MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
Uganda: StopEACOP Campaign Condemns Standard Bank’s Decision to Fund EACOP
Published
2 years agoon
Kampala — The StopEACOP Campaign is appalled by Standard Bank’s decision to help finance the East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP) project and condemns this decision in the strongest possible terms. This decision follows a years-long review process, during which environmental and social concerns raised by numerous stakeholders were evidently ignored.
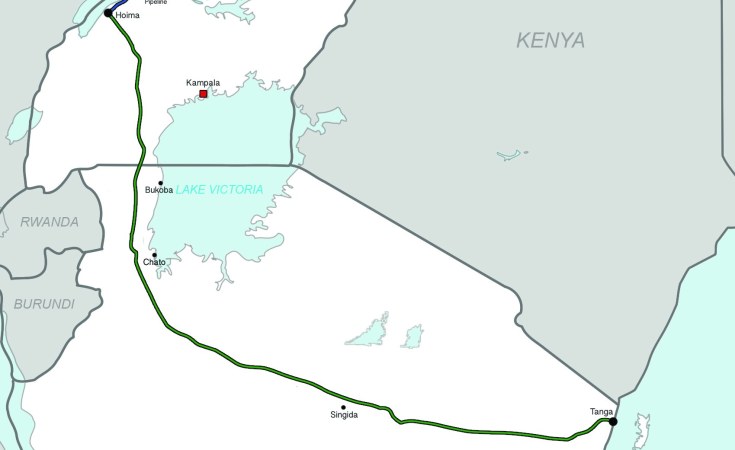
The $5 billion EACOP project, spearheaded by TotalEnergies, aims to transport crude oil from Uganda’s oil fields to a terminal in Tanga, Tanzania. Despite significant opposition from affected communities and environmental and human rights groups, Standard Bank, Africa’s largest lender, has decided to support this disastrous project.
Standard Bank chair Nonkululeko Nyembezi stated in a recent interview that they had conducted comprehensive environmental and social due diligence. However, the claim contradicts the project’s grave climate, environmental and human rights risks. The decision of Standard Bank is also at odds with the assessment of its peers, who have ruled out support for the EACOP for climate, environmental, and social concerns.
Standard Bank’s decision ignores local opposition and human rights abuses
In the last month alone, 11 pipeline critics have been arrested in Uganda and Tanzania after expressing their concerns about the project. In addition, one of the community leaders from the Kingfisher region in Uganda was abducted by the Uganda Peoples’ Defense Forces, bringing condemnation from the UN Special Rapporteur on Human Rights Defenders. Standard Bank’s untimely announcement of their decision to finance EACOP, in the midst of a brutal crackdown on human rights, environmental and land defenders in Uganda and Tanzania, illustrates their level of detachment from the realities and experiences of communities on the ground and calls into question their claim to have done thorough due diligence.
Environmental and human rights groups have persistently highlighted the potential hazards of the controversial EACOP, including severe impacts on wildlife habitats, the displacement of communities, and the exacerbation of climate change through increased greenhouse gas emissions. Many field investigation reports, including a recent Human Rights Watch report, have also documented and denounced the inadequate compensation and significant disruption experienced by residents displaced by the pipeline’s construction. Against this backdrop, Standard Bank’s decision to finance EACOP shows blatant disregard for the voices and rights of the communities in Uganda and Tanzania who will bear the brunt of the environmental and social devastation caused by this project.
Standard Bank cannot feign ignorance in relation to the concerns surrounding EACOP. It has faced consistent pressure from communities and climate and social justice organisations and groups in South Africa who have demonstrated outside the bank’s offices in Rosebank, Johannesburg on numerous occasions. These demonstrations, including a large protest with hundreds of participants on the day of the bank’s AGM in 2023, a 3-day-long occupation of the bank’s entrance in September of the same year, and weekly pickets held outside the bank’s parking lot by Extinction Rebellion, sought to bring the demands and experiences of EACOP-affected communities to their attention.
Standard Bank has refused to engage in meaningful and constructive dialogue and instead, its response has been characterized by repression and increased militarisation. The South African Police Service has also intervened to protect the interests of the bank and has arrested peaceful demonstrators on two occasions. It is a stark demonstration of Standard Bank’s prioritization of profit over people and the planet and its lip-service commitment to constructive dialogue and meaningful engagement with frontline communities and other key stakeholders.
