NGO WORK
Republic of Congo: expansion of tree plantations linked to the carbon market – the underside of an opaque business and greenwashing
Published
1 year agoon

In Congo-Brazzaville, tree planting projects intended for carbon markets have proliferated over the past four years. This concerns large-scale developments of monocultures initiated by oil companies under the seductive term of carbon neutrality and promises of job creation for communities. In reality, they are neither a solution to the climate crisis nor a benefit for the communities of Congo.
Oil and gas industries represent the main source of global emissions. (1) Instead of reducing their emissions, they take advantage of human concern about climate change to promote misleading plans for the expansion of tree planting as a solution to offsetting their emissions. (2) In a vicious circle, very opaque plantation projects are developing, generating new sources of income for plantation companies and providing multinationals a justification to continue to pollute. Twenty years earlier, organizations were already sounding the alarm over greenwashing claims that the expansion of plantations could offset carbon emissions. (3) The devastating effects of these projects, however, do not appear in the advertising messages.
In the Republic of Congo, reforestation projects began in 1936, after colonial destruction. (4) A National Reforestation Service was created and a national afforestation and reforestation program put in place to install one million hectares of plantations. (5) In 2013, the country launched its first carbon project as part of the REDD+ process, the financing of which has not yet been resolved. (6) The expansion of carbon projects initiated by private entities begins in 2019, after several reforms including the revision of the Forest Code, the adoption of a REDD+ strategy and the establishment of a Carbon Task Force. (7)
In the space of four years, between 2019 and 2023, seven long-term lease contracts were concluded between the government and the extractive industries for a total of approximately 570,000 hectares- an area larger than the country of Luxembourg (see the map
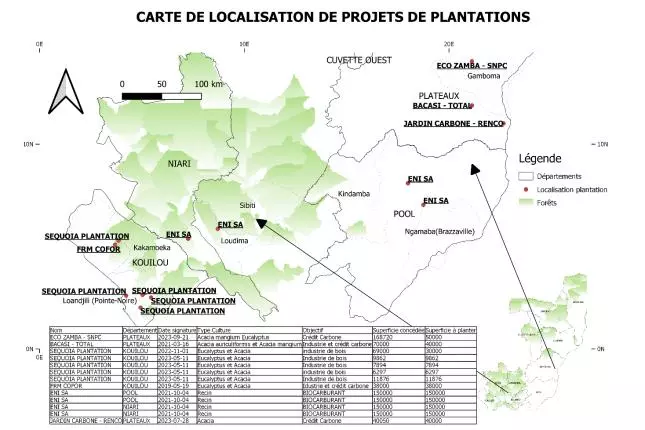
Among the signatories of these lease contracts are European multinationals operating in the country and the consultancy firm Forest Management Resource (FRM). FRM is the pioneer of carbon plantation projects in Congo and is now associated with the majority of multinationals, with its omnipresence carrying the scent of mixing roles and conflicts of interest.
Let’s come first to the contracts, these are lease contracts for land the state inherited from the colonial era, this time leased out for the development of carbon compensation projects, thus encouraging the continuity of carbon pollution. This lease contract system presents a colonial reconquest of agricultural land obtained through colonial heritage (9), in a very opaque and non-consensual approach. The architecture of this approach is generally characterized by the absence of a framework to make the lease contracts public, thus reinforcing opacity of information that ought to be public. Specifically, we note the absence of community consultation before the start of certain projects. (10) This has been strongly criticized in several carbon projects developed around the world.
Concerning the area granted, these plantation projects are developing in a logic of land grabbing in which the government facilitates the lease of land it claims to be the “public domain of the State”, under the law n°9-2004 of March 26 2004. But this claim of the State remains contested, especially since articles 2, 5 and 23 of the Constitution of October 25, 2015 advocate that national sovereignty is vested in the people. Another thing to note is that the ratio between the area granted in the leases and that targeted for plantations does not match. In fact, the total area to be planted adds up to 380,000 hectares out of the 570,000 hectares granted in leases. This raises the question about the use of those portions of land which these projects do not mention.
In addition to opaque information and land grabbing, we also note the use of misleading and seductive terms such as carbon neutrality and the promise of job creation for communities. According to various studies, monoculture tree plantations actually have a low sequestration potential compared to that of forests; monocultures also consume large quantities of water and negatively affect natural ecosystems. (11) In essence, to set up the plantations, all or part of the existing vegetation is destroyed in order to compensate for oil emissions.
Now, it is important to understand the impact of the expansion of these projects on forest-dependent communities and what is behind these projects.
FRM COFOR: communities question an opaque carbon market
In 2019, Forêt Ressources Management, created a subsidiary called Congo Forest Plantation (COFOR), a company under Congolese law. The same year, it signed a long-term lease contract with the government of Congo to develop the reforestation at Madingou-Kayes. The company is currently developing four projects with its investors. Interviewed by the Makanisi blog, the owner of the company stated that the projects will establish acacia-cassava and eucalyptus plantations, develop a sawmilling and plywood sector with an attractive promise of creating thousands jobs for communities. (12) Another objective of the project is to contribute to climate change mitigation through plantations. (13)
