implementing a more comprehensive approach, looking beyond individual complainants, among others.
These proposals stem from documented concerns that communities affected by KfW-funded projects struggle to access meaningful remedies.
According to the KFW irresponsible banking report, projects branded as sustainable and pro-development have, in several cases, been linked with forced displacement, inadequate consultation, and reprisals against those who speak out.
“KfW calls it ‘responsible banking’, but it’s using German taxpayers’ money to bankroll projects that displace Indigenous Peoples, destroy ecosystems, and endanger human rights defenders. If KfW wants to demonstrate real responsibility, it needs to listen to local communities and ensure their voices are not silenced.” Dalile Antunez, collaborative researcher at the Coalition for Human Rights in Development.
Being fully owned by the German government, CSOs emphasize that its operations must align with the United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights and Germany’s Supply Chain Due Diligence Act.
According to the United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights, business enterprises are expected to respect human rights, meaning they should avoid infringing on others’ human rights and address adverse human rights impacts with which they are involved. This is in addition to Germany’s Supply Chain Due Diligence Act, which requires enforcement of corporate accountability for human rights and environmental standards across global operations.
But such standards have never been adhered to by development projects such as KFW-funded projects.
KfW bank is further urged to adopt a comprehensive anti-reprisals framework, including concrete measures such as suspending project disbursements where threats persist, documenting all reported reprisals in a public registry, providing emergency assistance where needed, and communicating incidents to oversight bodies such as the German Institute for Human Rights.
Civil society groups argue that these recommendations demonstrate the need not only for stronger safeguards but also for genuine participation by affected communities in remedial processes.
The recommendations, therefore, propose that complainants have the authority to choose whether their case proceeds through dispute resolution, prior resolution, or compliance review.
They also call for guaranteed access to all information used in decision-making, publication of both admissible and inadmissible complaints, and extended deadlines for filing complaints to account for delayed discovery of harm.
Additionally, CSOs advocate for a simplified complaint process that allows grievances to be submitted orally or through accessible channels, recognizing the barriers faced by remote or marginalized communities.
“Many Indigenous communities in remote areas may face barriers such as limited access to technical support or a lack of experience in preparing formal written complaints, particularly in the absence of supporting NGOs. So, they should be able to file complaints verbally or in other forms and through various channels. The current system is overly complex, creating barriers for communities to submit grievances independently without supporting NGOs,” reads part of the recommendations.
CSOs argue that unless KfW Bank strengthens the independence of its Complaint Mechanism and adopts enforceable protections against reprisals, its sustainability commitments risk remaining utopian rather than realistic and transformative.
Related posts:

 CSOs call for meaningful changes in the World Bank’s Dispute Resolution Service to foster access to justice for project-affected communities.
CSOs call for meaningful changes in the World Bank’s Dispute Resolution Service to foster access to justice for project-affected communities.
 Joint Statement on World Bank Accountability Mechanism’s Decision to Limit Application of Operating Procedures
Joint Statement on World Bank Accountability Mechanism’s Decision to Limit Application of Operating Procedures
 Witness Radio, private companies, CSOs and local government officials are meeting to discuss alternative remedies to salvage the appalling land and environmental rights situation in Kiryandongo district.
Witness Radio, private companies, CSOs and local government officials are meeting to discuss alternative remedies to salvage the appalling land and environmental rights situation in Kiryandongo district.
 U.S. Congress Requires USAID to Create an Accountability Mechanism.
U.S. Congress Requires USAID to Create an Accountability Mechanism.
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
UPDF General on the spot over fresh evictions in Hoima
Published
1 week agoon
February 17, 2026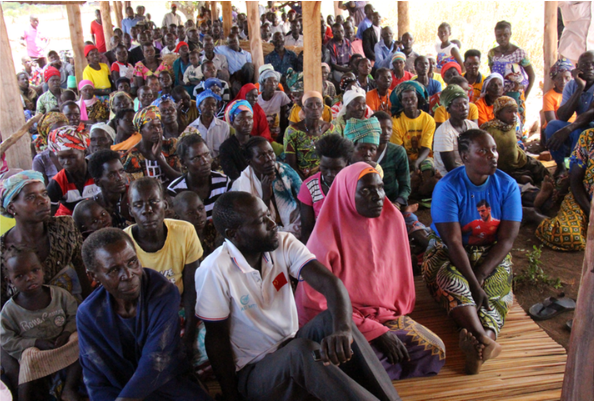
Over 1,000 residents in Kapapi Sub-County, Hoima District, are facing a second forced eviction from their ancestral land in three years, sparking widespread tension and anger among the community.
The latest evictions have been linked to a senior Uganda Peoples’ Defence Forces (UPDF) officer, Brigadier General Peter Nabasa, whom residents accuse of masterminding the displacement, allegedly in defiance of earlier government directives issued by the state minister for Lands, Dr. Sam Mayanja.
In October 2025, Minister Mayanja ordered that over 1,000 families who had been evicted from contested land in Kapapi Sub-County be resettled back onto their bibanja.
He also directed security commanders in the area to withdraw armed personnel and allow the affected communities to return. However, residents claim the situation has worsened, with renewed evictions pushing thousands into uncertainty once again.
The affected families, estimated to be over 1,000 and comprising over 4,000 people, include both cultivators and pastoralists. They were evicted from their homes in several villages, including Waaki North, Kapapi Central, Waaki South, Runga, Kiryatete, and Kiganja, all located in Kapapi and Kiganja sub-counties, Hoima District.
Residents insist the land has been their home for decades, passed down through generations, and accuse powerful individuals of using land titles and security enforcement to displace them.
“We were returned to our land in October last year on the orders of President Museveni and Minister Mayanja, but shortly after the elections, we were evicted again,” said Deusi Mugume, a resident of Runga.
“The Brigadier General came with armed security personnel and ordered us to vacate the land immediately. They even fired bullets in the air to disperse us, disrespecting the orders of both the Minister and the President.”
The residents were evicted from two titled pieces of land said to belong to businessmen and private individuals based in Hoima and Kampala. One of the contested titles measures approximately 2,545 acres (1,030 hectares) and is reportedly owned by seven individuals, including Ndahura William Gafayo, Aston Muhwezi, Alex Kyamanywa, Nathan Kiiza Byarugonjo, Bahuzya, Monica Rwashadika, and Wilber Kiiza. This land reportedly covers parts of Kapapi and Kiganja sub-counties.
Another title, measuring about three square miles, is said to belong to the family of the late Tito Byangire of Kigorobya, Hoima District. This land reportedly covers four villages, including Waaki South, Waaki North, Runga, Kapapi Central, and Kiryatete.
Brig Gen Nabasa claims he legally leased 700 acres of land from the Byangire family for 10 years starting in 2023.
“The residents were allowed to live there temporarily because elections were approaching, but they were supposed to leave immediately after the polls,” he said.
The residents, who are now living in temporary structures in Rwenyana, say their food and cash crops were destroyed after cattle were introduced onto the land following their eviction.
“We are going through many difficulties. We have no food, we are sleeping in makeshift shelters, children are not going to school, and we don’t know if we shall ever return to our land,” said Madinah Nyanjura and Nyarabiraho Cheya, both residents of Kapapi.
The Hoima Deputy Resident District Commissioner, Christopher Aine, blamed land brokers for misleading residents and bringing more people onto the contested land.
Minister Mayanja had previously directed the arrest of Brig Gen Peter Nabasa, Capt Rogers Karamagi, former Hoima Deputy Resident District Commissioner Michael Muramira Kyakashari, and William Ndahura Gafayo for allegedly illegally evicting residents from their bibanja land.
Mr Joshua Byangire, one of the administrators of the late Byangire estate, said the family has faced continued disruption and appealed to the government to buy off the land title.
“We have been disturbed on our family land. I request the government to buy off our land title. I don’t understand why soldiers have been deployed there, yet we are civilians and cannot access our property,” he said.
Original Source: monitor.co.ug
Related posts:

 Breaking: The army general, police chief, presidential representative, and others are appearing before the Hoima Chief Magistrate court today.
Breaking: The army general, police chief, presidential representative, and others are appearing before the Hoima Chief Magistrate court today.
 Court issues fresh criminal summonses against army general, police chief and presidential representative and others in a private criminal case.
Court issues fresh criminal summonses against army general, police chief and presidential representative and others in a private criminal case.
 Over 500 Kapapi families in Hoima district remain stranded after the district security committee fails to resettle them back on their land as directed by the minister.
Over 500 Kapapi families in Hoima district remain stranded after the district security committee fails to resettle them back on their land as directed by the minister.
 UPDF General, District Police Commander, and Presidential Representative defy Court summonses for the second time as DPP takes over the EACOP-PAP’s case.
UPDF General, District Police Commander, and Presidential Representative defy Court summonses for the second time as DPP takes over the EACOP-PAP’s case.
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
Small-scale fishers and coastal communities are pushing to testify before a human rights commission investigating the causes of food inequality in South Africa.
Published
1 week agoon
February 17, 2026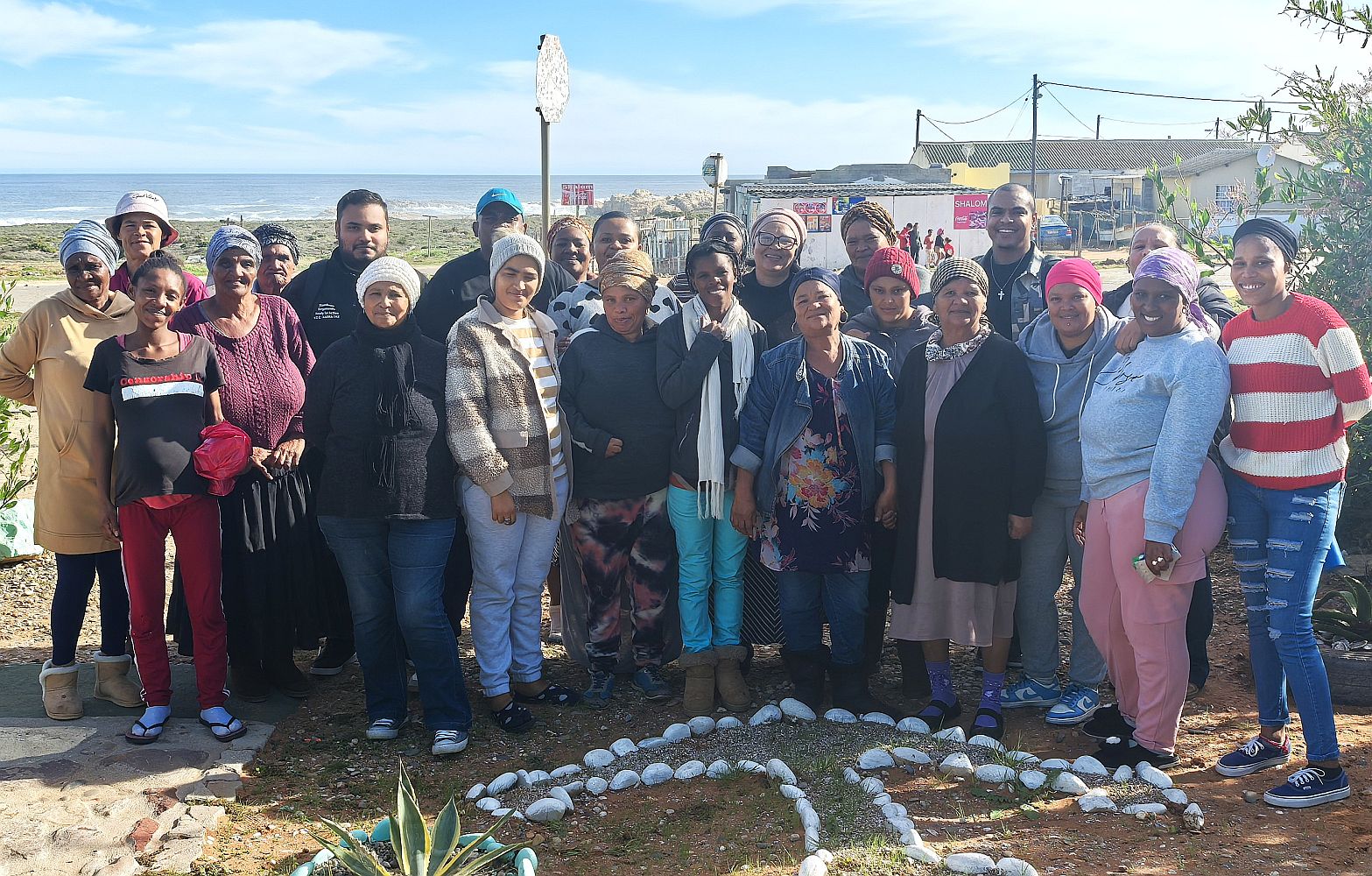
Fisher women play a vital role in sustaining household food security, yet remain under‑recognised, excluded from permits, and denied equal income opportunities in the fishing sector.Photo Credit: The Green Connection.
By Witness Radio team.
South Africa produces enough food to feed its population, yet millions go to bed hungry every night.
According to Statistics South Africa’s General Household Survey 2024, released in 2025, about 14 million people experienced hunger, representing 22.2% of households reporting inadequate or severely inadequate access to food. The Northern Cape (34.3%), Eastern Cape (31.3%), and Mpumalanga (30.4%) recorded the highest levels of food insecurity.
One in four children in South Africa is stunted due to chronic malnutrition. In the Eastern Cape alone, 70 children under the age of five reportedly died from malnutrition-related complications between January and July 2025.
In response to the growing problem, the South African Human Rights Commission, a national institution established to support constitutional democracy, declared last year that it would hold a National Public Inquiry into the Constitutional Right to Food. This inquiry will examine how communities, corporations, laws, and policies shape food systems and seek to address the structural causes of hunger.
As a result, the investigation will try to describe a future in which food is once again understood as sustenance, dignity, and justice.
Thousands of small-scale fishers along South Africa’s 3,000 km coastline depend on marine resources for their livelihoods, highlighting their vital role in the nation’s food security and cultural fabric.
Many fishing families struggle to make ends meet, even though they harvest food from the ocean. The livelihoods and food security of about 28,000 small-scale fishermen are directly reliant on marine resources. Yet, existing policies-such as restrictive permits and limited market access-exclude them from full participation, perpetuating food insecurity.
For these communities, food systems are not abstract policy concepts. They shape daily survival, dignity, livelihoods, and cultural identity.
“As part of our submission, we emphasize that concrete policy changes-such as recognizing customary fishing rights and improving market access-will directly enhance the livelihoods and food security of small-scale fishers and coastal communities, making the case for urgent reform.” Says Buthelezi