Standard Bank is also ignoring clear business risk
The decision to bankroll the project also casts doubt on Standard Bank’s assessment of the business and reputational risks stemming from the risks to local communities, environment and climate posed by the project.
Standard Bank’s decision comes after major financiers and insurers from North America, Europe, and Japan have publicly ruled out support for EACOP due to global outcry over the harmful project. The expected finance from China has also been delayed, while the Chinese state-owned insurers and banks have taken prolonged time to assess the outstanding risks. As a result, the EACOP project is facing significant challenges and project sponsors are reportedly in a cash crisis to fill the funding gap, which threatens to stall the construction.
These delays come as a result of the immense pressure that potential financiers have come under from communities, civil society, the international community and even shareholders and investor groups who express grave concern over the catastrophic socio-economic, biodiversity and climate change risks of the project.
Standard Bank’s decision to finance the EACOP project starkly contradicts industry trends, as leading banks and insurers have distanced themselves from this controversial initiative. This decision exposes Standard Bank to significant risks, including the potential for stranded assets, especially as the global economy transitions towards clean energy solutions. Furthermore, with Uganda already facing a severe debt crisis, worsened by the country’s oil induced borrowing spree, the environmental and social costs associated with EACOP could precipitate an economic disaster for the people of Uganda as well as financiers and their shareholders who opt to engage with this project.
It is clear that investing in EACOP threatens the stability of vulnerable communities and jeopardizes the financial health and reputational integrity of those who support it. A 2022 report assessing the EACOP and associated oil fields against internationally recognized environmental and human rights standards for financial institutions found numerous violations, putting banks at risk if they sign on to support the project. The assessment, undertaken by the Africa Institute for Energy Governance (AFIEGO), Inclusive Development International (IDI) and BankTrack, suggests that the project is not in compliance with many of the criteria set forth in the Equator Principles and the Environmental and Social Performance Standards of the International Finance Corporation (IFC), two internationally recognized standards for responsible finance.
We demand that Standard Bank review and rescind its decision to finance the EACOP project immediately. While it may be too late for Standard Bank to redeem its supposed commitment to people and the planet, there is still time for other potential lenders, particularly Chinese state-owned banks, to demonstrate their dedication to human rights and sustainability by refusing to support EACOP. We call upon the global community to continue its unwavering support for the StopEACOP campaign and the communities on the frontlines. It is not too late to halt this disastrous project and prevent the extensive environmental, social, and economic damage it promises to inflict.
Quotes
“For years, we have campaigned tirelessly against Standard Bank, bringing the grievances and aspirations of impacted communities directly to their doorstep time and time again. Each time, we are met either with deafening silence or with outright violence from an institution that has shown itself to be truly heartless and utterly indifferent to the well-being of ordinary people. Let it be known that this announcement will not deter us. We will continue to stand in solidarity with the communities affected by EACOP and will escalate our actions against Standard Bank in the coming months.” – Zaki Mamdoo, StopEACOP Campaign Coordinator
“Standard Bank prides itself on financing Africa’s development. However, the bank’s decision to finance the EACOP, not to mention its financing of other fossil fuel projects across Africa, earns the institution the title of an anti-people and an anti-development bank. Fossil fuel projects like EACOP that cause livelihood losses, enslave Ugandans by worsening indebtedness and drive all of us deeper into the climate crisis should not be financed by any bank.” – Diana Nabiruma, Senior Communications Officer, AFIEGO
“Standard Bank is contributing to the devastation of our communities including through the immense loss of land and livelihood. They have chosen to ignore the plight of our people and to support our exploitation and suffering at the hands of greedy multinational corporations. This is a decision that places them squarely on the wrong side of history and which marks them as an institution with no regard for human rights and justice.” – Richard Senkondo, Executive Director at the Organization for Community Engagement, Tanzania.
Original Source:350Africa.org Via allafrica.com
Related posts:

 A 29th Insurance Company withdraws support for controversial EACOP Project.
A 29th Insurance Company withdraws support for controversial EACOP Project.
 CSOs to African Development Bank: Don’t fund EACOP
CSOs to African Development Bank: Don’t fund EACOP
 The East Africa regional court dismisses a case challenging the construction of the EACOP project.
The East Africa regional court dismisses a case challenging the construction of the EACOP project.