But the reality looks very different. Madingou-Kayes communities interviewed state that “we do not have access to either the lease contract or the project document. We are even surprised to hear that there are carbon projects here. All we know is not to enter this forest…”. Apart from the lack of information, the consent of the communities was evidently not obtained before the start of the project.
BACASI: greenwashing, violence against communities, a useless project for the country
The BaCaSi project is a partnership of several entities, among others: French oil company Total Energies and the company Forêt Ressources Management, via its Congolese subsidiary Forest Neutral Congo and the Republic of Congo. The project aims to develop a 40,000-hectare monoculture plantation within a project area of 55,000 hectares (14), while paradoxically, the area conceded as lease in 2022 is 70,089 hectares. This raises questions about other unstated objectives of the project.
In addition, the project is said to involve ‘a partnership based on advanced local agriculture and forestry, serving integrated development and climate action, with co-benefits such as jobs as well as social projects in the areas of nutrition, health and education.’ (14)
However, research by local and international organizations has revealed that this is a very controversial project. In particular, farmers and indigenous populations were ordered to leave their land, an indication of the project’s grabbing policy, some land-owning communities also received low compensation from the authorities (some at a rate of one dollar per hectare) and lost their livelihoods, which reinforces their food insecurity and poverty. (15) The revelations about the Bakasi project do not stop there. “Because this is not only be about carbon credits, the plantation in reality will only offset 2 percent of the carbon emissions of the oil company Total Energies, so behind this operation, is a question of money and not a question of corporate philanthropy” remarks a human rights defender who concludes that this project is not useful for the Republic of Congo.
Sequoia plantation: wood processing and opaque credit ambition
After multiple attempts to develop a destructive plantation project which has been held in check by communities and civil society in Gabon (16, see also article in this bulletin), the company Séquoia Plantations found refuge in the Republic of Congo, thanks to significant support granted by the authorities, declared one of the company’s managers. (17) Sequoia, founded by the multinational OLAM, is now part of the Equitane group, based in Dubai. Two lease contracts have been concluded for two projects currently under development: a 36,000-hectare replanting project was granted in May 2023 and the 69,000-hectare project obtained a lease in 2022, representing a total investment of 96.5 million Euros. (18)
Although according to the project document (19), the project focus is on the establishment of new tree plantations, plantation wood is already being harvested and processed at the site, thus raising questions about adding new to old plantations. Indeed, comments by the company manager point to objectives beyond those acknowledged in the project documents. During an interview (19), the manager suggested that his company will carry out large-scale plantations, with a view to fighting climate change and while reducing their carbon footprint. On the other hand, a resident of Mandingou-Kaye denounces the lack of accessibility to the lease contract and a consultation process tailored to local authorities. It is important to ultimately establish the existence of an unacknowledged carbon agenda and that the projects were developed with only partial information available.
ECO ZAMBA : excessive opportunism and unpredictable impacts
EcoZamba is a project of the National Oil Company of Congo, taking place in the savannah zone of the Congo Plateau. A 30-year lease contract was concluded in 2024 with the government. The contract grants the company the use of 168,720 hectares of land. Afforestation and agroforestry projects said to cover 50,000 hectares aim, among other things, at the sale of carbon credits. (20)
Some NGOs are skeptical about the impacts of this project on communities and the environment. According to them, “reforestation is not the priority oil companies. Their calling is to produce and market oil. They are launching into a sector that is not theirs. It’s out of simple opportunism. Environmentally, we are losing our savannah ecosystem with impacts on animals, birds and insects that can only thrive in savannah areas.” The cost of financing the project has not been revealed, and neither has the lease contract been made public. (21)
RENCO : the Mbé carbon garden project
The government of the Republic of Congo and the company RENCO GREEN SARLU, a subsidiary of the Italian multinational RENCO SPA, signed a partnership agreement on July 28, 2023 as part of the Carbone-Mbé Garden initiative. The project aims to establish acacia plantations on 40,050 hectares and market the carbon of the planted trees. Project plans include the proposal to establish 1,200 hectares of agroforestry plantations for the benefit of communities, following an “Acacia-Manioc” agroforestry model, with the plan to set up one hundred and fifty (150) hectares per year and rotations of eight years. (22)