The Green Connection, a registered non-profit organisation, works with coastal communities to promote environmental justice, human rights, and accountable governance.
In the submission, the Green Connection states that the inquiry is timely as it will examine the structural and economic dynamics that perpetuate hunger. “It will assess the concentration of power in the food value chain, affordability and access, land and tenure security, policy coordination, and the realization of the constitutional right to food. This includes its links to dignity, health, water, culture, and a healthy environment.” The submission reads.
The Green Connection further argues that the Commission’s examination of governance, participation, and accountability must include scrutiny of marine and ocean policy.
“Poor implementation of the Small-Scale Fisheries Policy, limited market access, inadequate infrastructure, and weak consultation processes continue to undermine the sector. Women – who make up less than 30% of participants – remain under-recognised. At the same time, young people leave coastal communities due to declining economic prospects,” says Khetha Buthelezi, Economics Officer at The Green Connection, adding that, “Food and the systems we put in place to produce it cannot be separated from human dignity, livelihoods, and cultural rights. These issues are not abstract policy debates. For small-scale fishing communities, food from the ocean is not merely a commodity – it is a foundation of identity, survival, and social cohesion.”
The organisation also raises concerns about the potential impacts of offshore oil and gas expansion under Operation Phakisa. It further adds that Seismic surveys, drilling, and increased shipping activity can threaten fish stocks and restrict access to traditional fishing grounds, thereby directly affecting food security and livelihoods.
“For small-scale fishers, these are not abstract environmental issues. It is about income stability, cultural survival, and the constitutional rights to food, livelihoods, and participation in decision-making, and protecting these rights and resources for future generations,” says Buthelezi
Several fishing communities consulted shared testimonies describing worsening conditions.
“While small‑scale fishers support around 28000 people in South Africa, many of us can no longer catch or sell enough fish to feed our own families. Walter Steenkamp says on behalf of Aukotowa Small‑Scale Fishers Co‑operative in Port Nolloth, Northern Cape.
Steenkamp adds that Decisions are often made without consulting them, which reflects an intended exclusion from decision-making. “We hope this inquiry will result in the recognition of our customary rights, the return of our fishing grounds, and for the government to listen to those of us who live from the sea, so that we can feed our families with dignity.”
According to Kristie Links from the Sal-Diaz Small-Scale Fisher Co-operative in Saldanha Bay, Western Cape, farmers are forced to use larger boats that they cannot afford. “We have no money for the bigger boats they want us to use, and the areas we are given have little or no fish.
Industrial boats continue to overfish, especially at night, while our communities struggle to put food on the table. This situation is destroying our livelihoods, our food security, and our right to be recognised as small-scale fishers,” Kristie adds.
The organisation argues that poor implementation of the Small-Scale Fisheries Policy, weak consultation processes, and inadequate infrastructure continue to undermine the sector.
“Our message to the SAHRC is clear. If South Africa is serious about tackling hunger and inequality, it must ensure food systems governance is transparent, inclusive, and accountable. Coastal communities are not asking for charity – they are demanding justice.” Buthelezi concludes
The deadline for written submissions has been extended to 27 February 2026, with public hearings scheduled for March during Human Rights Month.
Related posts:

 About 41 million people food insecure in E. Africa amid COVID-19 pandemic: UN
About 41 million people food insecure in E. Africa amid COVID-19 pandemic: UN
 63 million people food insecure in Horn of Africa: report
63 million people food insecure in Horn of Africa: report
 “Vacant Land” Narrative Fuels Dispossession and Ecological Crisis in Africa – New report.
“Vacant Land” Narrative Fuels Dispossession and Ecological Crisis in Africa – New report.
 Community land rights at stake amid looming large-scale investment interests
Community land rights at stake amid looming large-scale investment interests

CSOs push for reforms at the KFW Accountability Mechanism after experts discovered that it has weak remedies in addressing grievous harms caused by its investments.

UPDF General on the spot over fresh evictions in Hoima

Small-scale fishers and coastal communities are pushing to testify before a human rights commission investigating the causes of food inequality in South Africa.

The Kenyan government insists on maintaining provisions of the Seed Act that the court nullified: farmers and legal experts question the motive.

Evicted from their land to host Refugees: A case of Uganda’s Kyangwali refugee settlement expansion, which left host communities landless.

US-DRC Strategic Partnership Agreement Faces Constitutional Challenge in Court

Why govt is launching a comprehensive digital land registry

Indigenous communities in Eastern Nepal accuse the World Bank’s Linked Cable Car Project of rights violations.

Innovative Finance from Canada projects positive impact on local communities.
Over 5000 Indigenous Communities evicted in Kiryandongo District
Petition To Land Inquiry Commission Over Human Rights In Kiryandongo District
Invisible victims of Uganda Land Grabs
Resource Center
- Land And Environment Rights In Uganda Experiences From Karamoja And Mid Western Sub Regions
- REPARATORY AND CLIMATE JUSTICE MUST BE AT THE CORE OF COP30, SAY GLOBAL LEADERS AND MOVEMENTS
- LAND GRABS AT GUNPOINT REPORT IN KIRYANDONGO DISTRICT
- THOSE OIL LIARS! THEY DESTROYED MY BUSINESS!
- RESEARCH BRIEF -TOURISM POTENTIAL OF GREATER MASAKA -MARCH 2025
- The Mouila Declaration of the Informal Alliance against the Expansion of Industrial Monocultures
- FORCED LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA TRENDS RIGHTS OF DEFENDERS IMPACT AND CALL FOR ACTION
- 12 KEY DEMANDS FROM CSOS TO WORLD LEADERS AT THE OPENING OF COP16 IN SAUDI ARABIA
Legal Framework
READ BY CATEGORY
Newsletter
Trending
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week agoSmall-scale fishers and coastal communities are pushing to testify before a human rights commission investigating the causes of food inequality in South Africa.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks agoFEATURE: What Lagos Can Learn From Kenya, Morocco, Uganda’s Forced Evictions
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week agoThe Kenyan government insists on maintaining provisions of the Seed Act that the court nullified: farmers and legal experts question the motive.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week agoUPDF General on the spot over fresh evictions in Hoima
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago13 years after the refugee host community was forcefully evicted to expand a refugee settlement, thousands remain unsettled.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK10 hours ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK10 hours agoCSOs push for reforms at the KFW Accountability Mechanism after experts discovered that it has weak remedies in addressing grievous harms caused by its investments.