 Appellate Division of the East African Court of Justice (EACJ) to hear an Appeal filed by CSOs which seeks to reinstate a petition against the construction of the EACOP project tomorrow.
Appellate Division of the East African Court of Justice (EACJ) to hear an Appeal filed by CSOs which seeks to reinstate a petition against the construction of the EACOP project tomorrow.
You may like
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
UPDF General on the spot over fresh evictions in Hoima
Published
21 hours agoon
February 17, 2026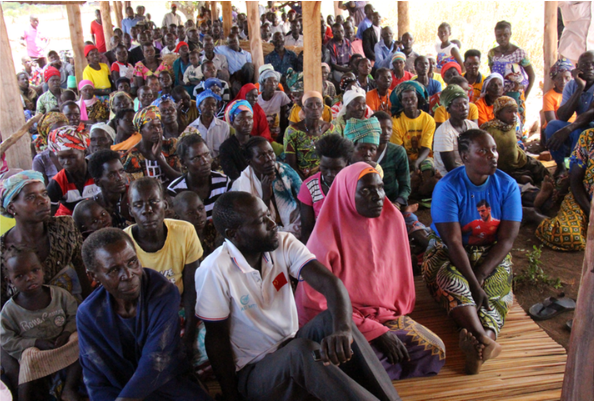
Over 1,000 residents in Kapapi Sub-County, Hoima District, are facing a second forced eviction from their ancestral land in three years, sparking widespread tension and anger among the community.
The latest evictions have been linked to a senior Uganda Peoples’ Defence Forces (UPDF) officer, Brigadier General Peter Nabasa, whom residents accuse of masterminding the displacement, allegedly in defiance of earlier government directives issued by the state minister for Lands, Dr. Sam Mayanja.
In October 2025, Minister Mayanja ordered that over 1,000 families who had been evicted from contested land in Kapapi Sub-County be resettled back onto their bibanja.
He also directed security commanders in the area to withdraw armed personnel and allow the affected communities to return. However, residents claim the situation has worsened, with renewed evictions pushing thousands into uncertainty once again.
The affected families, estimated to be over 1,000 and comprising over 4,000 people, include both cultivators and pastoralists. They were evicted from their homes in several villages, including Waaki North, Kapapi Central, Waaki South, Runga, Kiryatete, and Kiganja, all located in Kapapi and Kiganja sub-counties, Hoima District.
Residents insist the land has been their home for decades, passed down through generations, and accuse powerful individuals of using land titles and security enforcement to displace them.
“We were returned to our land in October last year on the orders of President Museveni and Minister Mayanja, but shortly after the elections, we were evicted again,” said Deusi Mugume, a resident of Runga.
“The Brigadier General came with armed security personnel and ordered us to vacate the land immediately. They even fired bullets in the air to disperse us, disrespecting the orders of both the Minister and the President.”
The residents were evicted from two titled pieces of land said to belong to businessmen and private individuals based in Hoima and Kampala. One of the contested titles measures approximately 2,545 acres (1,030 hectares) and is reportedly owned by seven individuals, including Ndahura William Gafayo, Aston Muhwezi, Alex Kyamanywa, Nathan Kiiza Byarugonjo, Bahuzya, Monica Rwashadika, and Wilber Kiiza. This land reportedly covers parts of Kapapi and Kiganja sub-counties.
Another title, measuring about three square miles, is said to belong to the family of the late Tito Byangire of Kigorobya, Hoima District. This land reportedly covers four villages, including Waaki South, Waaki North, Runga, Kapapi Central, and Kiryatete.
Brig Gen Nabasa claims he legally leased 700 acres of land from the Byangire family for 10 years starting in 2023.
“The residents were allowed to live there temporarily because elections were approaching, but they were supposed to leave immediately after the polls,” he said.
The residents, who are now living in temporary structures in Rwenyana, say their food and cash crops were destroyed after cattle were introduced onto the land following their eviction.
“We are going through many difficulties. We have no food, we are sleeping in makeshift shelters, children are not going to school, and we don’t know if we shall ever return to our land,” said Madinah Nyanjura and Nyarabiraho Cheya, both residents of Kapapi.
The Hoima Deputy Resident District Commissioner, Christopher Aine, blamed land brokers for misleading residents and bringing more people onto the contested land.