The existing law grants exclusivity of the carbon credits generated in the plantations established on the lease lands that are part of the State forest domain to the private company that holds the lease. Thus, ultimately, the project does not provide for any benefit sharing plan from the carbon sold with the communities.
Additional carbon projects have been awarded in the Republic of Congo, in the forestry and conservation industry sectors. Among others, the forest industry of Ouesso (23); the logging companies Congolaise Industrielle de Bois and Yuan Dong Forestry Company, and the conservation NGO Widlife Conservation Society have been awarded permits for carbon projects. (24) Also, African Park Network, manager of the Odzala-Kokoua National Park, has expressed its intention to diversify its field of activity into carbon credits. (25)
Ultimately, the interest of oil extraction companies remains to continue to extract fossil fuels, as well as to do business in the carbon market, which provides a double benefit for them. (26) To do this, they develop deceptive projects, seduce communities and use very opaque approaches. Meanwhile, the roots of the problem remain intact, including: climate change caused by the use of fossil fuels and communities lacking access and protection of their customary lands. So, no matter how large it is, no tree plantation will ever be able to absorb the carbon emitted by oil activities and will never solve the problems of communities dependent on land and forests.
Bernadin Yassine NGOUMBA, defender of human rights and the environment, and the WRM
(1) Rapport Agence internationale de l’énergie (AIE 2023) : 33 pour cent pour le pétrole et 23 pour cent pour le gaz naturel. https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-outlook-2023
(2) WRM. Expansion des plantations d’arbres pour les marchés du carbone. Décembre 2023.
(3) Déclaration du Groupe de Durban. 2004.
(4) Jean, B. et Delwaulle, – J.C. Les Reboisements en République Populaire du Congo. La Chronique Internationale. 1981, Vol. XIII, 2.
(5) Service National de Reboisement (http://snrcongo.free.fr/ ) créé en 1986 et Programme National d’Afforestation et de Reboisement (PRONAR) créé en 201. https://tinyurl.com/4cx47zuc
(6) RP Sangha Likouala, document de projet. https://tinyurl.com/4h9js8y3
(7) Code forestier revisé : Loi 33 du 08 juillet 2020 portant code forestier, art. Titre 10 sur les crédits carbone, art. 177 et suivant (https://www.sgg.cg/codes/congo-code-2020-forestier.pdf) ; strategie REDD : Stratégie REDD+, 2018; task force carbone : Communiqué de la session inaugurale de la mise en place de la Task-Force Carbone, février 2024.
(8) Pigeaud, Fanny. Dans le bassin du Congo, la Françafrique fait feu de tout bois. Pulitzer Center, 2024.
(9) Raison, Jean-Pierre. La colonisation des terres neuves intertropicales. Persée. 1968, 5-112.
(10) REDD Monitor, Les dirigeants autochtones n’ont pas été consultés sur l’accord REDD de 180 millions de
dollars conclu par la coalition LEAF dans l’État du Pará. https://reddmonitor.substack.com/p/indigenous-leaders-were-not-consulted
(11) Total au Congo, une opération de Greenwashing destructice. Comité catholique contre la faim et pour le développement – terre solidaire. 2022.
(12) Le Congo mise sur l’agroforesterie et les puits de carbone en savane. Malu-Malu, Muriel Devey. s.l. : Makanisi, 2021.
(13) Paul Bertaux et al. Les plantations forestières en Afrique Centrale. 2020.
(14) Le projet BaCaSi : un partenariat pionnier pour le développement durable en République du Congo. Total Energie. 2022. Voir aussi : Loi n°7-2022 du 26 janvier 2022 portant approbation de la convention de partenariat entre le gouvernement et les sociétés Total Nature Based, Congo Forest Company et Forest Neutral Congo.
(15) Des paysans expulsés pour des crédits carbone au Congo. Tiassou, Kossivi. 2023.
(16) Haut-Ogoou” : Sequoia plantations face au rejet des population malgré l’opportuinité d’emploi. Libreville : s.n., 19 septembre 2023, Ethique media Gabon.
(17) Singh, Satinder. Une déléguation de la société Sequoia chez Rosalie Matondo. Page facebook du MEF. Brazzaville, 19 Janvier 2024.
(18) SEQUOIA Plantation. Note d’information: La situation de l’eucalyptus en République du Congo. 2024. p. 4-5.
(19) Barot, Shailesh. Exploitation forestière: la société Sequoia plantation obtient une concession de 35 961 hectares. Brazzaville, 13 mai 2023.
(20) Signature d’un bail emphytéotique entre le gouvernement congolais et la SNPC. Agence d’information environnementale. s.l., 2024.¸ Projet Eco Zamba : la SNPC s’engage dans la plantation d’acacias pour compenser son impact environnemental au Congo. Fatshimetrie. s.l., 2023.
(21) Congo-B: la compagnie pétrolière nationale lance un projet de reforestation. RFI, 2023.
(22) Projet JACA-Mbé : RENCO Green Sarlu compte séquestrer 30 millions de tonnes équivalent carbone à l’horizon 2025. Agence d’information’environnementale. AIE. Voir aussi : Loi 33 du 08 juillet 2020 portant code forestier, art. Titre 10 sur les crédits carbone, art. 177 et suivant.
(23) Congo : Un accord pour commercialiser les réductions des émissions générées dans les Aac de Ngombé. Fédération Atlantique des Agences de Presse Africaine (FAAPA). s.l., 2024. Voir aussi : Projet Interholco AG
(24) Projet OLAM CIB; Projet SEFYD; Projet HIFOR de WCS, gestionnaire du Parc Nuabalé Ndoki;
(25) https://www.aci.cg/congo-economie-forestiere-necessite-de-diversifier-les-activites-du-parc-national-dodzala-kokoua-pour-promouvoir-lecotourisme/?amp=1
(26) La région de la Sangha en République du Congo. WRM. 2022.
Original Source: World Rainforest Movement (WRM)
Related posts:

 12 Replies to 12 Lies about Industrial Tree Plantations: New edition of a WRM briefing paper
12 Replies to 12 Lies about Industrial Tree Plantations: New edition of a WRM briefing paper
 MONOCULTURE TREE PLANTATIONS – Uganda – Promotion of plantation agriculture – a disgrace to human kind and environment
MONOCULTURE TREE PLANTATIONS – Uganda – Promotion of plantation agriculture – a disgrace to human kind and environment
 The African Development Bank and the Tree Plantations Industry
The African Development Bank and the Tree Plantations Industry
 Witness Radio – Uganda, Community members from Mozambique and other organizations around the world say NO to more industrial tree plantations
Witness Radio – Uganda, Community members from Mozambique and other organizations around the world say NO to more industrial tree plantations
You may like
NGO WORK
Climate wash: The World Bank’s Fresh Offensive on Land Rights
Published
5 days agoon
November 13, 2025
Climate wash: The World Bank’s Fresh Offensive on Land Rights reveals how the Bank is appropriating climate commitments made at the Conference of the Parties (COP) to justify its multibillion-dollar initiative to “formalize” land tenure across the Global South. While the Bank claims that it is necessary “to access land for climate action,” Climatewash uncovers that its true aim is to open lands to agribusiness, mining of “transition minerals,” and false solutions like carbon credits – fueling dispossession and environmental destruction. Alongside plans to spend US$10 billion on land programs, the World Bank has also pledged to double its agribusiness investments to US$9 billion annually by 2030.
This report details how the Bank’s land programs and policy prescriptions to governments dismantle collective land tenure systems and promote individual titling and land markets as the norm, paving the way for private investment and corporate takeover. These reforms, often financed through loans taken by governments, force countries into debt while pushing a “structural transformation” that displaces smallholder farmers, undermines food sovereignty, and prioritizes industrial agriculture and extractive industries.
Drawing on a thorough analysis of World Bank programs from around the world, including case studies from Indonesia, Malawi, Madagascar, the Philippines, and Argentina, Climatewash documents how the Bank’s interventions are already displacing communities and entrenching land inequality. The report debunks the Bank’s climate action rhetoric. It details how the Bank’s efforts to consolidate land for industrial agriculture, mining, and carbon offsetting directly contradict the recommendations of the IPCC, which emphasizes the protection of lands from conversion and overexploitation and promotes practices such as agroecology as crucial climate solutions.
Read full report: Climatewash: The World Bank’s Fresh Offensive on Land Rights
Source: The Oakland Institute
Related posts:

 30 civil society organizations have written to the World Bank Group demanding to publicly disclose the Africa Energy Approach paper.
30 civil society organizations have written to the World Bank Group demanding to publicly disclose the Africa Energy Approach paper.
 World Bank’s new scheme to privatize land in the developing world exposed
World Bank’s new scheme to privatize land in the developing world exposed
 World Bank is backing dozens of new coal projects, despite climate pledges
World Bank is backing dozens of new coal projects, despite climate pledges
 Communities Under Siege: New Report Reveals World Bank Failures in Safeguard Compliance and Human Rights Oversight in Tanzania
Communities Under Siege: New Report Reveals World Bank Failures in Safeguard Compliance and Human Rights Oversight in Tanzania
NGO WORK
Africa’s Land Is Not Empty: New Report Debunks the Myth of “Unused Land” and Calls for a Just Future for the Continent’s Farmland
Published
5 days agoon
November 13, 2025
A new report challenges one of the most persistent and harmful myths shaping Africa’s development agenda — the idea that the continent holds vast expanses of “unused” or “underutilised” land waiting to be transformed into industrial farms or carbon markets.
Titled Land Availability and Land-Use Changes in Africa (2025), the study exposes how this colonial-era narrative continues to justify large-scale land acquisitions, displacements, and ecological destruction in the name of progress.
Drawing on extensive literature reviews, satellite data, and interviews with farmers in Zambia, Mozambique, South Africa, and Zimbabwe, the report systematically dismantles five false assumptions that underpin the “land abundance” narrative:
-
That Africa has vast quantities of unused arable land available for cultivation
-
That modern technology can solve Africa’s food crisis
-
That smallholder farmers are unproductive and incapable of feeding the continent
-
That markets and higher yields automatically improve food access and nutrition
-
That industrial agriculture will generate millions of decent jobs
Each of these claims, the report finds, is deeply flawed. Much of the land labelled as “vacant” is, in reality, used for grazing, shifting cultivation, foraging, or sacred and ecological purposes. These multifunctional landscapes sustain millions of people and are far from empty.
The study also shows that Africa’s food systems are already dominated by small-scale farmers, who produce up to 80% of the continent’s food on 80% of its farmland. Rather than being inefficient, their agroecological practices are more resilient, locally adapted, and socially rooted than the industrial models promoted by external donors and corporations.
Meanwhile, the promise that industrial agriculture will lift millions out of poverty has not materialised. Mechanisation and land consolidation have displaced labour, while dependency on imported seeds and fertilisers has trapped farmers in cycles of debt and dependency.
A Continent Under Pressure
Beyond these myths, the report reveals a growing land squeeze as multiple global agendas compete for Africa’s territory: the expansion of mining for critical minerals, large-scale carbon-offset schemes, deforestation for timber and commodities, rapid urbanisation, and population growth.
Between 2010 and 2020, Africa lost more than 3.9 million hectares of forest annually — the highest deforestation rate in the world. Grasslands, vital carbon sinks and grazing ecosystems, are disappearing at similar speed.
Powerful actors — from African governments and Gulf states to Chinese investors, multinational agribusinesses, and climate-finance institutions — are driving this race for land through opaque deals that sideline local communities and ignore customary tenure rights.
A Call for a New Vision
The report calls for a radical shift away from high-tech, market-driven, land-intensive models toward people-centred, ecologically grounded alternatives. Its key policy recommendations include:
-
Promoting agroecology as a pathway for food sovereignty, ecological regeneration, and rural livelihoods.
-
Reducing pressure on land by improving agroecological productivity, cutting food waste, and prioritising equitable distribution.
-
Rejecting carbon market schemes that commodify land and displace communities.
-
Legally recognising customary land rights, particularly for women and Indigenous peoples.
-
Upholding the principle of Free, Prior, and Informed Consent (FPIC) for all land-based investments.
This report makes it clear: Africa’s land is not “empty” — it is lived on, worked on, and cared for. The future of African land must not be dictated by global capital or outdated development theories, but shaped by the people who depend on it.
Download the Report
Read the full report Land Availability and Land-Use Changes in Africa (2025) to explore the evidence and policy recommendations in detail.
Related posts:

 Financial Institutions from Africa have made a monumental commitment of $100 billion to Africa’s green industrialization, a decision of immense significance that has the potential to shape Africa’s future.
Financial Institutions from Africa have made a monumental commitment of $100 billion to Africa’s green industrialization, a decision of immense significance that has the potential to shape Africa’s future.
 Africa adopts the Africa Climate Innovation Compact (ACIC) Declaration to drive the continent towards innovative climate solutions.
Africa adopts the Africa Climate Innovation Compact (ACIC) Declaration to drive the continent towards innovative climate solutions.
 One in three people sleeps on an empty stomach – World Bank Report.
One in three people sleeps on an empty stomach – World Bank Report.
 Transforming Africa’s livestock sector is key to food security-Report
Transforming Africa’s livestock sector is key to food security-Report
NGO WORK
Discover How Foreign Interests and Resource Extraction Continue to Drive Congo’s Crisis
Published
6 days agoon
November 12, 2025
Whereas Donald Trump hailed the “peace” agreement between Rwanda and DRC as marking the end of a deadly three-decade war, a new report from the Oakland Institute, Shafted: The Scramble for Critical Minerals in the DRC, exposes it as the latest US maneuver to control Congolese critical minerals.
Under the Guise of Peace
After three decades of deadly wars and atrocities, the June 2025 “peace” deal between Rwanda and the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) lays bare the United States’ role in entrenching the extraction of minerals under the guise of diplomacy. For decades, US backing of Rwanda and Uganda has fueled the violence, which has ripped millions of Congolese lives apart while enabling the looting of the country’s mineral wealth. Today, Washington presents itself as a broker of peace, yet its longstanding support for Rwanda made it possible for M23 to seize territory, capture key mining sites, and forced Kinshasa to the negotiation table with hands tied behind its back. By legitimizing Rwanda’s territorial advances, the US-brokered agreement effectively rewards aggression while sidelining accountability, justice for victims, and the sovereignty of the Congolese people.
The incorporation of “formalized” mineral supply chains from eastern DRC to Rwanda exposes the pact’s true aim: Securing access to and control over minerals under the guise of diplomacy and “regional integration.” Framed as peacemaking, this is part of United States’ broader geopolitical struggle with China for control over critical resources. Far from fostering peace – over a thousand civilians have been killed since the deal was signed while parallel negotiations with Rwanda’s rebel force have collapsed – this arrangement risks deepening Congo’s subjugation. Striking deals with the Trump administration and US firms, the DRC government is surrendering to a new era of exploitation while the raging war continues, driving the unbearable suffering of the Congolese people.
Introduction
The conflict in eastern DRC, which dates back three decades to the aftermath of the 1994 Rwandan genocide and subsequent Congo Wars, has claimed over six million lives, displaced millions more, and inflicted widespread suffering. Since late 2021, Rwanda and its proxy militia, M23, have stormed through mineral-rich lands and regional capitals, inflicting brutal violence and triggering mass displacement. While billions of dollars in natural resources are extracted from the area, Congolese communities toil in extreme poverty.
On June 27, 2025, a “peace” agreement was signed between Rwanda and the DRC under the auspices of the Trump administration, with diplomatic assistance from Qatar.1 The deal included pledges to respect the territorial integrity of both countries, to promote peaceful relations through the disarmament of armed groups, the return of refugees, and the creation of a joint security mechanism. A key clause commits the countries to launch a regional economic integration framework that would entail “mutually beneficial partnerships and investment opportunities,” specifically for the extraction of the DRC’s mineral wealth by US private interests.
Placing the deal in a historical perspective – after three decades of conflict and over seven decades of US chess game around Congolese minerals – this report examines its implications for the Congolese people as well as the interests involved in the plunder of the country’s resources.
The report begins by retracing 30 years of war, fueled by the looting of Congo’s mineral wealth and devastating for the people of eastern DRC. It then examines how US policy in Central Africa, from the Cold War to the present, has been shaped by its interest in Congolese minerals, sustained alliances with Rwanda and Uganda, and a consistent pattern of overlooking atrocities in support of these allies.
The report then analyses the implications of the regional economic integration aspect of the deal, which aims to link mineral supply chains in the DRC and Rwanda with US investors. The last sections examine the prospect for lasting peace and security resulting from the deal and the impact of growing involvement of US private actors in DRC and Rwanda.
Original Source: Oakland Institute
Related posts:

 Profit off Peace? Meet the Corporations Poised to Benefit from the DRC Peace Deal
Profit off Peace? Meet the Corporations Poised to Benefit from the DRC Peace Deal
 DR Congo: RIAO-RDC calls for the immediate release of four leaders from the community of Mwingi who were arrested after a peaceful protest against the oil palm plantation company PHC
DR Congo: RIAO-RDC calls for the immediate release of four leaders from the community of Mwingi who were arrested after a peaceful protest against the oil palm plantation company PHC
 DR Congo oil palm company bankrolled by development banks unleashes wave of violence against villagers after peaceful protests
DR Congo oil palm company bankrolled by development banks unleashes wave of violence against villagers after peaceful protests
 Operations of civil society organizations will continue to be stifled until government understands their work – New Book.
Operations of civil society organizations will continue to be stifled until government understands their work – New Book.
“Vacant Land” Narrative Fuels Dispossession and Ecological Crisis in Africa – New report.

Uganda’s Army is on the spot for forcibly grabbing land for families in Pangero Chiefdom in Nebbi district.

Climate wash: The World Bank’s Fresh Offensive on Land Rights

Africa’s Land Is Not Empty: New Report Debunks the Myth of “Unused Land” and Calls for a Just Future for the Continent’s Farmland

StopEACOP Coalition warns TotalEnergies and CNOOC investors of escalating ‘financial and reputational’ Risks

Seed Boot Camp: A struggle to conserve local and indigenous seeds from extinction.

Know Your Land rights and environmental protection laws: a case of a refreshed radio program transferring legal knowledge to local and indigenous communities to protect their land and the environment at Witness Radio.

Failed US-Brokered “Peace” Deal Was Never About Peace in DRC

Innovative Finance from Canada projects positive impact on local communities.
Over 5000 Indigenous Communities evicted in Kiryandongo District
Petition To Land Inquiry Commission Over Human Rights In Kiryandongo District
Invisible victims of Uganda Land Grabs
Resource Center
- REPARATORY AND CLIMATE JUSTICE MUST BE AT THE CORE OF COP30, SAY GLOBAL LEADERS AND MOVEMENTS
- LAND GRABS AT GUNPOINT REPORT IN KIRYANDONGO DISTRICT
- THOSE OIL LIARS! THEY DESTROYED MY BUSINESS!
- RESEARCH BRIEF -TOURISM POTENTIAL OF GREATER MASAKA -MARCH 2025
- The Mouila Declaration of the Informal Alliance against the Expansion of Industrial Monocultures
- FORCED LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA TRENDS RIGHTS OF DEFENDERS IMPACT AND CALL FOR ACTION
- 12 KEY DEMANDS FROM CSOS TO WORLD LEADERS AT THE OPENING OF COP16 IN SAUDI ARABIA
- PRESENDIANTIAL DIRECTIVE BANNING ALL LAND EVICTIONS IN UGANDA
Legal Framework
READ BY CATEGORY
Newsletter
Trending
-

 SPECIAL REPORTS AND PROJECTS2 weeks ago
SPECIAL REPORTS AND PROJECTS2 weeks agoThe Environmental Crisis Is a Capitalist Crisis
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks agoReport reveals ongoing Human Rights Abuses and environmental destruction by the Chinese oil company CNOOC
-
 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK5 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK5 days ago“Vacant Land” Narrative Fuels Dispossession and Ecological Crisis in Africa – New report.
-

 SPECIAL REPORTS AND PROJECTS2 weeks ago
SPECIAL REPORTS AND PROJECTS2 weeks agoGlobal use of coal hit record high in 2024
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK7 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK7 days agoSeed Sovereignty: Most existing and emerging laws and policies on seeds are endangering seed saving and conservation on the African continent.
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK2 weeks agoLands ministry rejects call to save over 300 Masaka residents facing eviction
-

 MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK5 days ago
MEDIA FOR CHANGE NETWORK5 days agoUganda’s Army is on the spot for forcibly grabbing land for families in Pangero Chiefdom in Nebbi district.
-

 NGO WORK6 days ago
NGO WORK6 days agoDiscover How Foreign Interests and Resource Extraction Continue to Drive Congo’s Crisis