Minister Mayanja had previously directed the arrest of Brig Gen Peter Nabasa, Capt Rogers Karamagi, former Hoima Deputy Resident District Commissioner Michael Muramira Kyakashari, and William Ndahura Gafayo for allegedly illegally evicting residents from their bibanja land.
Mr Joshua Byangire, one of the administrators of the late Byangire estate, said the family has faced continued disruption and appealed to the government to buy off the land title.
“We have been disturbed on our family land. I request the government to buy off our land title. I don’t understand why soldiers have been deployed there, yet we are civilians and cannot access our property,” he said.
Original Source: monitor.co.ug
Related posts:

 Breaking: The army general, police chief, presidential representative, and others are appearing before the Hoima Chief Magistrate court today.
Breaking: The army general, police chief, presidential representative, and others are appearing before the Hoima Chief Magistrate court today.
 Court issues fresh criminal summonses against army general, police chief and presidential representative and others in a private criminal case.
Court issues fresh criminal summonses against army general, police chief and presidential representative and others in a private criminal case.
 Over 500 Kapapi families in Hoima district remain stranded after the district security committee fails to resettle them back on their land as directed by the minister.
Over 500 Kapapi families in Hoima district remain stranded after the district security committee fails to resettle them back on their land as directed by the minister.
 UPDF General, District Police Commander, and Presidential Representative defy Court summonses for the second time as DPP takes over the EACOP-PAP’s case.
UPDF General, District Police Commander, and Presidential Representative defy Court summonses for the second time as DPP takes over the EACOP-PAP’s case.
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
Small-scale fishers and coastal communities are pushing to testify before a human rights commission investigating the causes of food inequality in South Africa.
Published
1 day agoon
February 17, 2026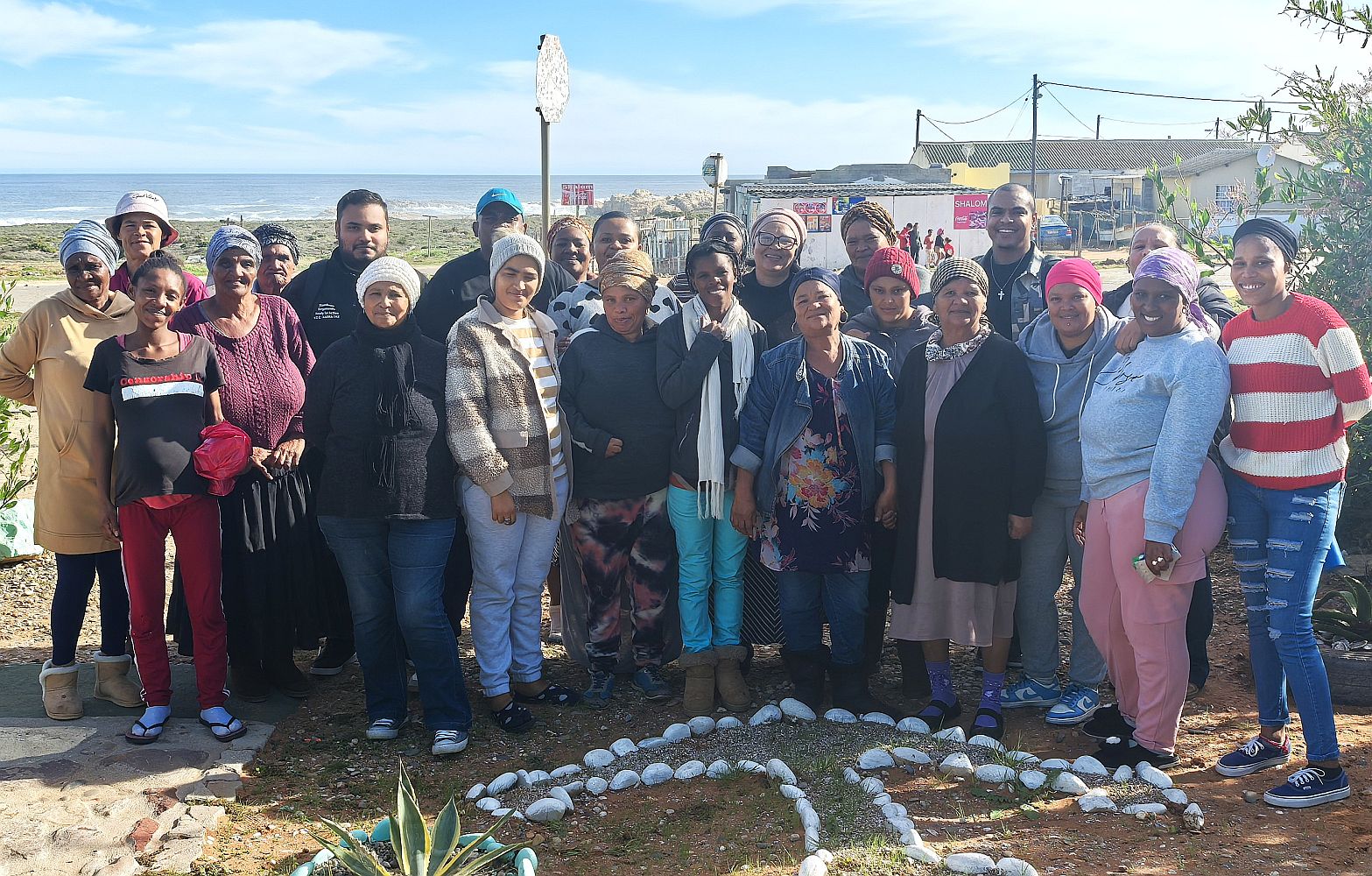
Fisher women play a vital role in sustaining household food security, yet remain under‑recognised, excluded from permits, and denied equal income opportunities in the fishing sector.Photo Credit: The Green Connection.
By Witness Radio team.
South Africa produces enough food to feed its population, yet millions go to bed hungry every night.
According to Statistics South Africa’s General Household Survey 2024, released in 2025, about 14 million people experienced hunger, representing 22.2% of households reporting inadequate or severely inadequate access to food. The Northern Cape (34.3%), Eastern Cape (31.3%), and Mpumalanga (30.4%) recorded the highest levels of food insecurity.
One in four children in South Africa is stunted due to chronic malnutrition. In the Eastern Cape alone, 70 children under the age of five reportedly died from malnutrition-related complications between January and July 2025.
In response to the growing problem, the South African Human Rights Commission, a national institution established to support constitutional democracy, declared last year that it would hold a National Public Inquiry into the Constitutional Right to Food. This inquiry will examine how communities, corporations, laws, and policies shape food systems and seek to address the structural causes of hunger.
As a result, the investigation will try to describe a future in which food is once again understood as sustenance, dignity, and justice.
Thousands of small-scale fishers along South Africa’s 3,000 km coastline depend on marine resources for their livelihoods, highlighting their vital role in the nation’s food security and cultural fabric.
Many fishing families struggle to make ends meet, even though they harvest food from the ocean. The livelihoods and food security of about 28,000 small-scale fishermen are directly reliant on marine resources. Yet, existing policies-such as restrictive permits and limited market access-exclude them from full participation, perpetuating food insecurity.
For these communities, food systems are not abstract policy concepts. They shape daily survival, dignity, livelihoods, and cultural identity.
“As part of our submission, we emphasize that concrete policy changes-such as recognizing customary fishing rights and improving market access-will directly enhance the livelihoods and food security of small-scale fishers and coastal communities, making the case for urgent reform.” Says Buthelezi
The Green Connection, a registered non-profit organisation, works with coastal communities to promote environmental justice, human rights, and accountable governance.
In the submission, the Green Connection states that the inquiry is timely as it will examine the structural and economic dynamics that perpetuate hunger. “It will assess the concentration of power in the food value chain, affordability and access, land and tenure security, policy coordination, and the realization of the constitutional right to food. This includes its links to dignity, health, water, culture, and a healthy environment.” The submission reads.
The Green Connection further argues that the Commission’s examination of governance, participation, and accountability must include scrutiny of marine and ocean policy.
“Poor implementation of the Small-Scale Fisheries Policy, limited market access, inadequate infrastructure, and weak consultation processes continue to undermine the sector. Women – who make up less than 30% of participants – remain under-recognised. At the same time, young people leave coastal communities due to declining economic prospects,” says Khetha Buthelezi, Economics Officer at The Green Connection, adding that, “Food and the systems we put in place to produce it cannot be separated from human dignity, livelihoods, and cultural rights. These issues are not abstract policy debates. For small-scale fishing communities, food from the ocean is not merely a commodity – it is a foundation of identity, survival, and social cohesion.”
The organisation also raises concerns about the potential impacts of offshore oil and gas expansion under Operation Phakisa. It further adds that Seismic surveys, drilling, and increased shipping activity can threaten fish stocks and restrict access to traditional fishing grounds, thereby directly affecting food security and livelihoods.
“For small-scale fishers, these are not abstract environmental issues. It is about income stability, cultural survival, and the constitutional rights to food, livelihoods, and participation in decision-making, and protecting these rights and resources for future generations,” says Buthelezi
Several fishing communities consulted shared testimonies describing worsening conditions.
“While small‑scale fishers support around 28000 people in South Africa, many of us can no longer catch or sell enough fish to feed our own families. Walter Steenkamp says on behalf of Aukotowa Small‑Scale Fishers Co‑operative in Port Nolloth, Northern Cape.
Steenkamp adds that Decisions are often made without consulting them, which reflects an intended exclusion from decision-making. “We hope this inquiry will result in the recognition of our customary rights, the return of our fishing grounds, and for the government to listen to those of us who live from the sea, so that we can feed our families with dignity.”
According to Kristie Links from the Sal-Diaz Small-Scale Fisher Co-operative in Saldanha Bay, Western Cape, farmers are forced to use larger boats that they cannot afford. “We have no money for the bigger boats they want us to use, and the areas we are given have little or no fish.
Industrial boats continue to overfish, especially at night, while our communities struggle to put food on the table. This situation is destroying our livelihoods, our food security, and our right to be recognised as small-scale fishers,” Kristie adds.
The organisation argues that poor implementation of the Small-Scale Fisheries Policy, weak consultation processes, and inadequate infrastructure continue to undermine the sector.
“Our message to the SAHRC is clear. If South Africa is serious about tackling hunger and inequality, it must ensure food systems governance is transparent, inclusive, and accountable. Coastal communities are not asking for charity – they are demanding justice.” Buthelezi concludes
The deadline for written submissions has been extended to 27 February 2026, with public hearings scheduled for March during Human Rights Month.
Related posts:

 About 41 million people food insecure in E. Africa amid COVID-19 pandemic: UN
About 41 million people food insecure in E. Africa amid COVID-19 pandemic: UN
 63 million people food insecure in Horn of Africa: report
63 million people food insecure in Horn of Africa: report
 “Vacant Land” Narrative Fuels Dispossession and Ecological Crisis in Africa – New report.
“Vacant Land” Narrative Fuels Dispossession and Ecological Crisis in Africa – New report.
 Community land rights at stake amid looming large-scale investment interests
Community land rights at stake amid looming large-scale investment interests
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK
The Kenyan government insists on maintaining provisions of the Seed Act that the court nullified: farmers and legal experts question the motive.
Published
2 days agoon
February 16, 2026
By Witness Radio team.
Mr. Francis Njiri, a small-scale farmer from Makongo and a member of the Seed Savers Network Kenya, questions the spirit behind the Kenyan government and the Kenya Plant Health Inspectorate Service (KEPHIS) in appealing against the recent High Court ruling on seed rights, including saving and exchange.
The landmark judgment delivered in November 2025 declared key sections of the Seed and Plant Varieties Act unconstitutional, directly affirming farmers’ rights to save, share, and exchange seeds outside formal systems, which many smallholder farmers like Mr. Njiri see as a victory for traditional practices and their livelihoods.
15 smallholder farmers from the Seed Savers Network filed a constitutional petition in 2022, claiming that Kenya’s Seeds and Plant Varieties Act (SPVA) and the Seeds and Plant Varieties (Seeds) Regulations, 2016, have restrictive provisions that violate fundamental rights protected by Kenya’s Constitution, which the Kenya’s High Court in Machakos ruled in their favor.
According to court documents seen by Witness Radio, the Kenyan government and KEPHIS have appealedagainst the court ruling, claiming that the High Court judge misinterpreted key legal provisions, underscoring the ongoing legal battle over seed rights.
“Take notice that The Kenya Plant Health Inspectorate Service and The Attorney General, the above-named Appellants, appeal to the Court of Appeal against the whole of the above-mentioned decision,” documents seen by Witness Radio reveal.
“The Learned Judge erred in law and in fact by misinterpreting and conflating Sections 8(1) and 8A of the Seeds and Plant Varieties Act with Article 11(3)(b) of the Constitution, and by wrongly concluding that those provisions limit or undermine Section 27A, while in fact Sections 8(1), 8A and 27A operate harmoniously to give full effect to Article 11(3)(b) of the Constitution.
The Learned Judge erred in law and in fact by holding that Sections 8(1) and 10(4)(c), (d), (e), (f) and (g) of the Seeds and Plant Varieties Act, together with Regulations 6, 16 and 19 of the Seed and Plant Varieties (Seed) Regulations are unconstitutional based on discrimination under Article 27(2) of the Constitution, when no distinction had been demonstrated…” further reveals.
The government’s decision to appeal has alarmed farming communities and civil society, raising fears that their interests are being overlooked.
“I don’t think the government is working in the interests of farmers. We suspect these actions serve multinational corporations’ interests because farmers were not consulted in the first place.” Mr. Njiri says.
Mr. Njiri, who has practiced agroecological farming for years, is one of the petitioners in the case. Alongside other farmers from across the country, he challenged the constitutionality of provisions that restricted the use of farm-saved seeds. He argues that such laws disproportionately favored commercial seed companies while undermining indigenous seed systems that have sustained communities for generations.
According to him, the lack of consultation with smallholder farmers, who constitute the majority of Kenya’s agricultural producers, raises serious questions about whose interests are being prioritized.
For generations, farmers have saved, exchanged, and improved seeds-these practices are part of our heritage and vital for our survival. Decisions about seeds should involve those who depend on them most.
In the case that had been determined in favor of the local farmers, Advocate Wambugu Wanjohi says the Government of Kenya and KEPHIS were challenging mostly seed sovereignty, the right to save, share, and replant seeds, and the right to participate in seed policies.
“Now, the Seed and Plant Varieties Amendment Act aligned Kenya with UPOV of 1991, and seed exchange outside the normal certification process became illegal. And the consequence was that the government pushed indigenous seed systems underground.” He mentioned.
Wanjohi describes the High Court ruling as a constitutional milestone.
“This case was not simply about regulatory compliance. The Court approached it as a human rights matter. It examined whether criminalizing seed sharing unjustifiably limited constitutional rights such as the right to food, the protection of culture, equality, and fair administrative action,” he said.
“We argued on a constitutional basis. The farmers sought to have these sections declared unconstitutional because the Act and regulations unjustifiably limited the right to food and eroded cultural rights and equality.”
According to Wanjohi, the Court found that the impugned provisions disproportionately burdened smallholder farmers while privileging commercial seed interests.
“The Constitution does not permit legislation that effectively punishes the survival practices of small-scale farmers. The judgment reaffirmed that seed governance must align with constitutional protections,” he added.
Dr. David Kabanda, Director of the Center for Food and Adequate Living Rights in Uganda, views the ruling as significant beyond Kenya’s borders.
“Seed is not merely a commercial commodity; it is the foundation of food systems and community resilience. When laws shift control of seed away from farmers without meaningful participation, they raise fundamental legal and human rights questions,” Kabanda says.
He adds that the case introduces a constitutional perspective that could influence similar debates across East Africa, particularly in countries aligning seed laws with international intellectual property standards.
“Seed determines protection of our land, because in an ordinary African city, if you don’t have seed, then you cannot plant. Seed and food give land relevance in many communities. So, if someone takes our seed from you, especially in the current region where some countries, like Kenya, want to create what they call seed merchants and impose exorbitant fees on you to operate the seed trade or business, it is alienating people from the livelihood they should have. Because if any state or multinational takes away the seed, the propagating material, whether for food or agriculture, it is touching the nerve of your existence.” Kabanda added.
As the appeal process unfolds, farmers like Mr. Njiri say they remain committed to defending what they consider fundamental rights: the right to seed, the right to food, and the right to participate in decisions that directly affect their livelihoods.
“We will continue to stand firm. Seeds are our life. Without them, there is no farming, and without farming, there is no food. We will fight and fight and fight until we win. And we believe we shall win the entire battle. Because we wouldn’t let that freedom, which God gives, be taken away from us because someone wants to protect their interests or farmers’ interests,” he concluded.
With the government and KEPHIS appealing the High Court’s landmark decision, it is now more important than ever for judges, lawyers, and civil society across Africa to actively support farmers in defending their constitutional seed rights. “Strategic litigation has set a precedent on the continent, showing that courts can and must uphold food sovereignty and protect the rights of smallholder farmers.” Advocate Wanjohi added.
Related posts:

 Kenyan farmers secure right to share local seeds in court ruling
Kenyan farmers secure right to share local seeds in court ruling
 The EAC Seed & Plant Varieties Bill, 2025, is a potential threat to smallholder farmers, as it aims to disengage them from the agriculture business, according to experts.
The EAC Seed & Plant Varieties Bill, 2025, is a potential threat to smallholder farmers, as it aims to disengage them from the agriculture business, according to experts.
 Seed Sovereignty: Most existing and emerging laws and policies on seeds are endangering seed saving and conservation on the African continent.
Seed Sovereignty: Most existing and emerging laws and policies on seeds are endangering seed saving and conservation on the African continent.
 The Witness Radio and Seed Savers Network Joint Radio program boosts Farmers’ knowledge of seed and food sovereignty.
The Witness Radio and Seed Savers Network Joint Radio program boosts Farmers’ knowledge of seed and food sovereignty.

UPDF General on the spot over fresh evictions in Hoima

Small-scale fishers and coastal communities are pushing to testify before a human rights commission investigating the causes of food inequality in South Africa.

The Kenyan government insists on maintaining provisions of the Seed Act that the court nullified: farmers and legal experts question the motive.

FEATURE: What Lagos Can Learn From Kenya, Morocco, Uganda’s Forced Evictions

Women environmental rights defenders in Africa are at the most significant risk of threats and attacks – ALLIED New report

Uganda moves toward a Bamboo Policy to boost environmental conservation and green growth.

Evicted from their land to host Refugees: A case of Uganda’s Kyangwali refugee settlement expansion, which left host communities landless.

200 farmers demonstrate at parliament, worried about new seed monopoly

Innovative Finance from Canada projects positive impact on local communities.
Over 5000 Indigenous Communities evicted in Kiryandongo District
Petition To Land Inquiry Commission Over Human Rights In Kiryandongo District
Invisible victims of Uganda Land Grabs
Resource Center
- Land And Environment Rights In Uganda Experiences From Karamoja And Mid Western Sub Regions
- REPARATORY AND CLIMATE JUSTICE MUST BE AT THE CORE OF COP30, SAY GLOBAL LEADERS AND MOVEMENTS
- LAND GRABS AT GUNPOINT REPORT IN KIRYANDONGO DISTRICT
- THOSE OIL LIARS! THEY DESTROYED MY BUSINESS!
- RESEARCH BRIEF -TOURISM POTENTIAL OF GREATER MASAKA -MARCH 2025
- The Mouila Declaration of the Informal Alliance against the Expansion of Industrial Monocultures
- FORCED LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA TRENDS RIGHTS OF DEFENDERS IMPACT AND CALL FOR ACTION
- 12 KEY DEMANDS FROM CSOS TO WORLD LEADERS AT THE OPENING OF COP16 IN SAUDI ARABIA
Legal Framework
READ BY CATEGORY
Newsletter
Trending
-

 NGO WORK2 weeks ago
NGO WORK2 weeks agoUS-DRC Strategic Partnership Agreement Faces Constitutional Challenge in Court
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks agoClose to six years on, Pangero Chiefdom subjects still linger in pain after the government army’s forceful takeover of their ancestral land.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks agoIndigenous communities’ complaint against World Bank-linked Nepal Cable Car Project declared eligible for investigation.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks agoDecades of land loss and chronic poverty: Salala Rubber Plantation prioritizes profit over the well-being of local Liberian communities.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks agoThe Witness Radio and Seed Savers Network Joint Radio program boosts Farmers’ knowledge of seed and food sovereignty.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK7 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK7 days agoFEATURE: What Lagos Can Learn From Kenya, Morocco, Uganda’s Forced Evictions
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK1 week ago13 years after the refugee host community was forcefully evicted to expand a refugee settlement, thousands remain unsettled.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 days agoThe Kenyan government insists on maintaining provisions of the Seed Act that the court nullified: farmers and legal experts question the motive.